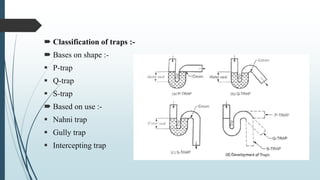
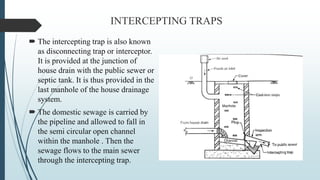
The document discusses the drainage system for buildings, emphasizing its role in efficiently discharging domestic sewage into public sewers. It outlines the components of the system, including various types of pipes, traps, and their functions to maintain sanitary conditions and prevent foul gas entry. Additionally, different types of traps are classified and their specific uses in managing waste water from kitchens and bathrooms are explained.