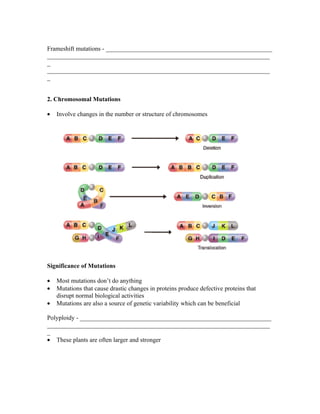
The document provides information about DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. It discusses the structure of DNA and chromosomes, DNA replication, the structure and types of RNA, transcription, translation, and the genetic code. The key points are:
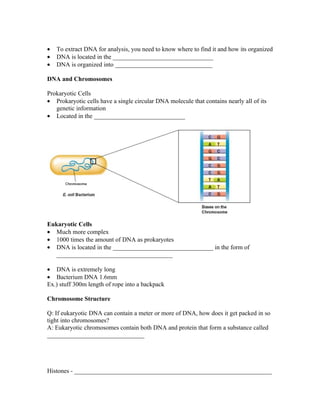
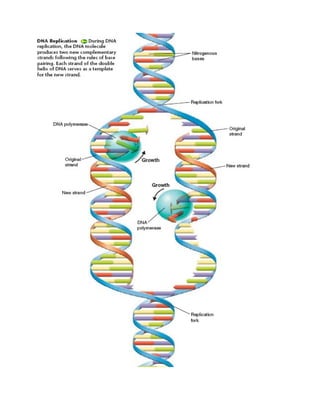
1) DNA is organized into chromosomes in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. During replication, the DNA double helix unwinds and each strand acts as a template to make a new complementary strand.
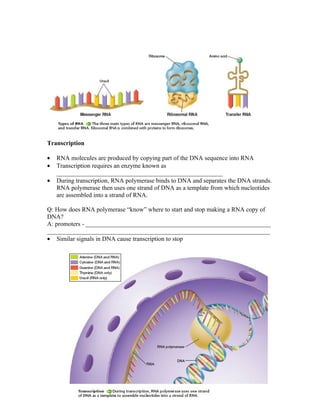
2) There are three main types of RNA - mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. mRNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and transports the genetic code to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis.
3) During translation, mRNA instructs the assembly of amino acids onto


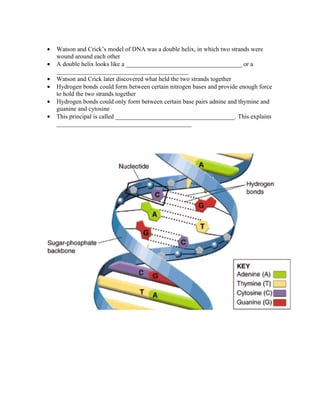
![• There are 4 kinds of nitrogenous bases
1.
2.
3.
4.
Chargaff’s Rules
• Erwin Chargaff discovered that the percentages of guanine [G] and cytosine [C] are
almost equal and the percentages of adnine [A] and thymine [T]
Chargaff’s Rule
X-Ray Evidence
• Rosalind Franklind
• British Scientist
• Used a technique called X-Ray diffraction
• Provided important clues about the structure of DNA
o
o
o
The Double Helix
• Francis Crick & James Watson
o Trying to understand the structure of DNA
by building models
o Unsuccessful until early 1953, Watson was
shown a copy of Franklin’s X-ray pattern
o “The instant I saw the picture my mouth fell
open and my pulse began to race.”
- James Watson
o Within weeks Watson and Crick had figured
out the structure of DNA
o Published their results in a historic one page
paper in April of 1953](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biology-chapter12notes-dnarna-110828132112-phpapp01/85/Biology-Chp-12-DNA-and-RNA-Notes-3-320.jpg)