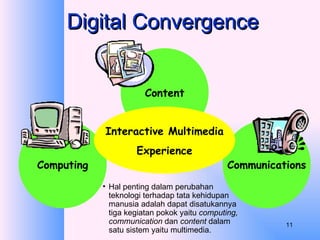
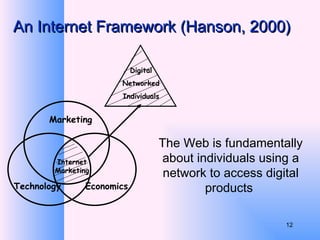
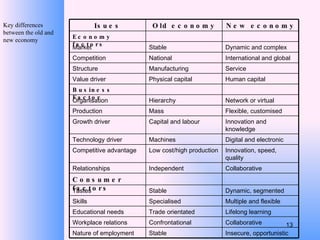
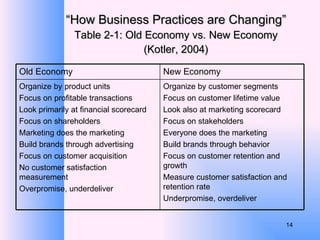
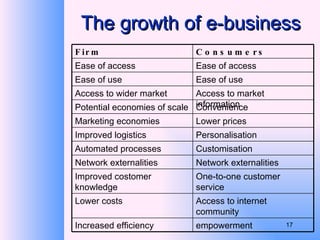
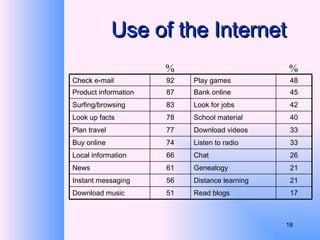
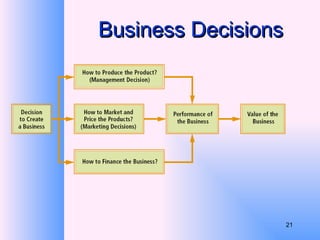
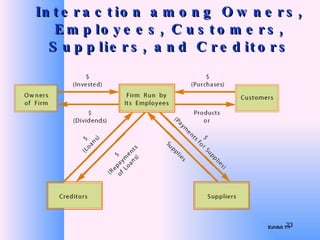
This document provides an overview of e-business management and strategy. It defines e-business and e-commerce, and discusses how businesses have transformed from the old economy to the new digital economy. Key aspects of e-business include types of e-business models, the growth of e-commerce, and how technology has impacted business functions and decisions. Developing an e-business strategy involves formulation, implementation, and evaluation.