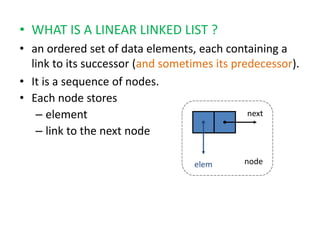
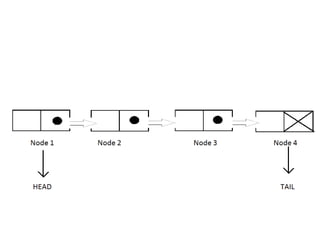
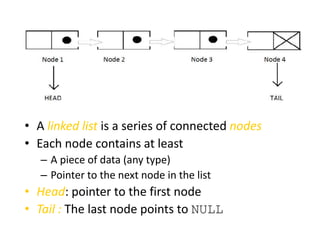
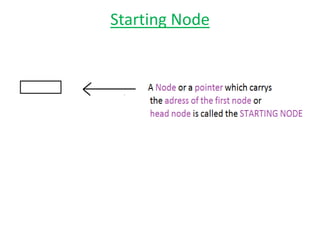
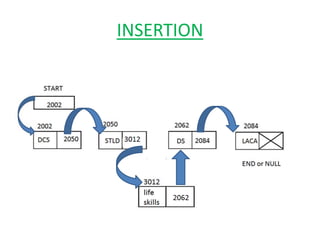
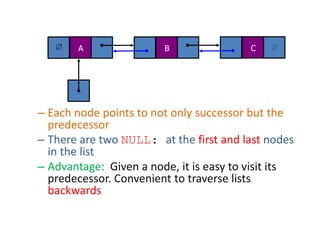
The document discusses dynamic data structures, primarily focusing on linked lists and their advantages over static arrays, such as memory allocation flexibility and easier insertion and deletion operations. It covers linear linked lists, circular linked lists, and doubly linked lists, explaining their structures, benefits, and specific use cases. Overall, linked lists are presented as versatile data structures that simplify various operations in data management.