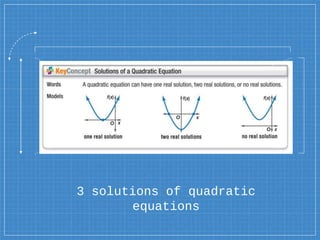
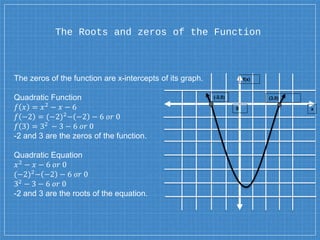
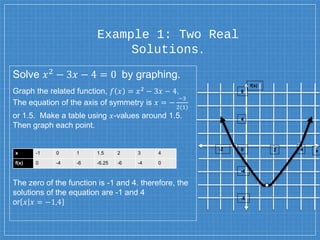
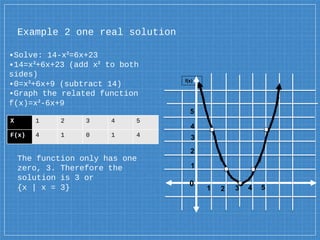
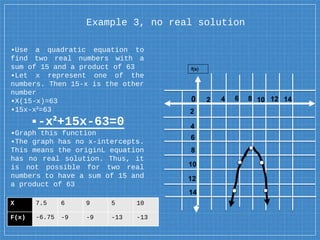
The document explains solving quadratic equations by graphing, emphasizing the standard form ax2 + bx + c = 0 and the roots or zeros of the related quadratic function. It provides examples demonstrating two real solutions, one real solution, and no real solution scenarios, illustrating how to graph the functions to find these solutions. Additionally, it includes a real-world application involving the height of a package dropped from a helicopter, showing how to determine the time it takes to reach the ground.