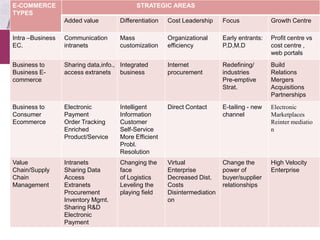
The document discusses various aspects of e-commerce including definitions, examples, patterns, and strategic impacts. It describes how e-commerce can be used for intra-business, business-to-business, and business-to-consumer exchanges. It provides examples of how e-commerce enables added value, differentiation, cost leadership, and a strategic focus. Key applications include improved communication, mass customization, efficiency gains, and penetrating new markets.