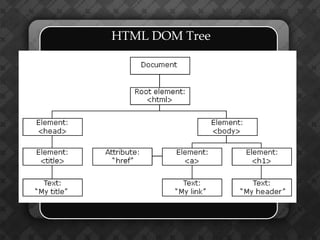
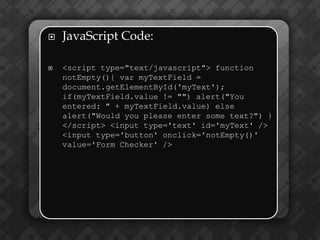
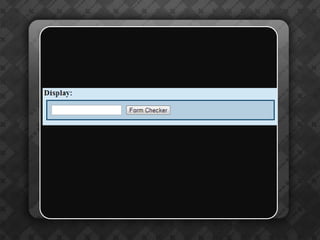
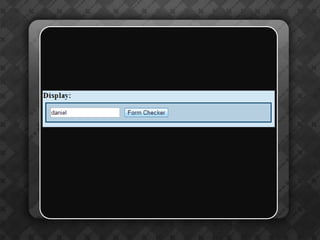
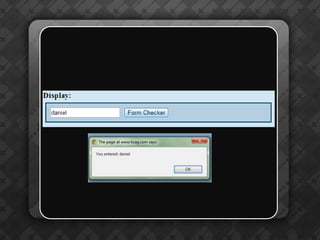
Dynamic HTML (DHTML) is a collection of technologies that enhances HTML by integrating JavaScript, CSS, and the Document Object Model (DOM) for interactivity. It treats HTML elements as objects, allowing for easier manipulation via JavaScript using methods like getElementById(). The document also emphasizes the importance of unique identifiers (IDs) for elements in enhancing accessibility and functionality within web pages.