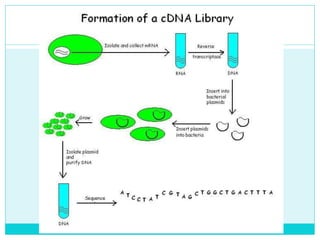
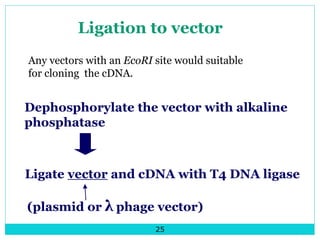
This document describes DNA libraries and the process of creating them. It discusses genomic libraries, which contain an organism's entire genome, and cDNA libraries, which contain copies of mRNA. The key steps to create a library are: 1) isolating and fragmenting DNA, 2) cloning the fragments into vectors, 3) transforming the vectors into host cells, 4) multiplying and screening the clones to identify fragments of interest. cDNA libraries are useful for studying eukaryotic genes as they remove non-coding regions.