This document discusses the interpretation of various types of Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy. It describes:
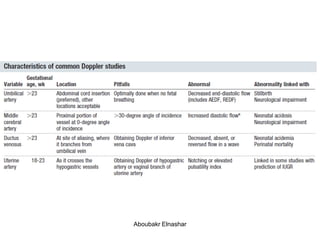
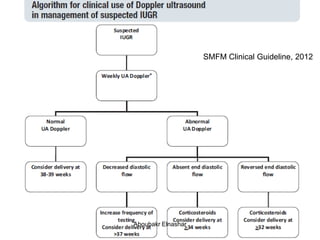
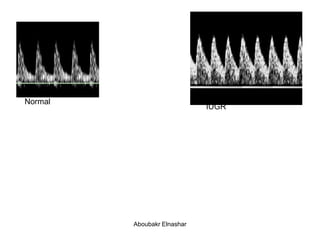
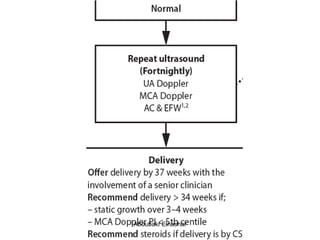
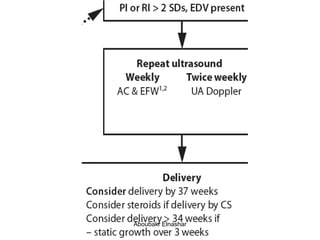
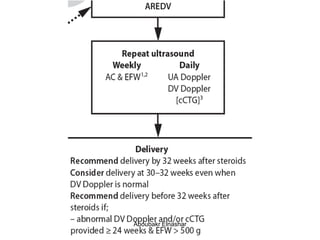
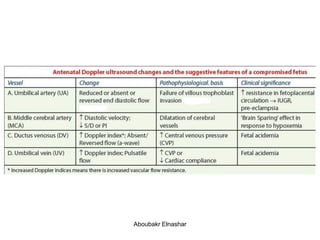
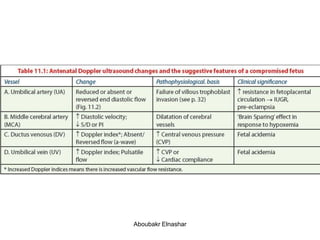
1. Umbilical artery Doppler which can detect placental hypoxia and increased resistance, predicting abnormal outcomes. Abnormal readings include increased resistance index and absent/reversed end diastolic flow.
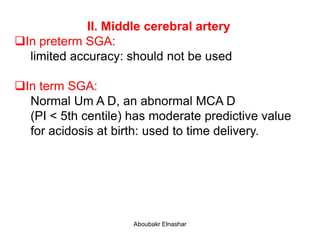
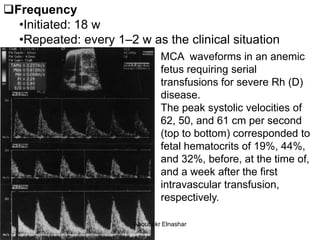
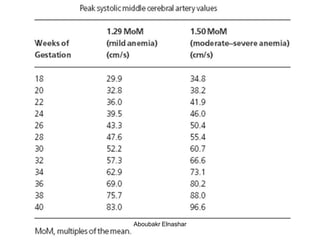
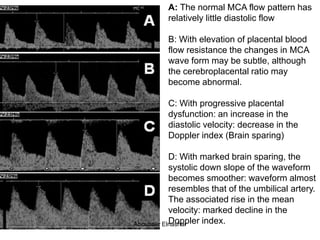
2. Middle cerebral artery Doppler which can detect fetal anemia by increased blood flow to the brain. It is also used to time delivery of growth restricted infants.
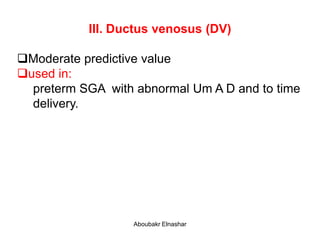
3. Ductus venosus Doppler which has moderate predictive value for growth restriction in preterm infants.
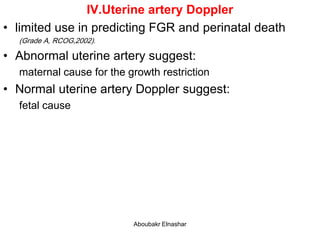
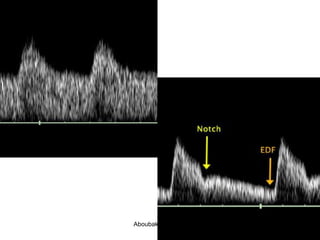
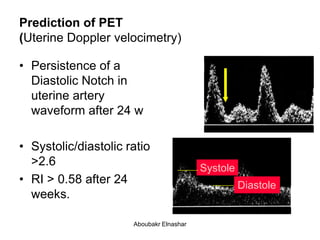
4. Uterine artery Doppler has limited use in predicting fetal growth restriction but can identify maternal causes by abnormal readings.