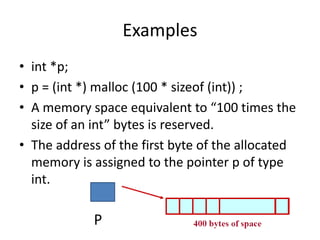
Dynamic memory allocation allows programs to request memory from the operating system at runtime. This memory is allocated on the heap. Functions like malloc(), calloc(), and realloc() are used to allocate and reallocate dynamic memory, while free() releases it. Malloc allocates a single block of uninitialized memory. Calloc allocates multiple blocks of initialized (zeroed) memory. Realloc changes the size of previously allocated memory. Proper use of these functions avoids memory leaks.












![C program to read and print the student details
using structure and Dynamic Memory
Allocation.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct student
{
char name[30];
int roll;
float perc;
};
int main()
{
struct student *pstd;
/*Allocate memory dynamically*/
pstd=(struct student*)malloc(1*sizeof(struct student));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicmemoryallocation-200415105950/85/Dynamic-memory-allocation-15-320.jpg)

![C program to read and print the N student
details using structure and Dynamic Memory
Allocation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct student
{
char name[30];
int roll;
float perc;
};
int main()
{
struct student *pstd;
int n,i;
printf("Enter total number of
elements: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
/*Allocate memory dynamically for n
objetcs*/
pstd=(struct
student*)malloc(n*sizeof(struct
student));
if(pstd==NULL)
{
printf("Insufficient Memory,
Exiting... n");
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicmemoryallocation-200415105950/85/Dynamic-memory-allocation-17-320.jpg)
![/*read and print details*/
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("nEnter detail of
student [%3d]:n",i+1);
printf("Enter name: ");
scanf(" "); /*clear input
buffer*/
gets((pstd+i)->name);
printf("Enter roll number:
");
scanf("%d",&(pstd+i)->roll);
printf("Enter percentage: ");
scanf("%f",&(pstd+i)->perc);
}
printf("nEntered details
are:n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("nEntered details
are:n"); for(i=0; i<n; i++) {
printf("%30s t %5d t
%.2fn",(pstd+i)->name,(pstd+i)-
>roll,(pstd+i)->perc); }
return 0;}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicmemoryallocation-200415105950/85/Dynamic-memory-allocation-18-320.jpg)







![Dynamically Allocating 2D Array
float **A; /* A is an array (pointer) of float pointers */
int I;
A = (float **) calloc(5,sizeof(float *));
/* A is a 1D array (size 5) of float pointers */
for (I = 0; I < 5; I++)
A[I] = (float *) calloc(4,sizeof(float));
/* Each element of array points to an array of 4 float variables */
/* A[I][J] is the Jth entry in the array that the Ithmember of A
points to */](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicmemoryallocation-200415105950/85/Dynamic-memory-allocation-26-320.jpg)