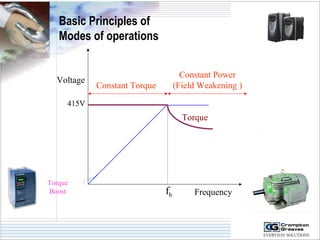
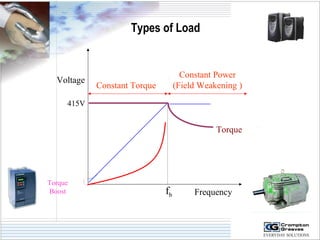
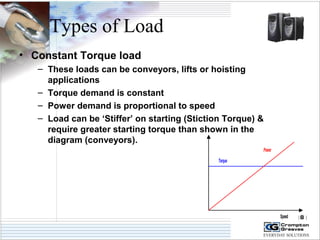
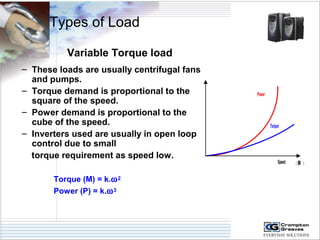
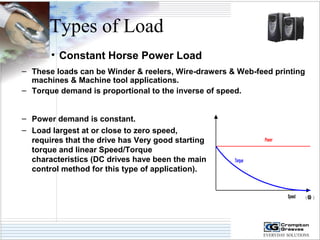
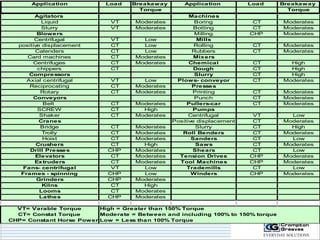
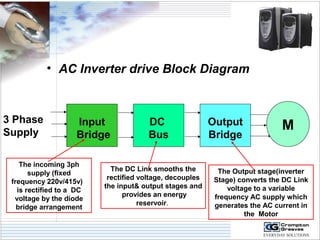
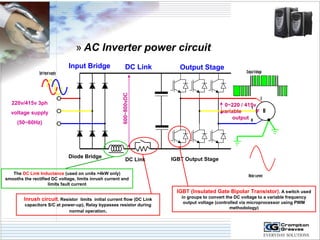
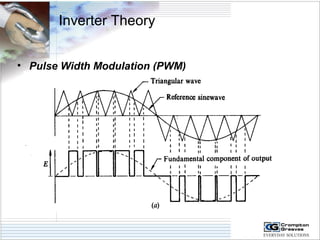
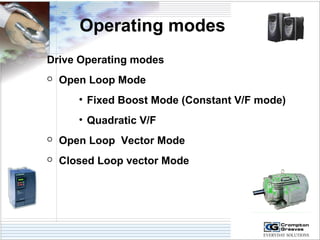
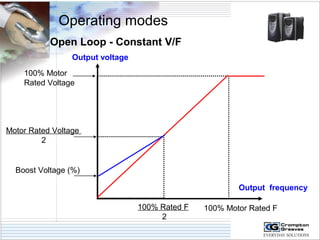
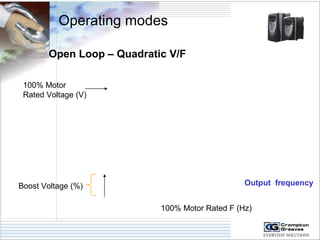
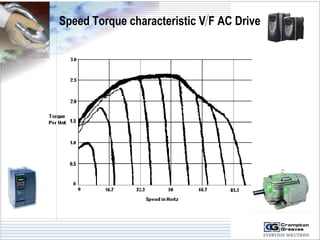
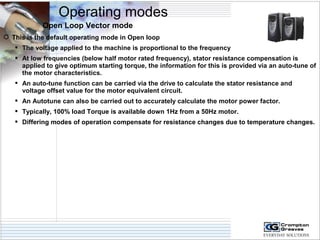
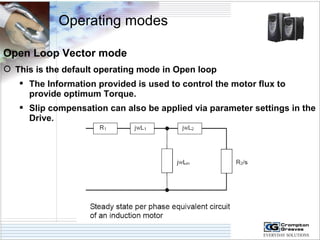
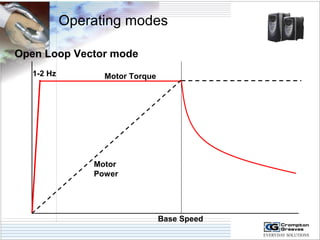
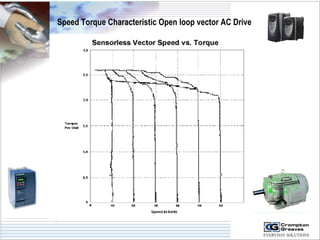
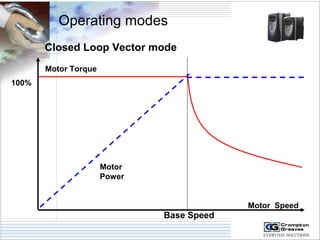
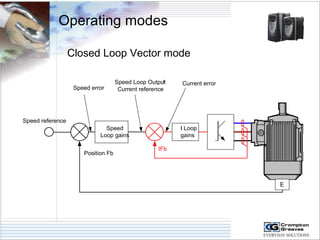
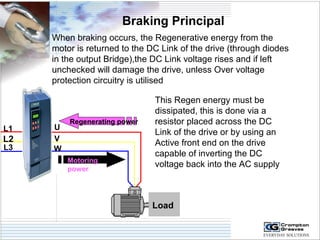
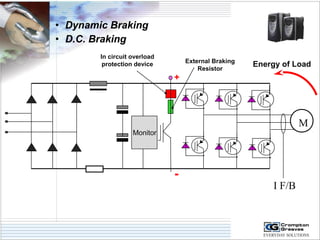
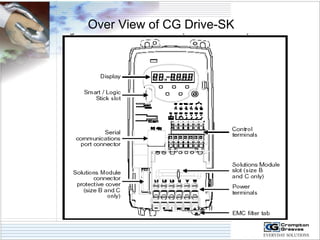
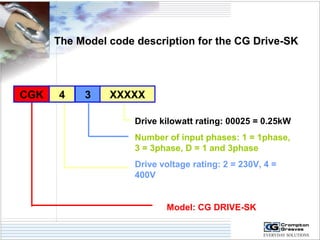
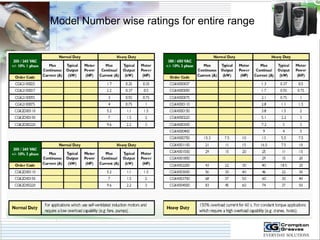
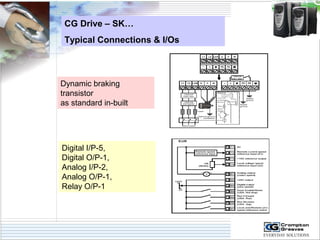
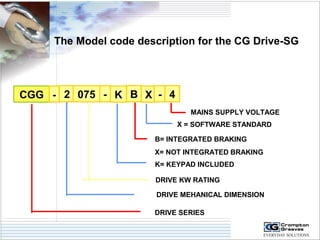
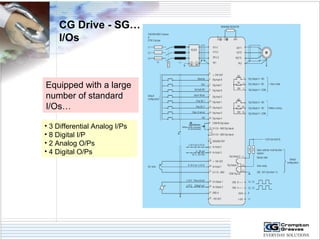
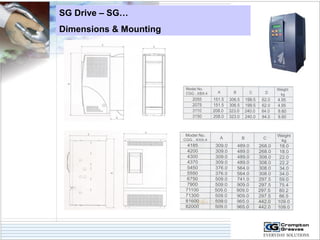
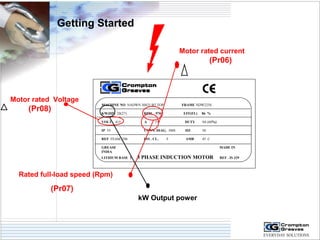
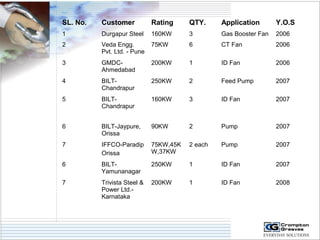
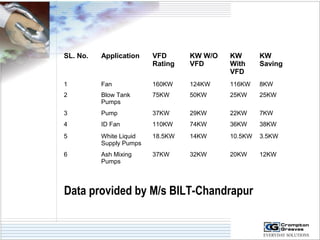
The document provides information on AC drives from CG Drives, including their advantages, basic principles of operation, operating modes, braking types, and models. It discusses constant torque and variable torque loads, open loop V/F and vector control modes, closed loop vector control using feedback, and dynamic, DC injection, and regenerative braking methods. It also introduces the CG Drive-SK and CG Drive-SG product lines, specifying their features, connections, dimensions, and optional additions.