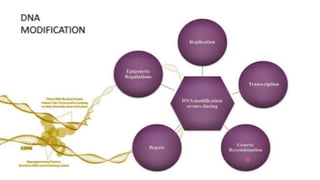
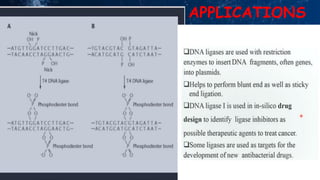
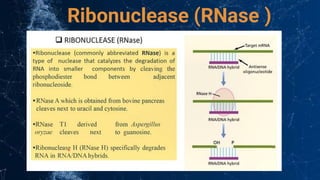
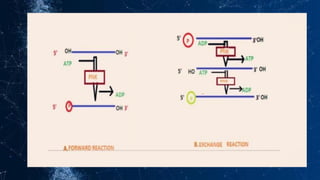
DNA modifying enzymes play important roles in genetic engineering and manipulating DNA. These enzymes include polymerases, DNase, RNase, polynucleotide kinase, alkaline phosphatase, and nucleases. Polymerases are involved in DNA synthesis, DNase and RNase degrade DNA and RNA, respectively, and polynucleotide kinase and alkaline phosphatase modify the phosphate groups on DNA and RNA. These enzymes are used in applications such as eliminating contamination, mapping mutations, DNA footprinting, radiolabeling, and DNA fragmentation.