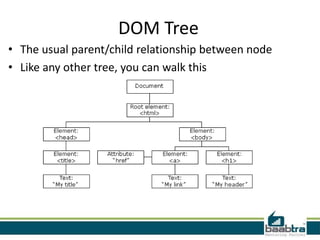
This document provides an overview of the Document Object Model (DOM) including:
- The DOM is a programming model that represents objects in an HTML or XML document as a tree structure.
- It describes the DOM standard levels developed by the W3C for handling documents.
- JavaScript can be used to manipulate the DOM tree programmatically for things like form validation.
- Web pages need to be well-formed XHTML and include IDs to identify elements for DOM manipulation.