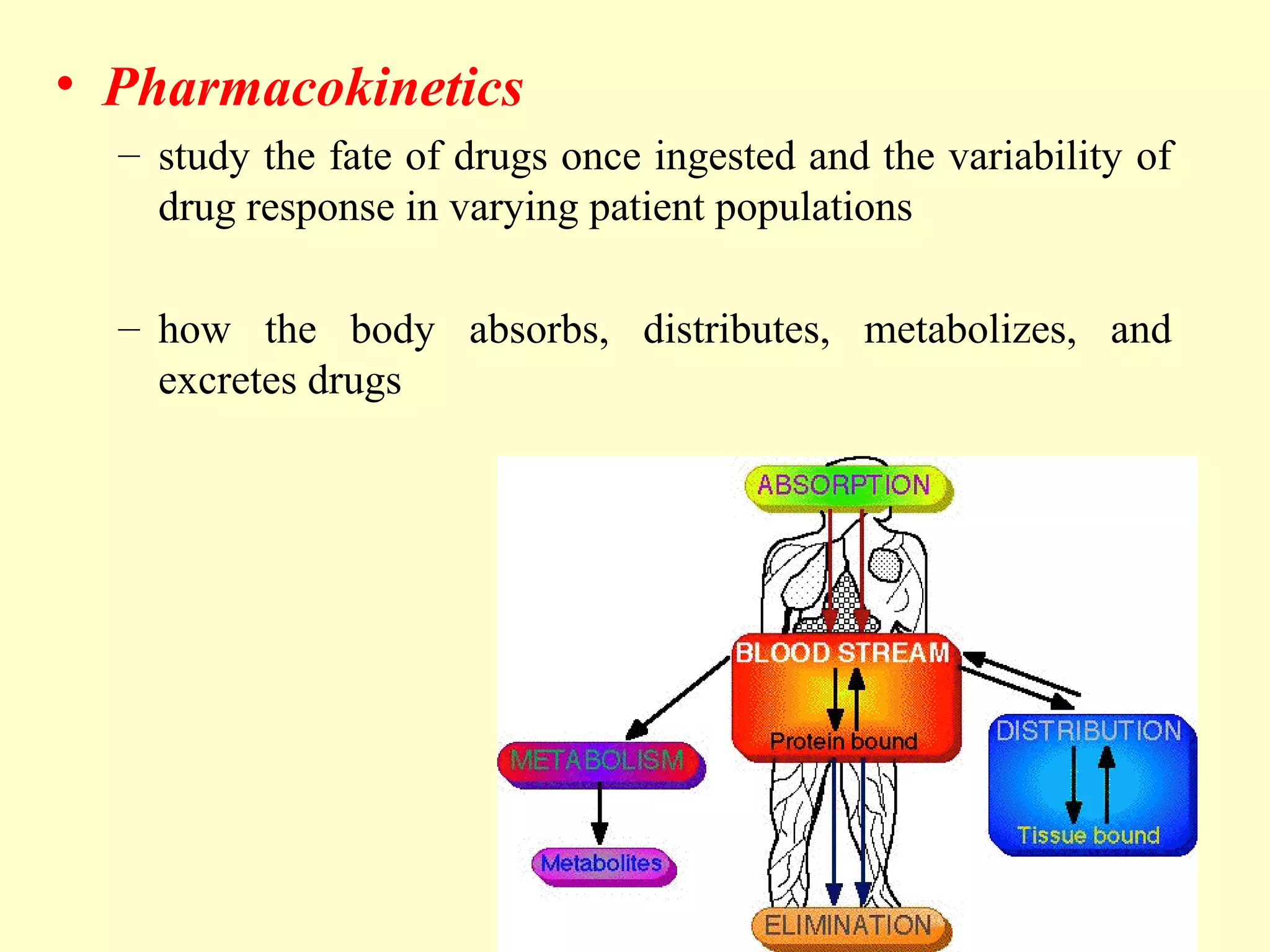
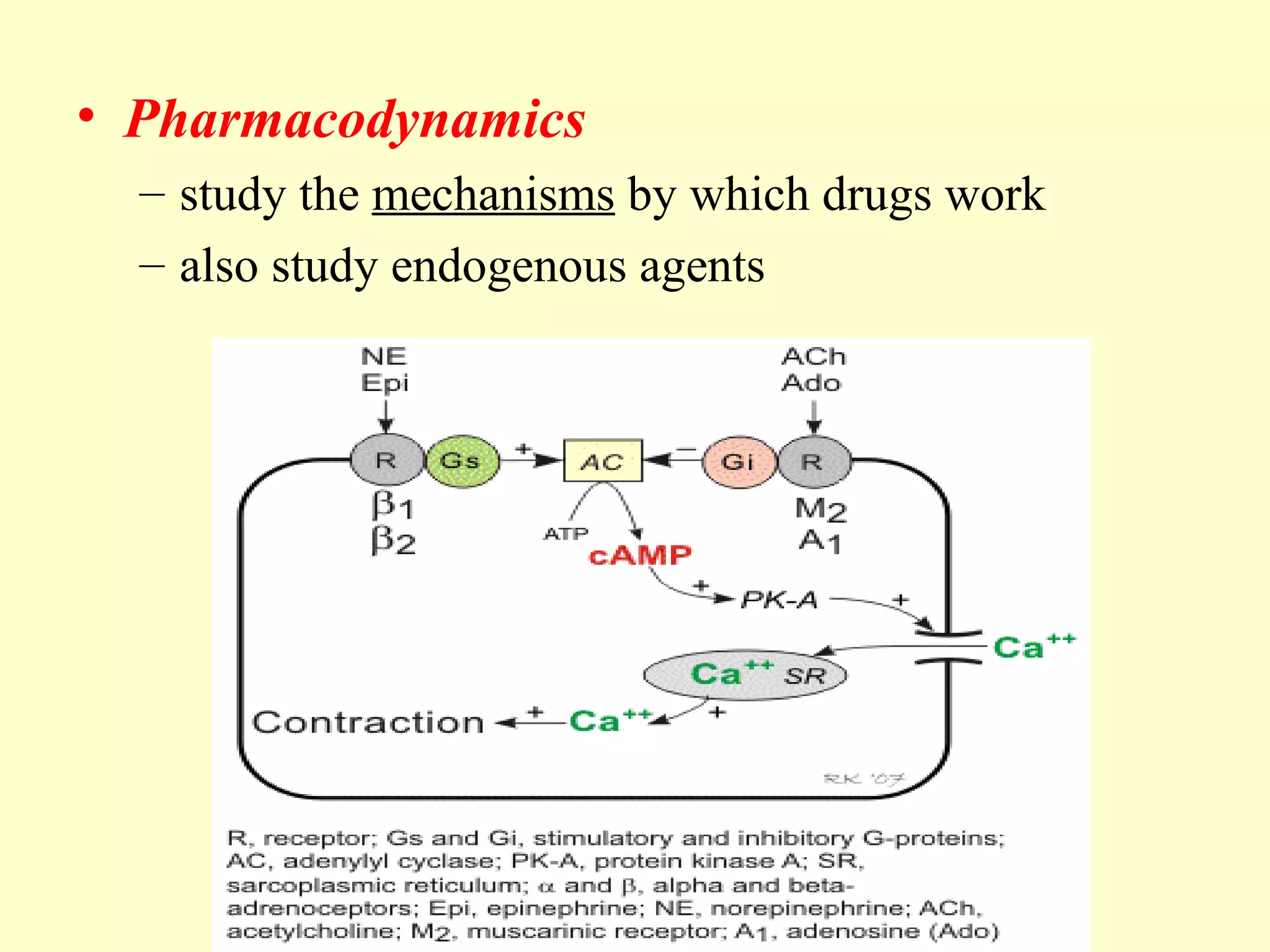
Pharmacology is the study of drugs and how they work in the body. It has two main areas: pharmacokinetics, which studies how the body affects drugs; and pharmacodynamics, which studies how drugs affect the body. Some key examples are that acetylsalicylic acid reduces inflammation through inhibiting an enzyme, penicillin kills bacteria by disrupting cell wall synthesis through another enzyme inhibition, and neuropharmacology examines drug effects on the nervous system.