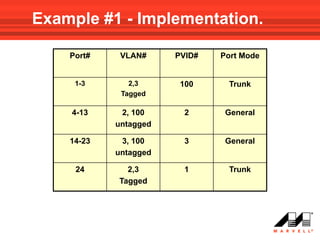
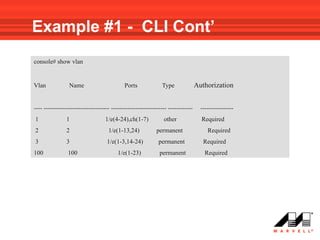
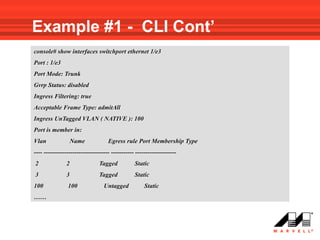
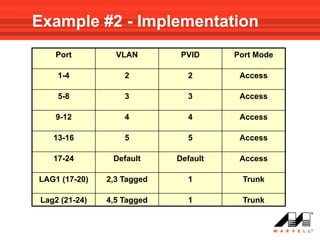
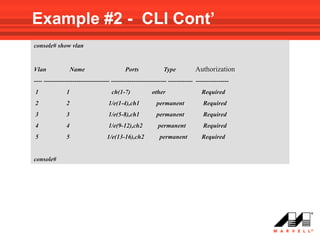
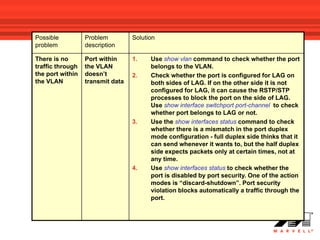
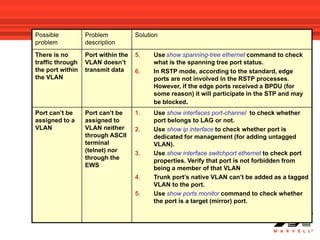
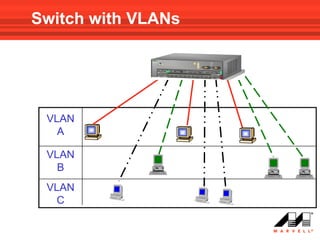
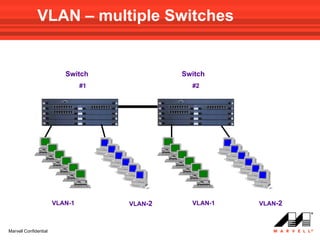
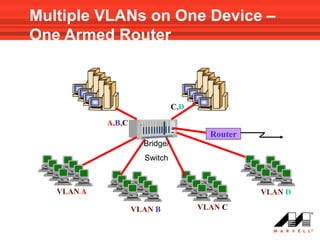
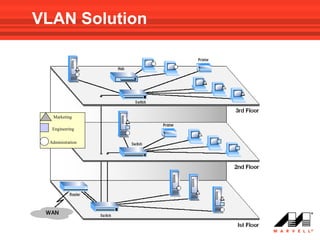
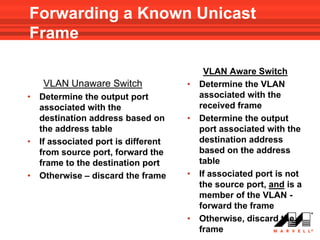
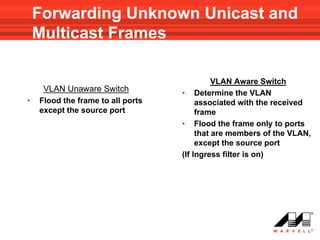
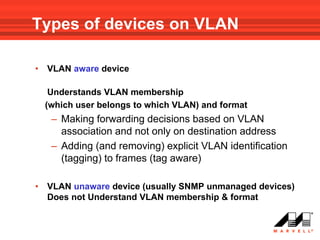
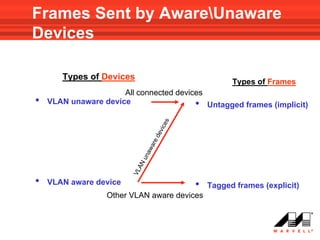
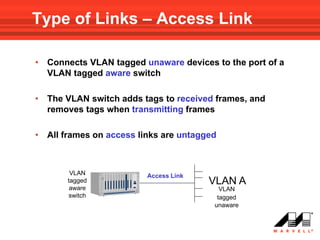
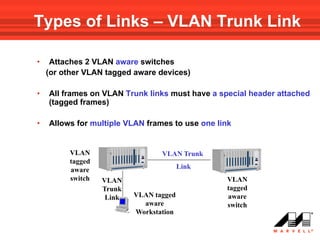
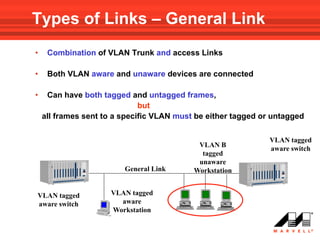
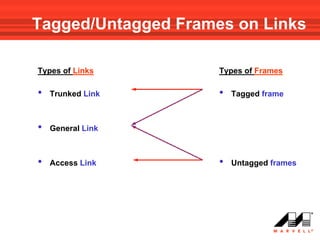
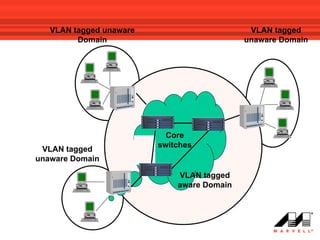
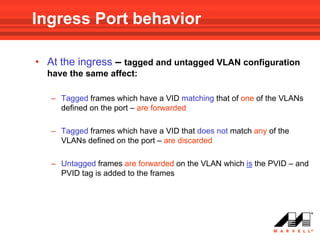
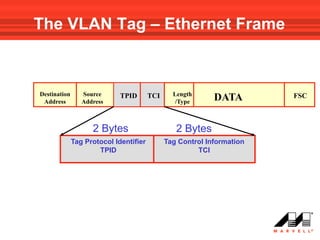
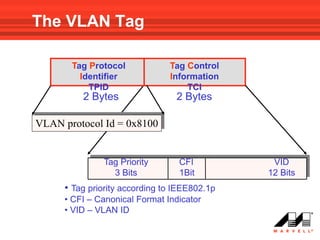
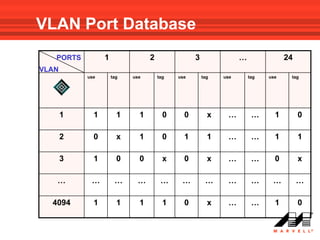
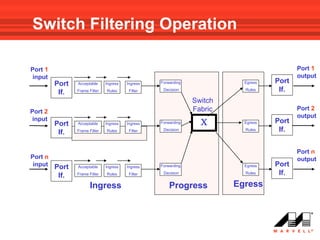
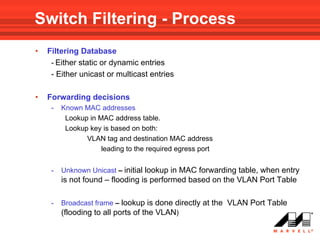
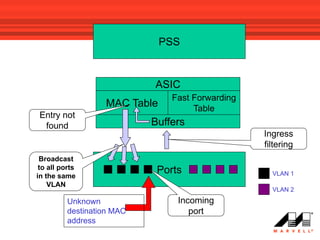
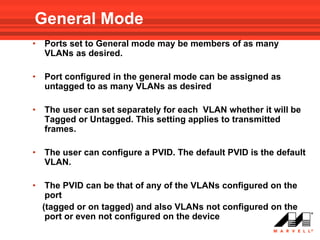
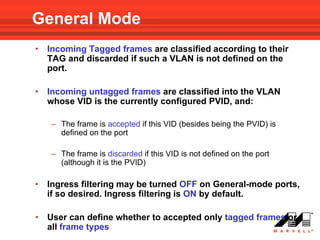
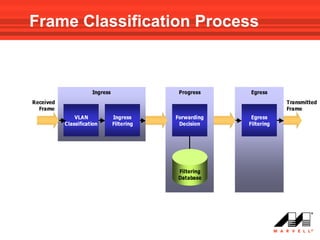
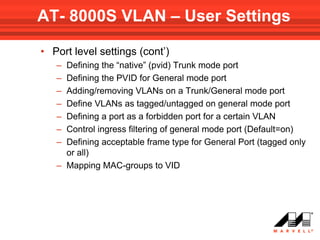
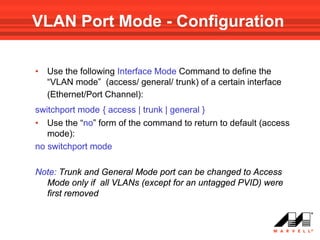
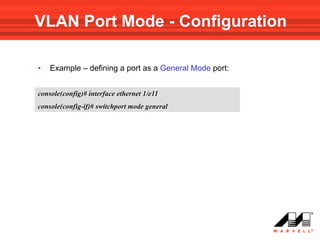
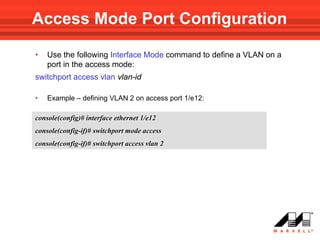
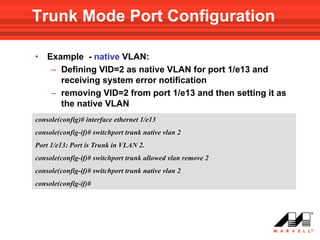
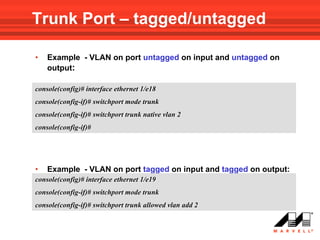
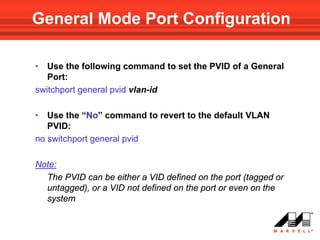
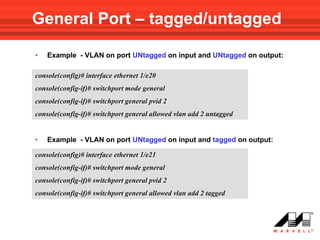
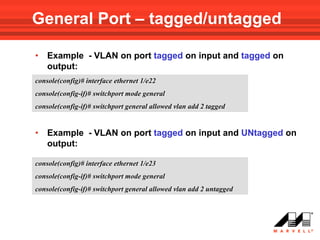
VLANs logically divide the LAN into separate broadcast domains without using routers. Switches with VLAN capability allow ports to be configured as access, trunk, or general ports. Access ports belong to one VLAN and use untagged frames. Trunk ports can belong to multiple VLANs and use tagged frames, with a native VLAN using untagged frames. Ingress filtering ensures frames are tagged with an associated VLAN.



















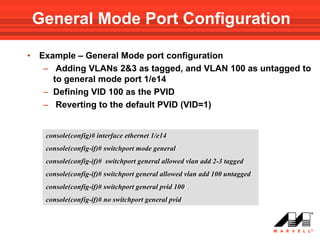
![General Mode Port Configuration
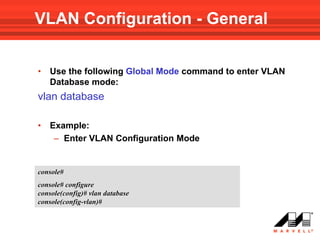
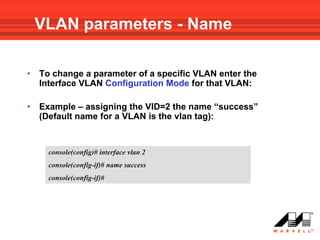
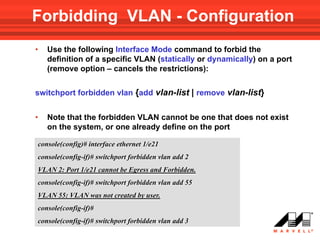
• Use the following Interface Mode command to add VLAN(s)
to a General Mode port:
switchport general allowed vlan add vlan-list [ tagged | untagged ]
Note!!! default is tagged
• To remove a VLAN(s) from the list:
switchport general allowed vlan remove vlan-list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/at8000sconfigurandovlans-100706145232-phpapp01/85/At8000-s-configurando-vla_ns-62-320.jpg)




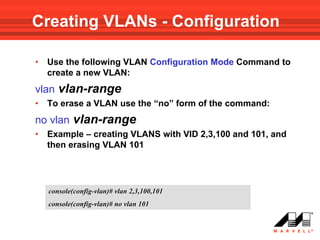
![Adding a Static MAC Address
• Use the following VLAN interface mode command to add a
static MAC entry to one of the ports in the VLAN:
bridge address mac-address {ethernet interface | port-channel
port-channel-number} [permanent | delete-on-reset | delete-
on-timeout | secure]
MAC Address format:
H.H.H or H:H:H:H:H:H or H-H-H-H-H-H
• User can define whether the entry will be:
– permanent
– deleted after reset
– aged out on time out – as with dynamic entries
– Secure – entry is deleted if port mode changes to “ unlock”
(used when port is in locked mode)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/at8000sconfigurandovlans-100706145232-phpapp01/85/At8000-s-configurando-vla_ns-75-320.jpg)
![Adding a Static MAC Address
• Note
– The MAC addresses are added per VLAN, and not per device
– The type of entry (permanent secure etc) has to be entered
before interface (if no type is mentioned default is permanent)
– You can configure an address on a port even if it does not
belong to a VLAN
• The “no” form of the command deletes a static MAC entry from the
table:
no bridge address [mac-address]
if no mac-address is specified in the command, all static entries are
erased from the table](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/at8000sconfigurandovlans-100706145232-phpapp01/85/At8000-s-configurando-vla_ns-76-320.jpg)


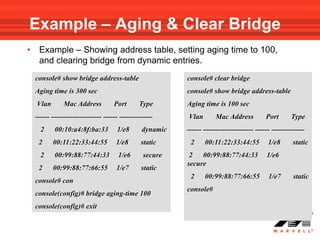
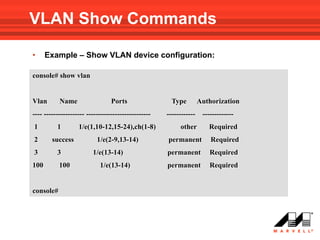
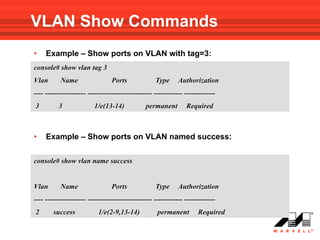
![Address Table Show Commands
• Use the following Privileged EXEC mode command to show
the MAC address table of device :
show bridge address-table
• Use the following Privileged EXEC mode command to show
addresses on specific VLAN:
show bridge address-table vlan vlan [ethernet interface | port-
channel port-channel-number]
• Use the following Privileged EXEC mode command to show
addresses on specific port:
show bridge address-table { ethernet interface | port-channel port-
channel-number} [vlan vlan]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/at8000sconfigurandovlans-100706145232-phpapp01/85/At8000-s-configurando-vla_ns-79-320.jpg)