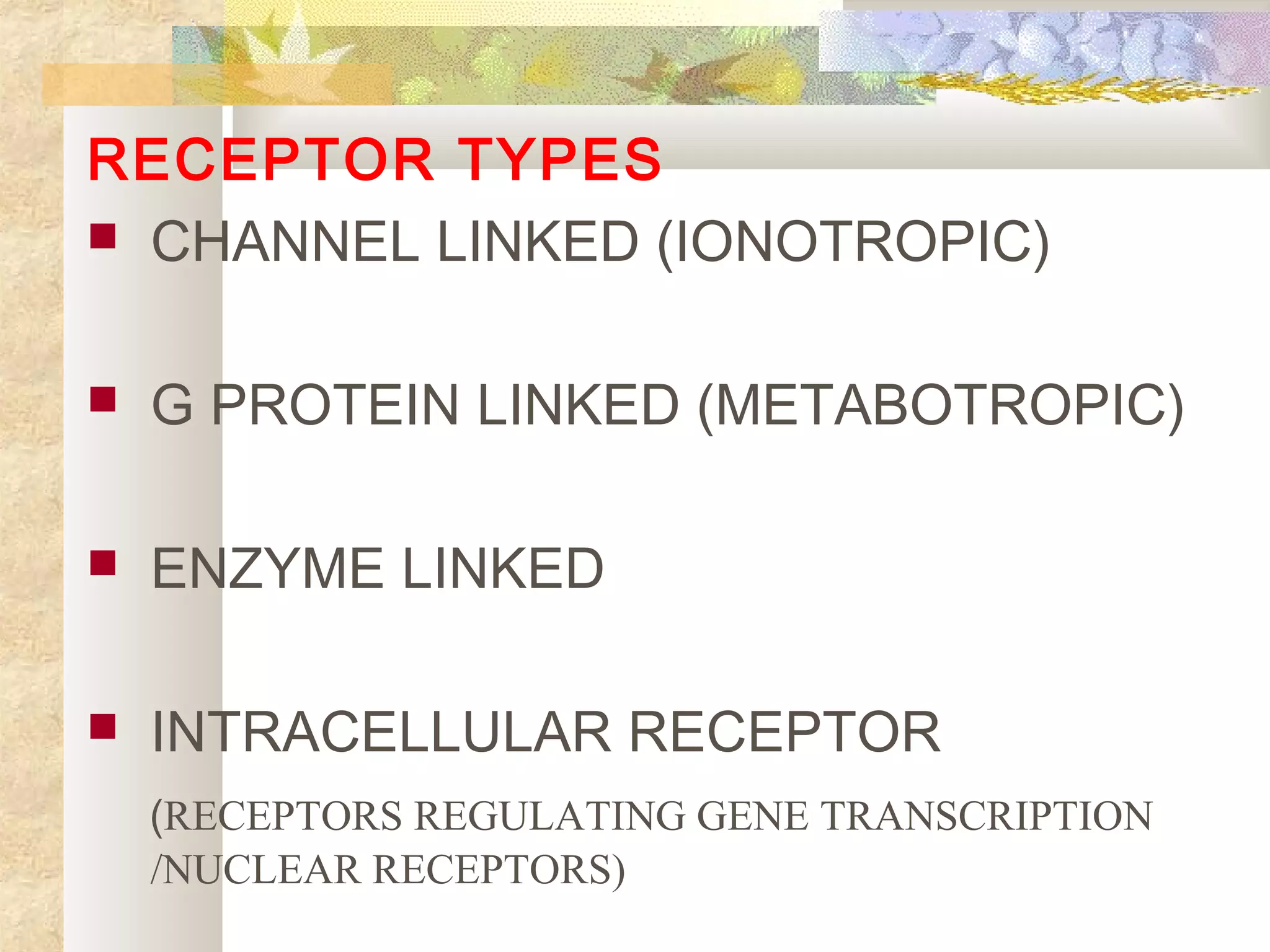
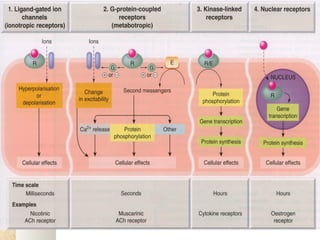
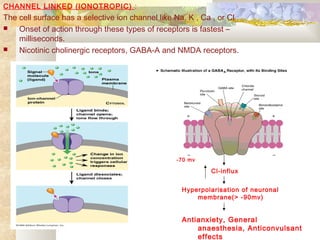
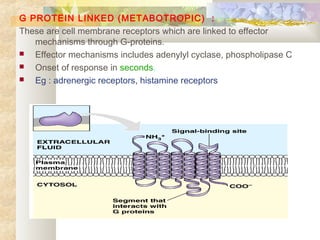
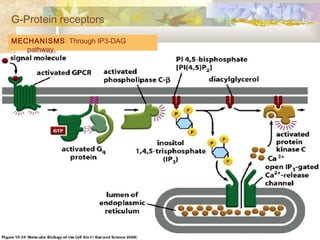
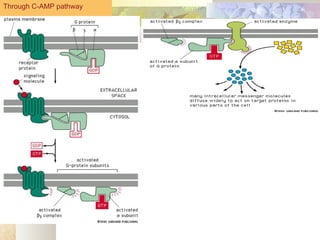
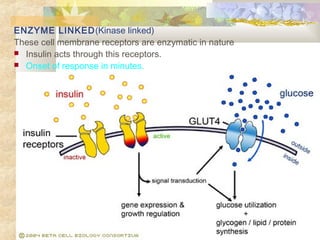
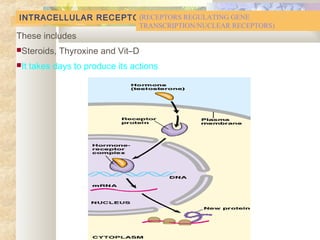
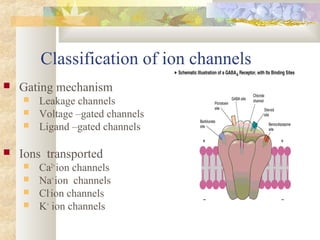
There are four main types of receptors: channel-linked (ionotropic) receptors, G protein-linked (metabotropic) receptors, enzyme-linked receptors, and intracellular receptors. Channel-linked receptors have the fastest onset of action, in milliseconds, and include nicotinic cholinergic and NMDA receptors. G protein-linked receptors signal through second messenger systems and have an onset of seconds, such as adrenergic receptors. Enzyme-linked receptors signal through kinase pathways and have an onset of minutes, such as insulin receptors. Intracellular receptors include steroid receptors and regulate gene transcription with effects over days.