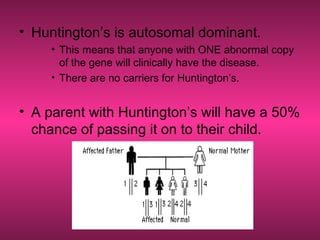
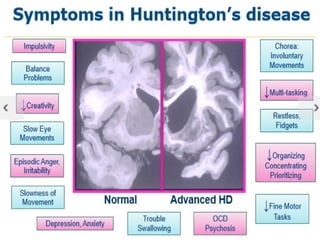
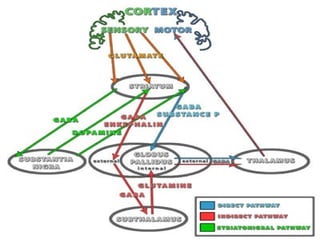
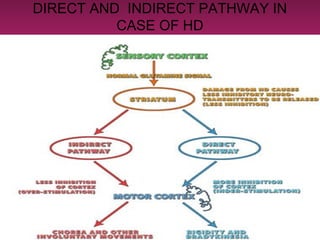
Huntington's disease is a genetic neurodegenerative disorder that typically causes movement, cognitive, and psychiatric problems. It is caused by an expanded CAG repeat in the Huntington gene, which leads to damage and death of nerve cells in the brain over time. The signs and symptoms of Huntington's disease usually appear between ages 30 and 50 and worsen over 10 to 25 years, progressing through distinct stages of mild, moderate, and severe problems with movement, thinking, and behavior. While there is no cure for Huntington's disease currently, medications and therapies can help manage some of the symptoms.