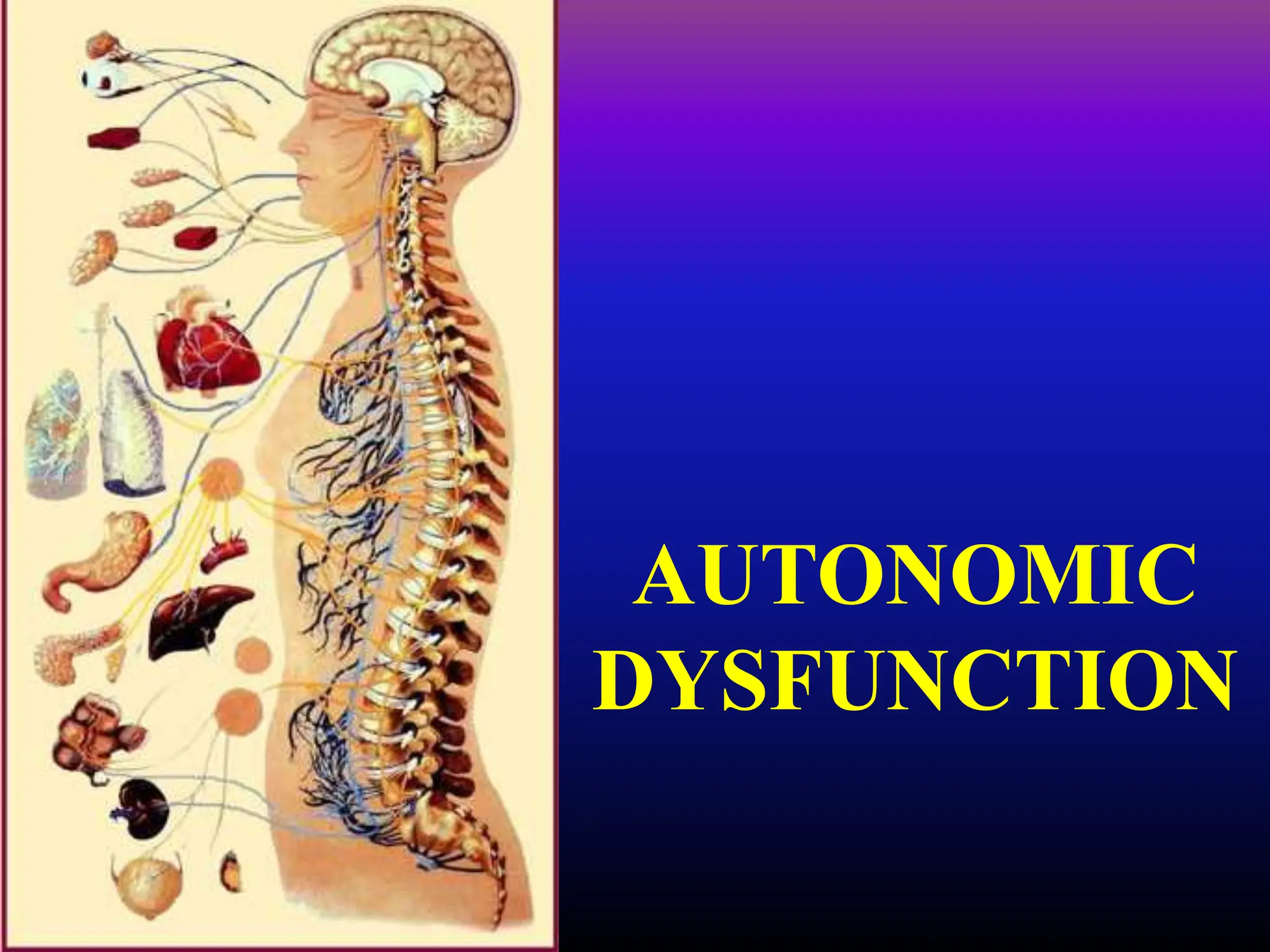
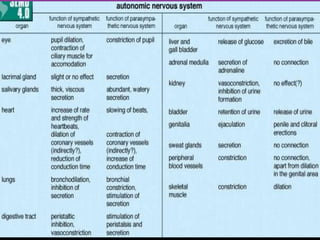
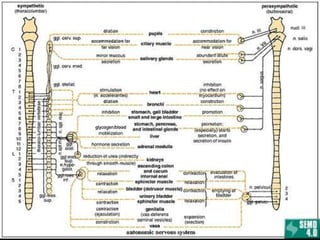
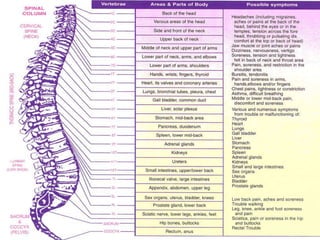
The document discusses autonomic dysfunction, or dysautonomia, which affects the autonomic nervous system's regulation of involuntary body functions such as heart rate and blood pressure. It details symptoms, classifications, diagnostic challenges, and various treatment approaches including allopathic medicine and alternative therapies like yoga. The prognosis for individuals varies widely based on the specific type and severity of the dysfunction.