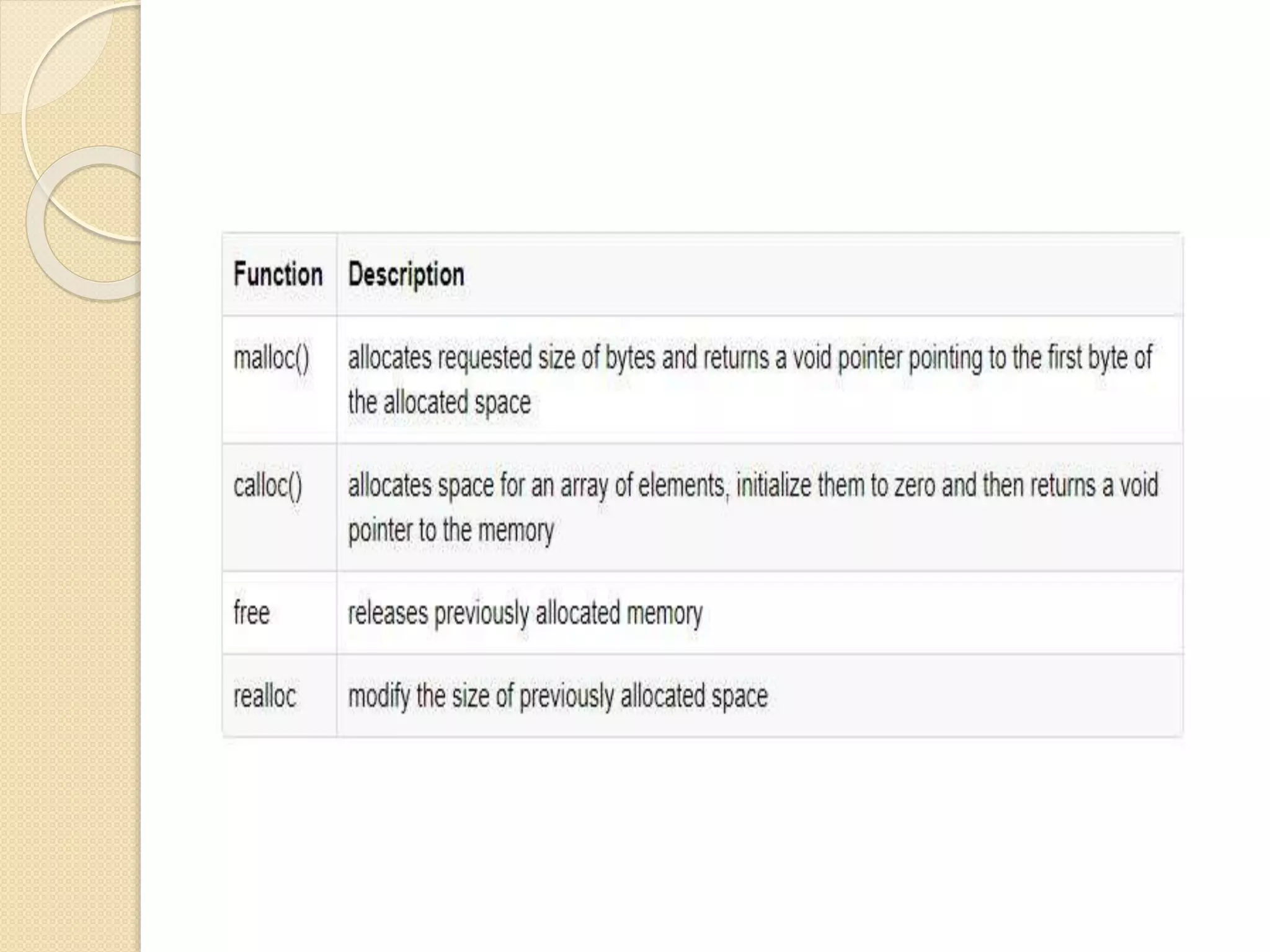
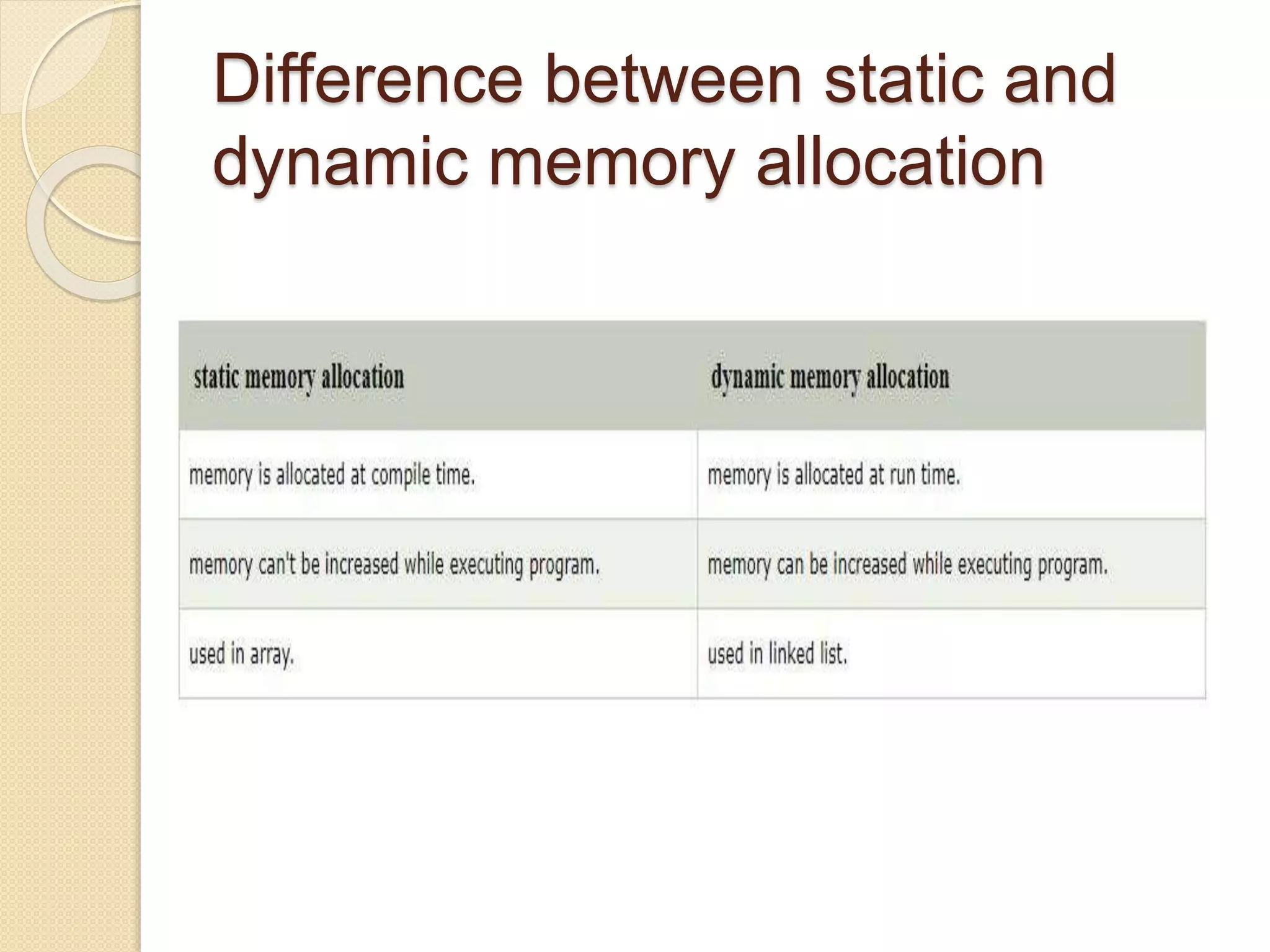
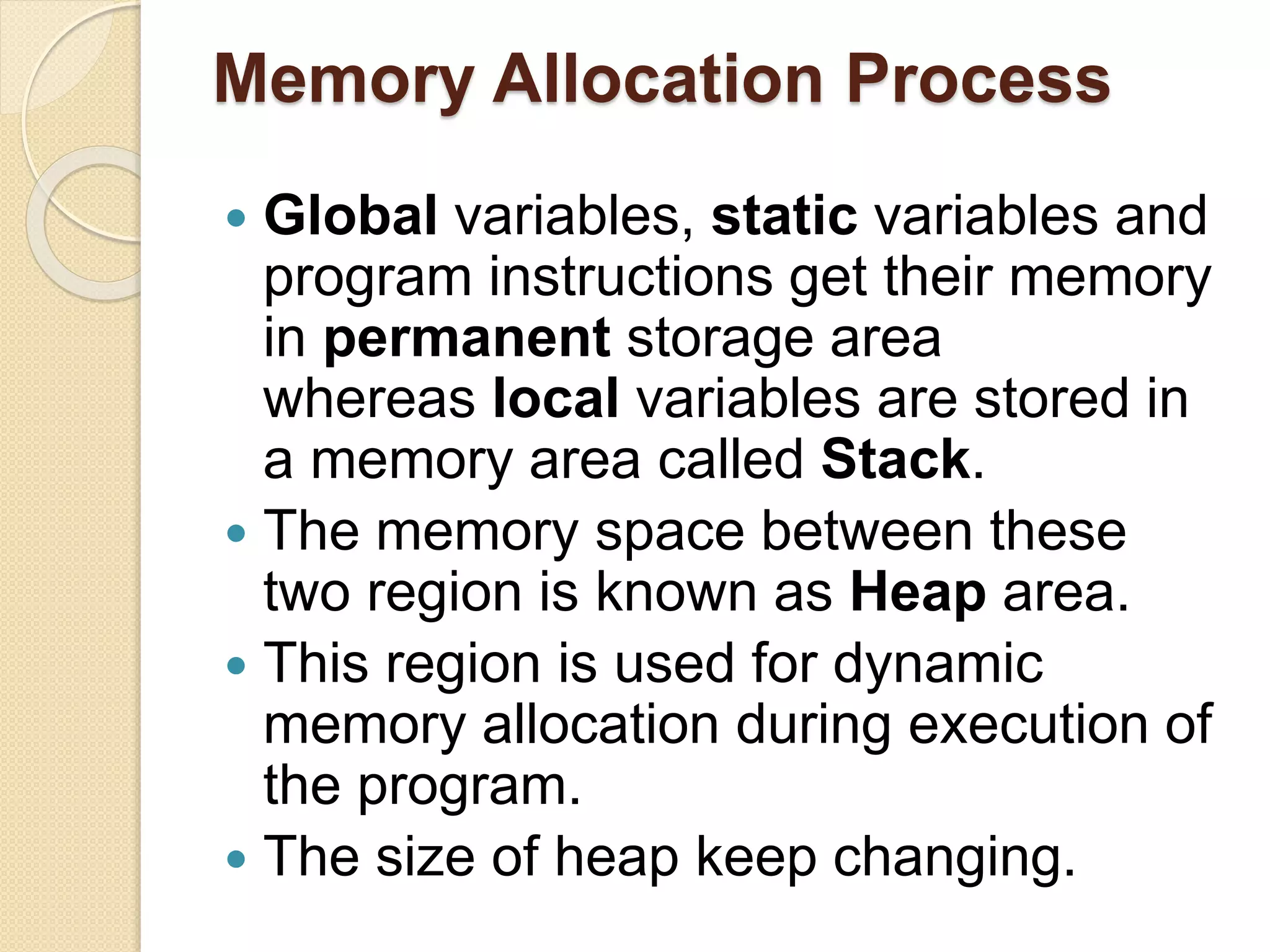
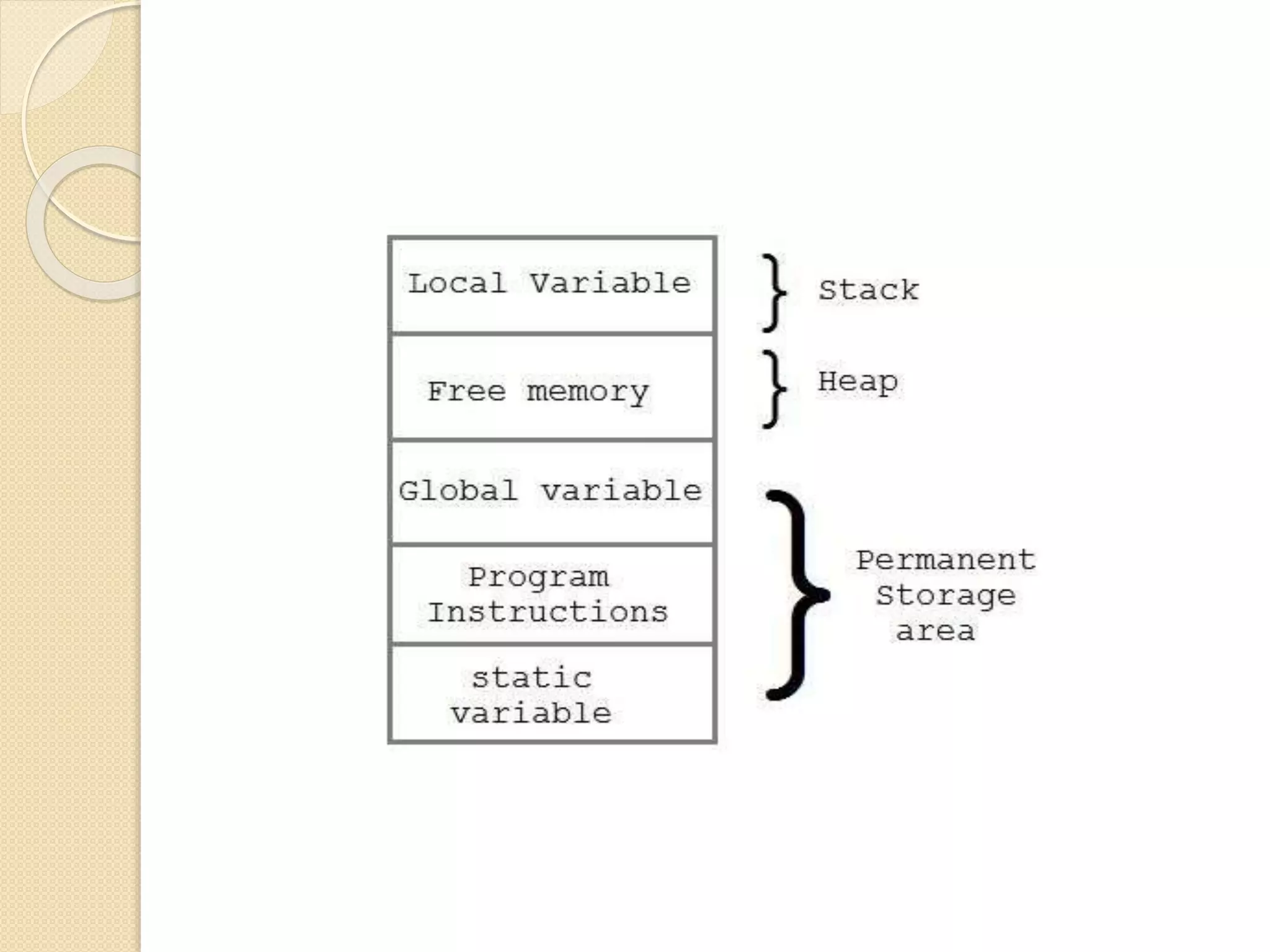
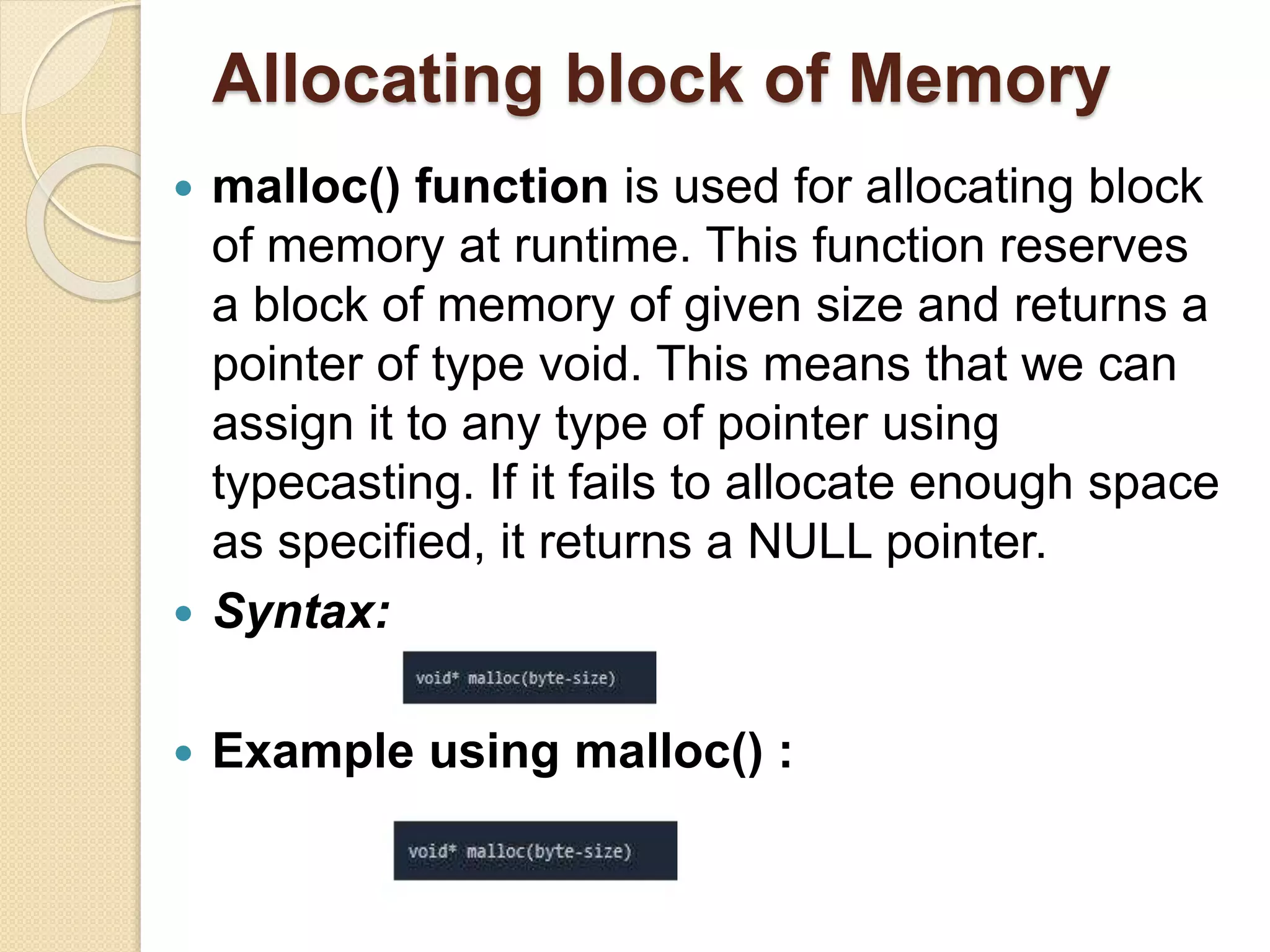
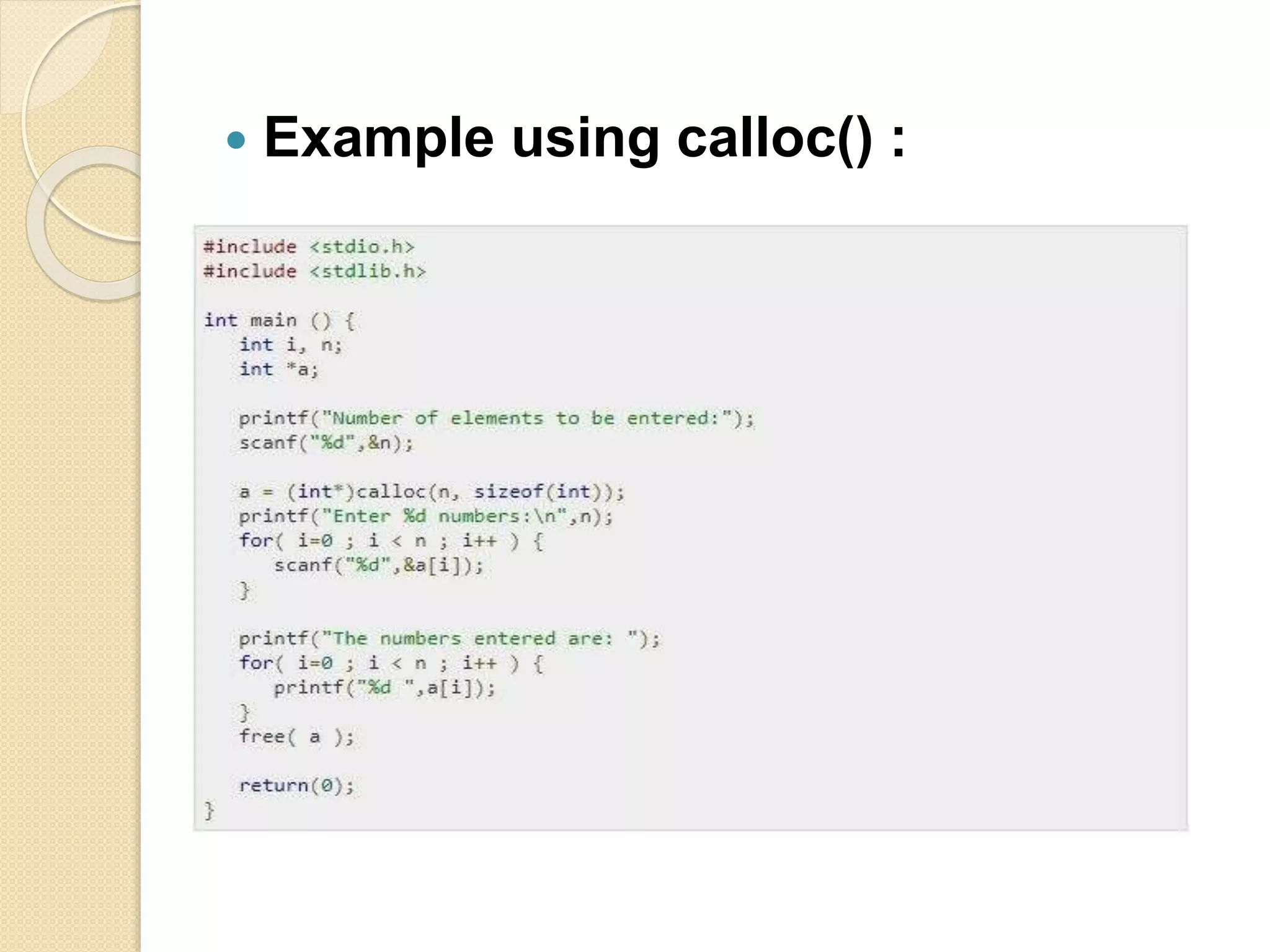
The document explains dynamic memory allocation, which is the process of allocating memory at runtime using memory management functions from stdlib.h. It distinguishes between static and dynamic memory allocation, highlighting the roles of heap and stack, and details functions such as malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), and free() for managing memory. It emphasizes the importance of releasing memory to prevent resource leaks.