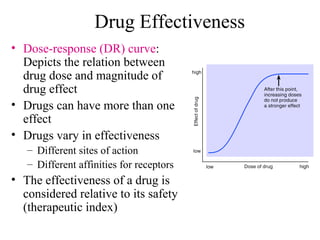
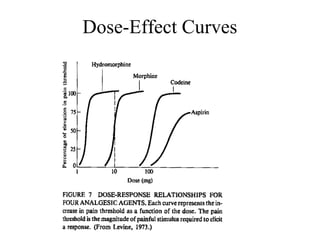
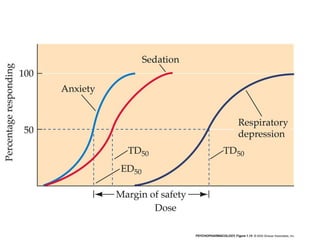
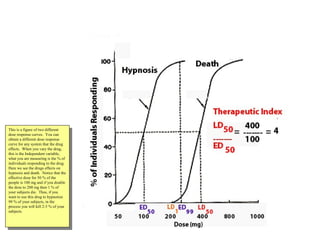
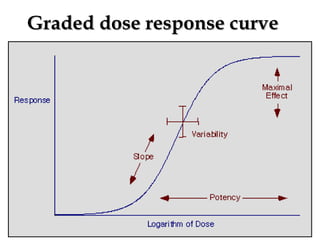
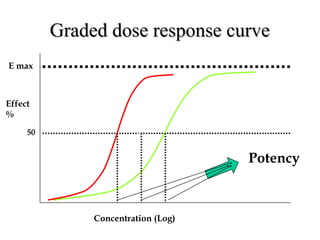
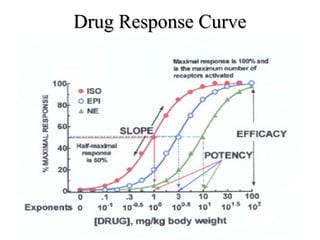
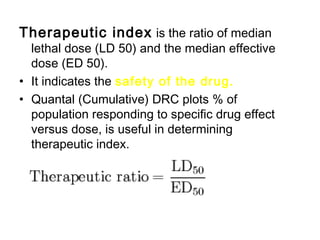
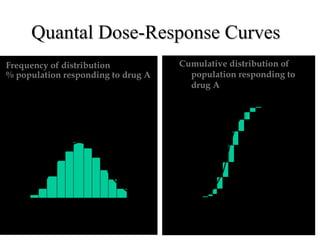
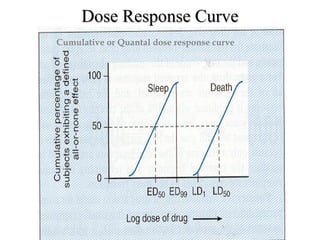
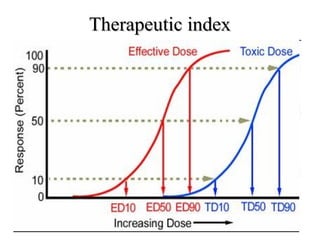
The documents discuss graded dose response curves which depict the relationship between drug dose and magnitude of effect. The potency of a drug refers to the amount needed to produce a response, which can be measured by the dose required to produce half the maximum effect. Effectiveness considers both response and safety, which is measured by the therapeutic index - the ratio of lethal to effective doses. Quantal dose response curves plot the percentage of a population responding at given doses and are useful in determining therapeutic indices.