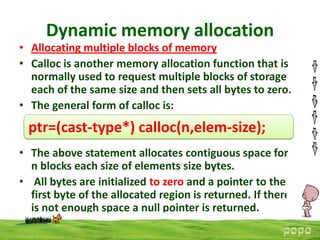
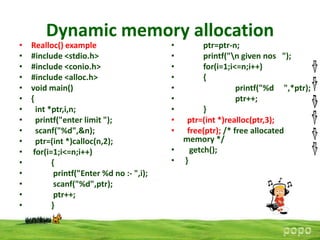
Dynamic memory allocation allows programs to allocate memory at runtime using functions like malloc(), calloc(), free(), and realloc(). Malloc allocates memory and returns a pointer, calloc allocates and initializes to 0, free releases previously allocated memory, and realloc changes the size of allocated memory. Memory allocation occurs on the heap which changes size during program execution. Out of memory errors can occur if allocation requests exceed available heap space.