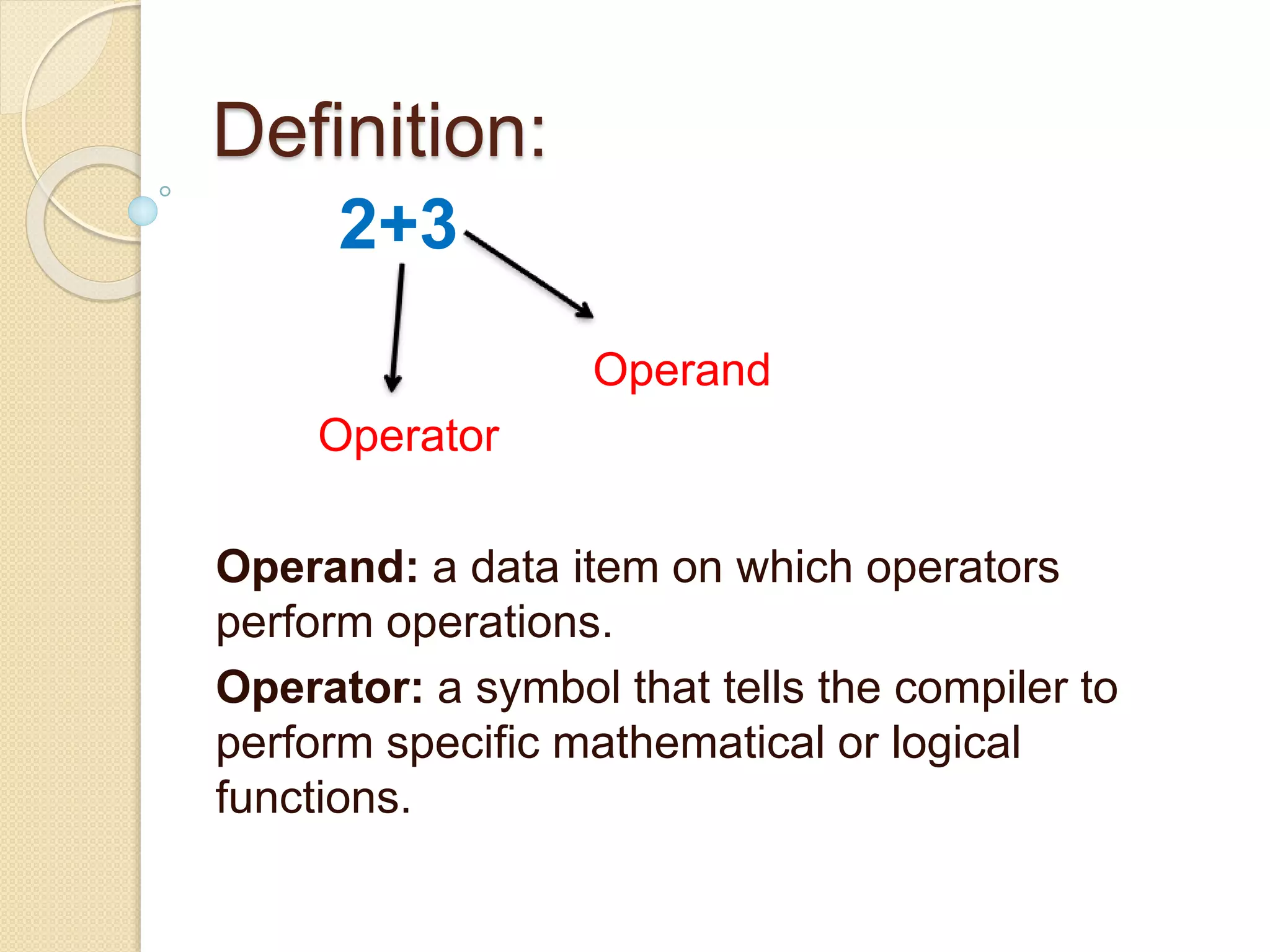
This document discusses operators and expressions in C. It defines operands and operators, and describes the different types of operators in C including arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, increment/decrement, conditional, bitwise, and comma operators. It explains the properties of operators such as precedence and associativity. Examples are provided to demonstrate how each operator works. The document also discusses the rules for evaluating expressions and provides additional examples.








































![Right Shift
It is denoted by >>
Bit Pattern of the data can be shifted by
specified number of Positions to Right
When Data is Shifted Right , leading zero’s
are filled with zero.
Right shift Operator is Binary Operator [Bi –
two]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsincv206092017-190725164449/75/Operators-inc-c-language-42-2048.jpg)

![Left Shift
It is denoted by <<
Bit Pattern of the data can be shifted by
specified number of Positions to Left
When Data is Shifted Left , trailing zero’s
are filled with zero.
Left shift Operator is Binary Operator [Bi –
two]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsincv206092017-190725164449/75/Operators-inc-c-language-44-2048.jpg)

