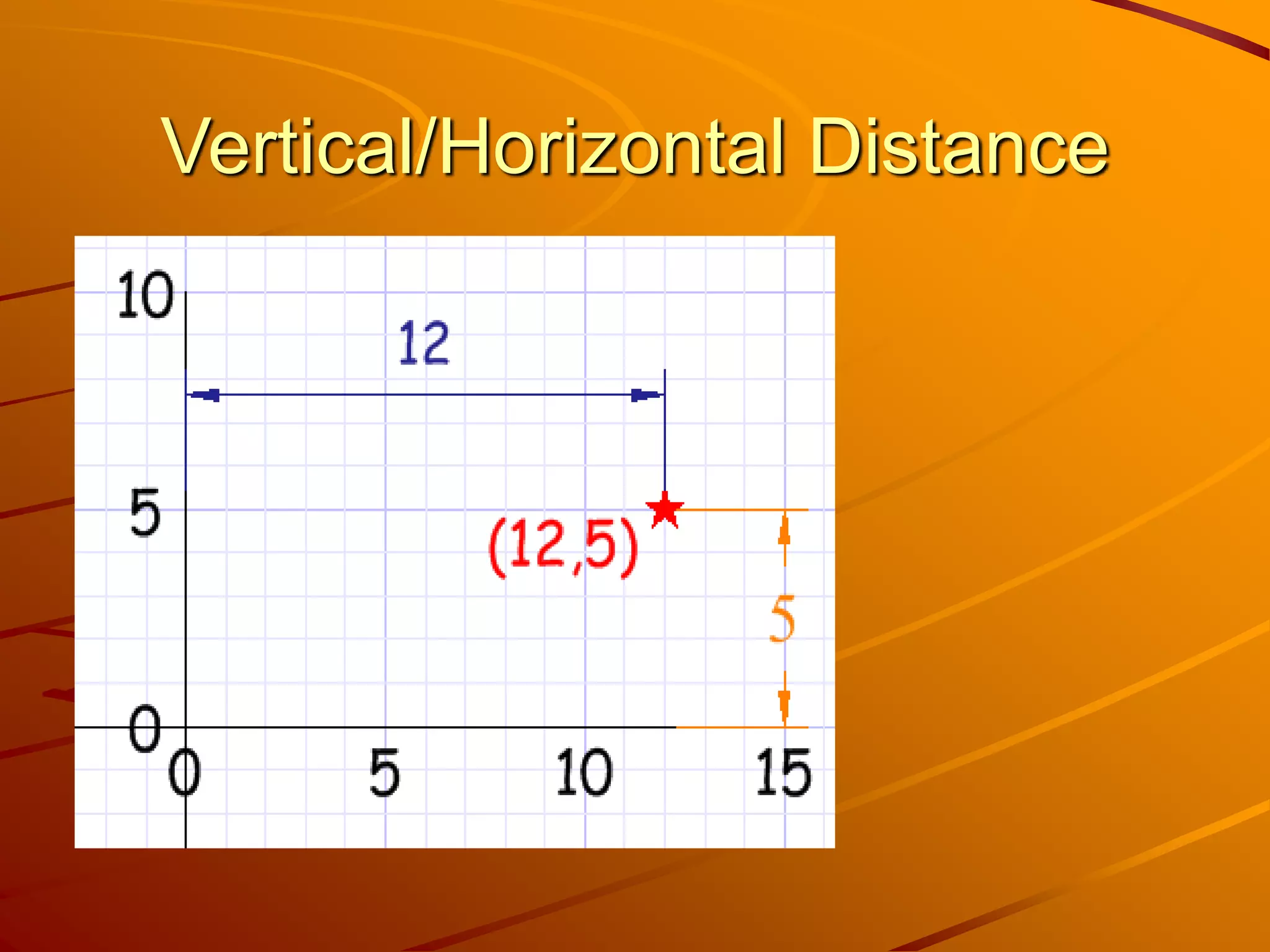
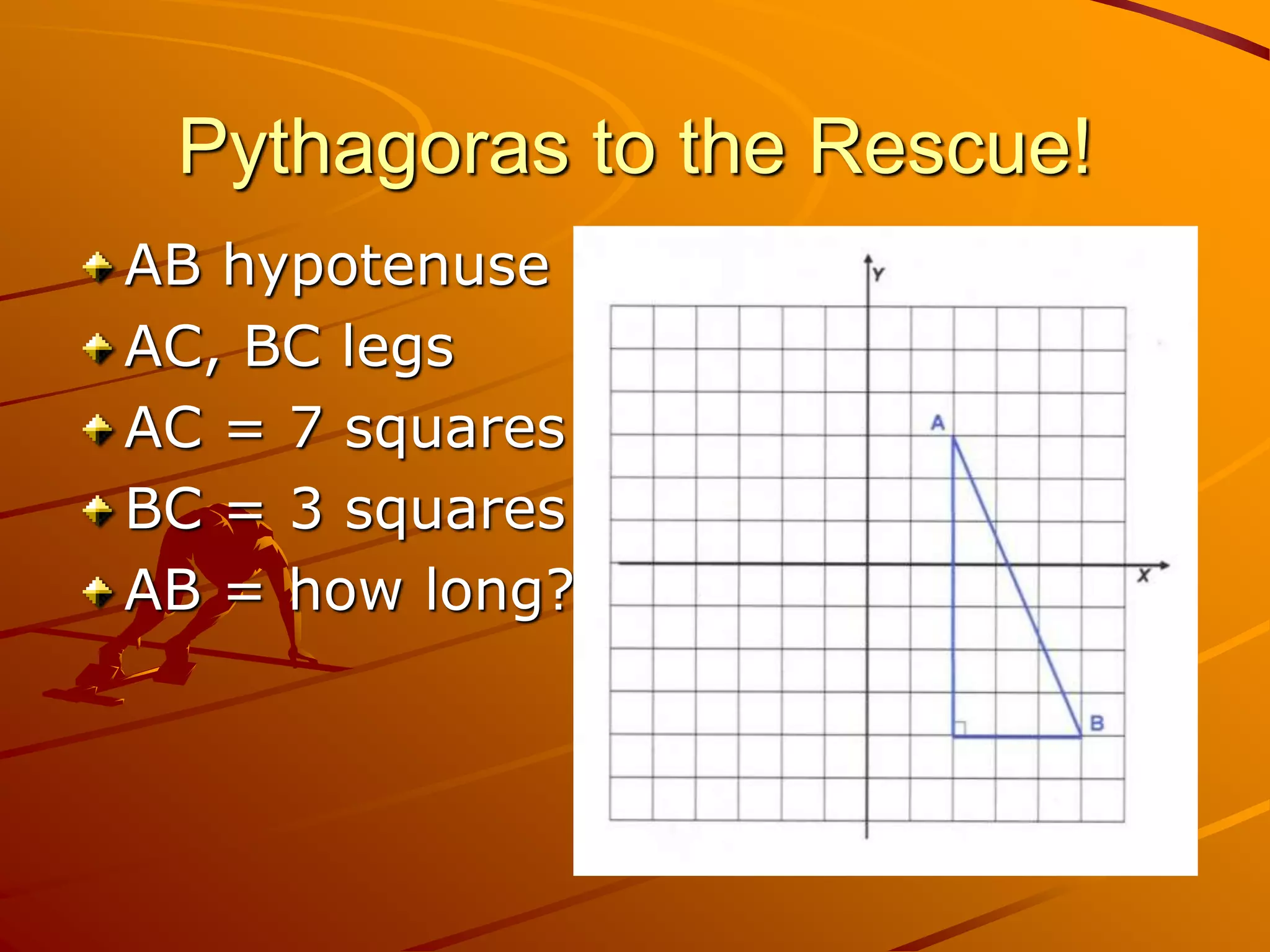
The document summarizes key concepts about finding distance in the Cartesian plane. It outlines three cases for distance between two points: horizontal, vertical, and oblique (diagonal) distance. It then explains how to calculate each type of distance and introduces the distance formula. The Pythagorean theorem is used to calculate oblique distance. Additional topics covered include finding the midpoint between two points, solving problems involving equidistant points, and the relationship between distance and parabolas.