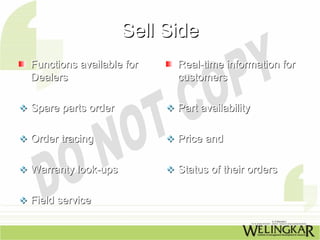
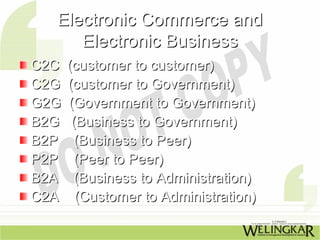
The document provides a comprehensive overview of electronic commerce, detailing its definition, main activities, goals, advantages, and disadvantages. It highlights the significance of technology in transforming e-commerce and outlines the various components and processes involved. Additionally, it discusses the applications of e-commerce across different sectors and the impact of online transactions on consumer behavior.