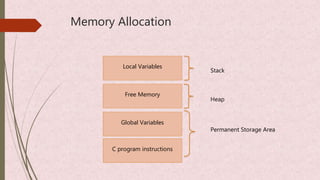
The document discusses dynamic memory allocation in C programming, detailing methods like malloc and calloc. It explains the functions' differences, including initialization and arguments for memory allocation, as well as their applications in handling local and global variables. Additionally, it provides code examples for both malloc and calloc alongside references for further reading.