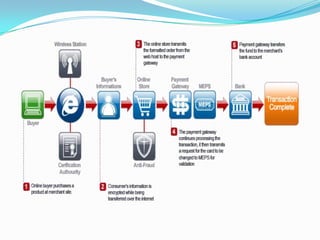
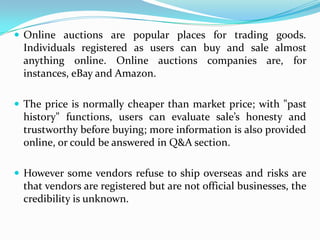
The document defines electronic business (e-business) and e-commerce, and distinguishes between the two terms. E-business refers more broadly to the strategic use of electronic capabilities across a business's functions and value chain, while e-commerce is a subset focusing on online transactions. Effective e-business allows companies to link internal and external systems more efficiently to better satisfy customers and collaborate with partners. While e-commerce involves monetary transactions online, e-business does not necessarily require money exchanges.