This document discusses disruptive technologies, specifically how Moore's Law has impacted the technology industry and networking. It provides three key points:
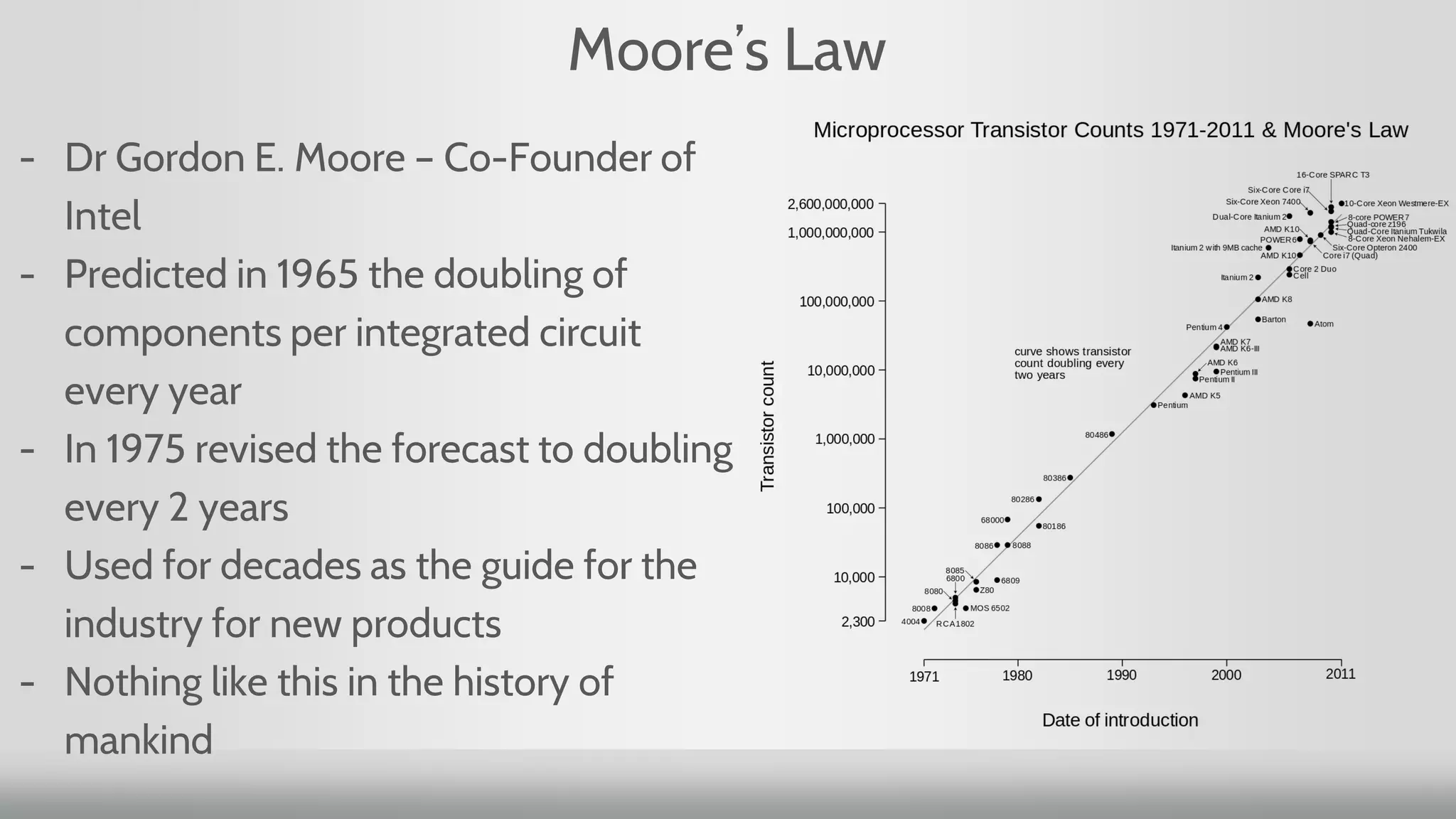
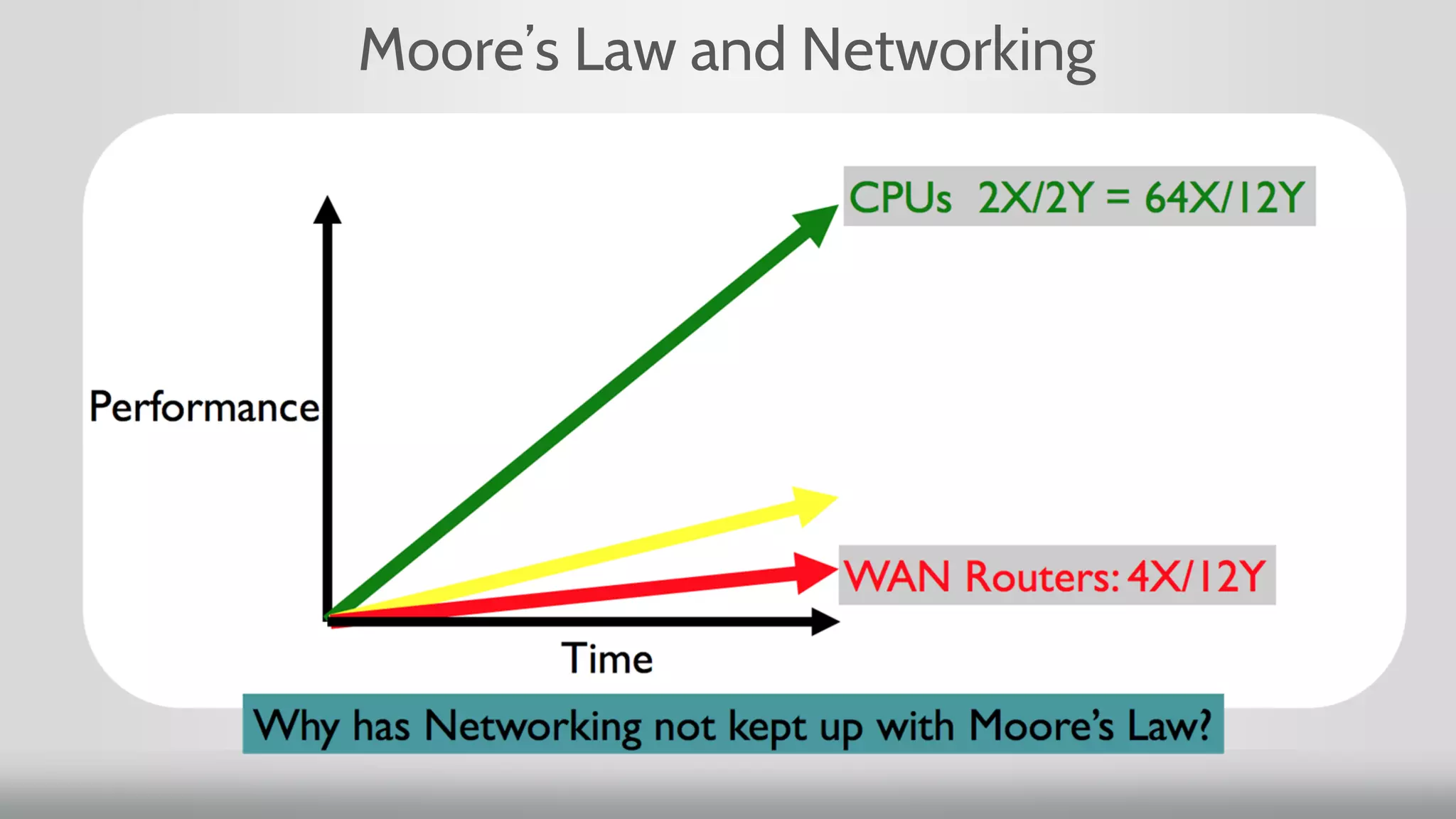
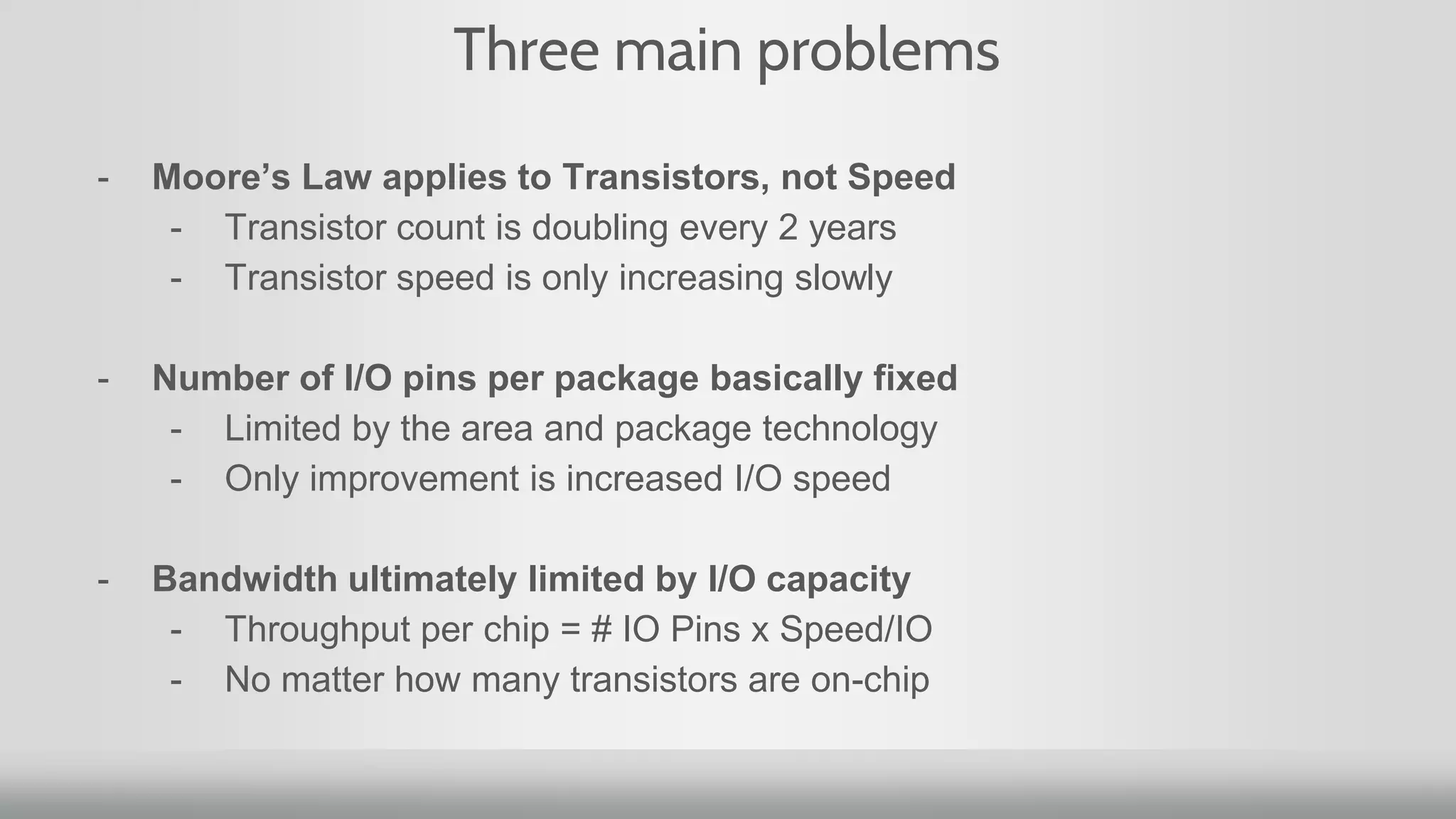
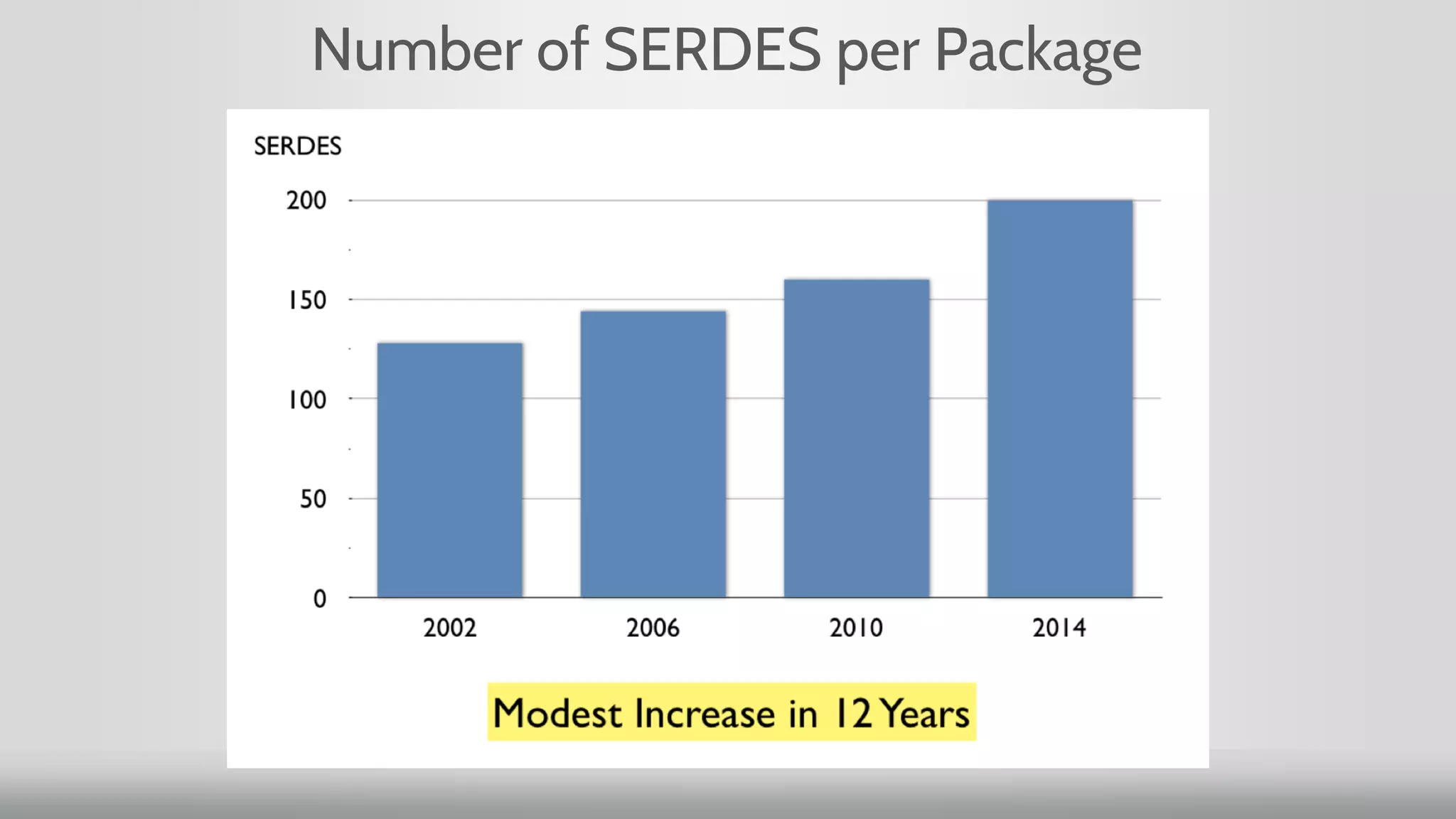
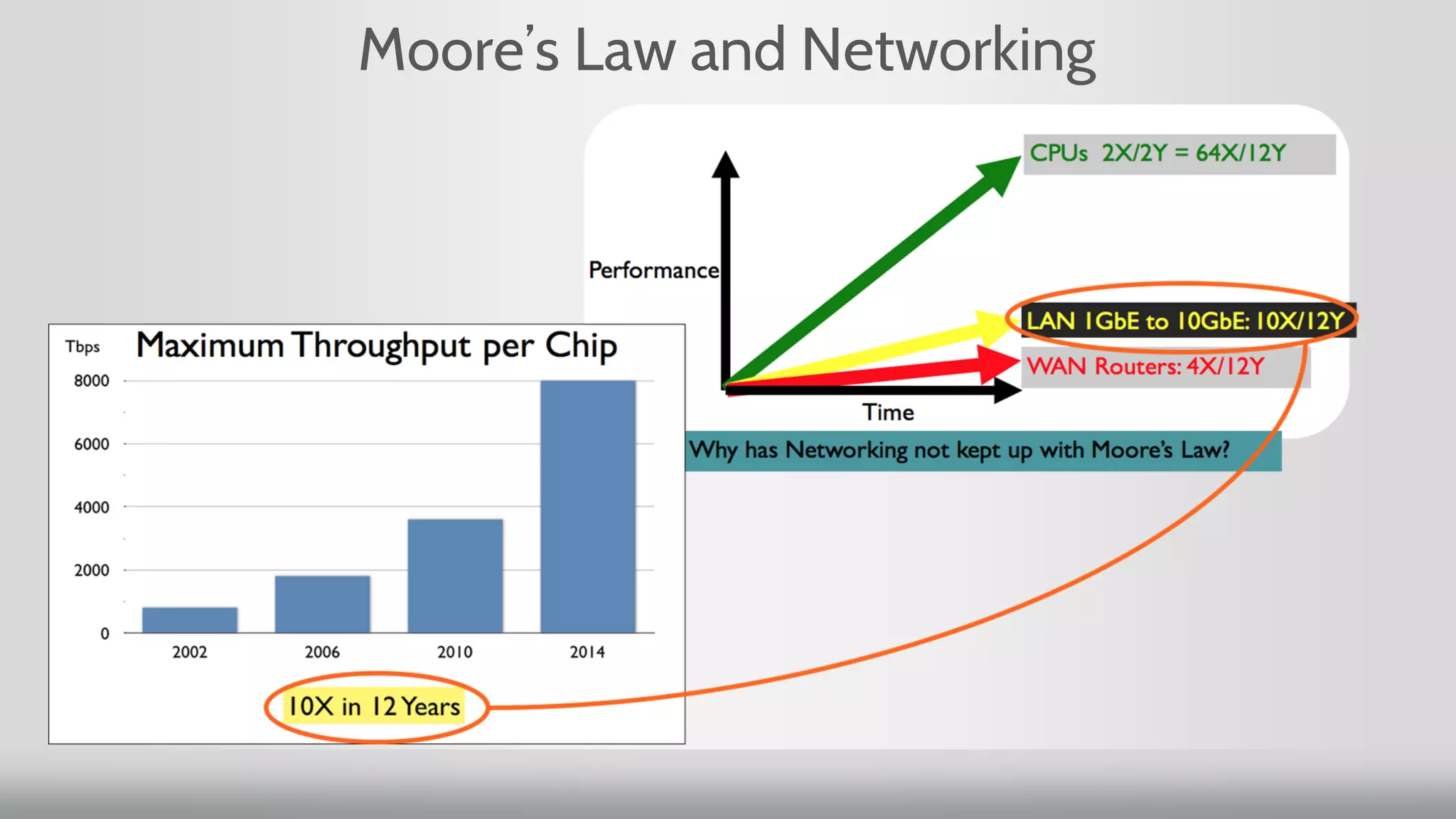
1. Moore's Law, which predicted the doubling of transistors on integrated circuits every two years, has been the guiding principle for new product development. However, for networking, transistor count has doubled but speed has increased slowly.
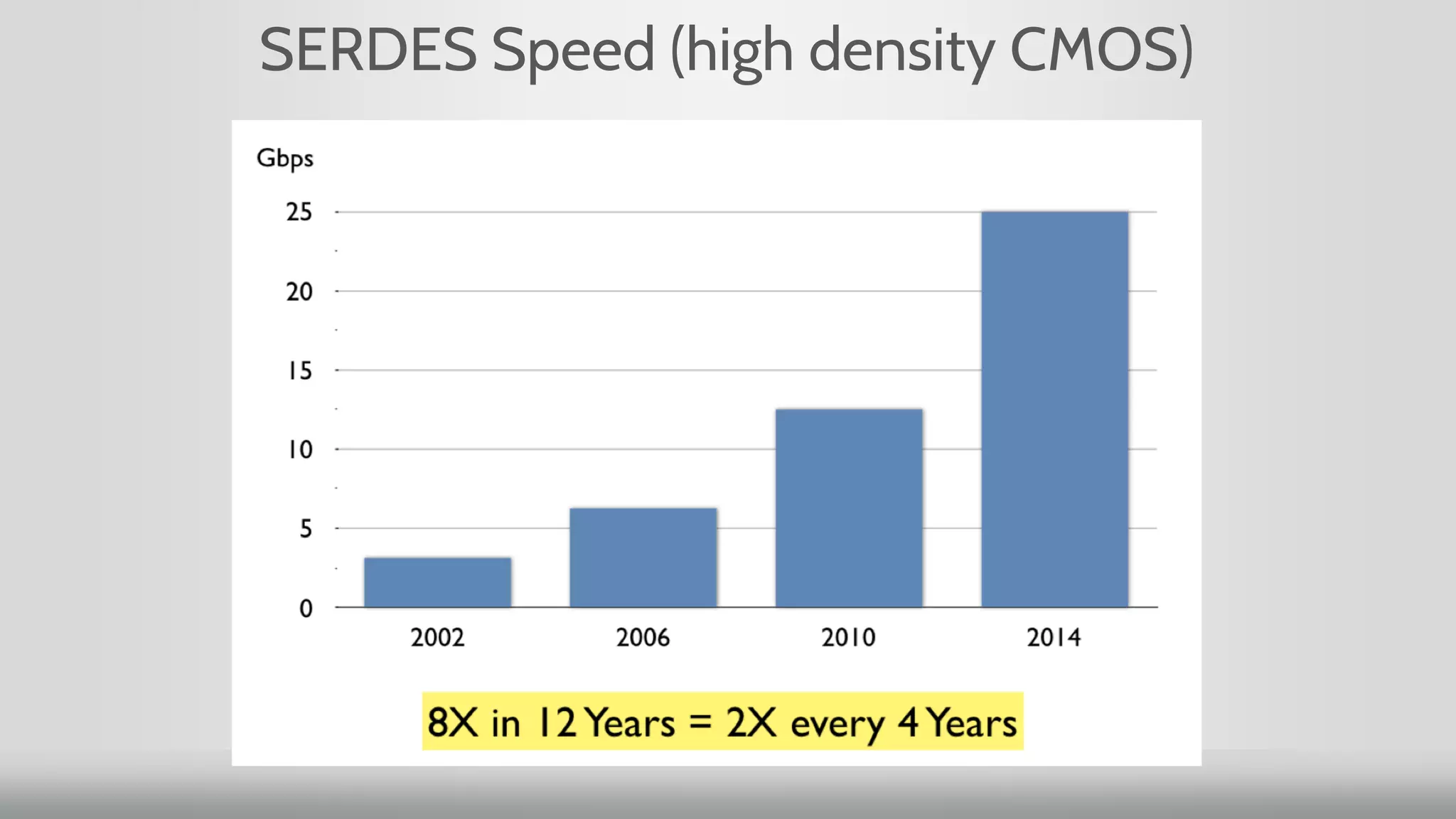
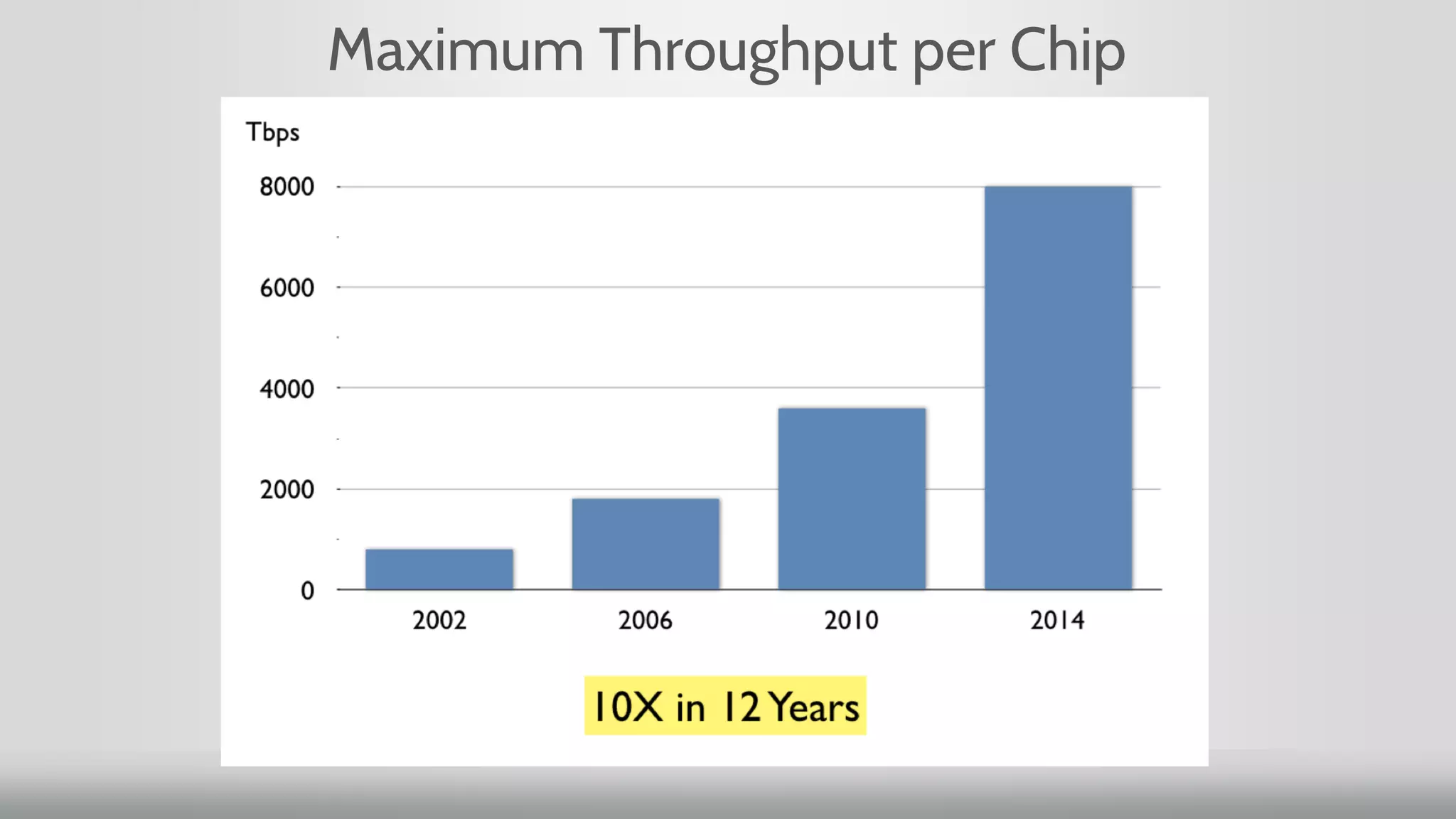
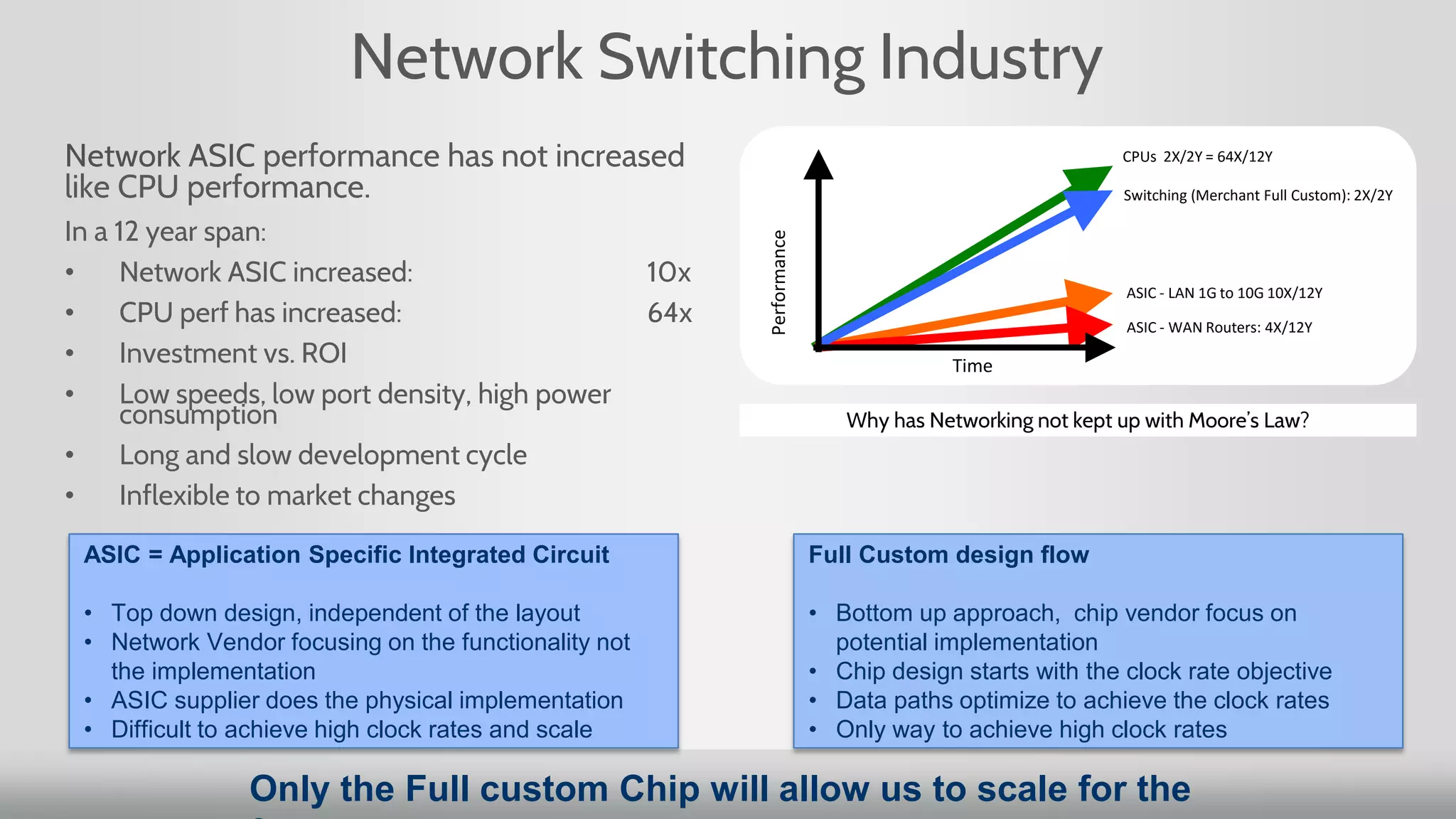
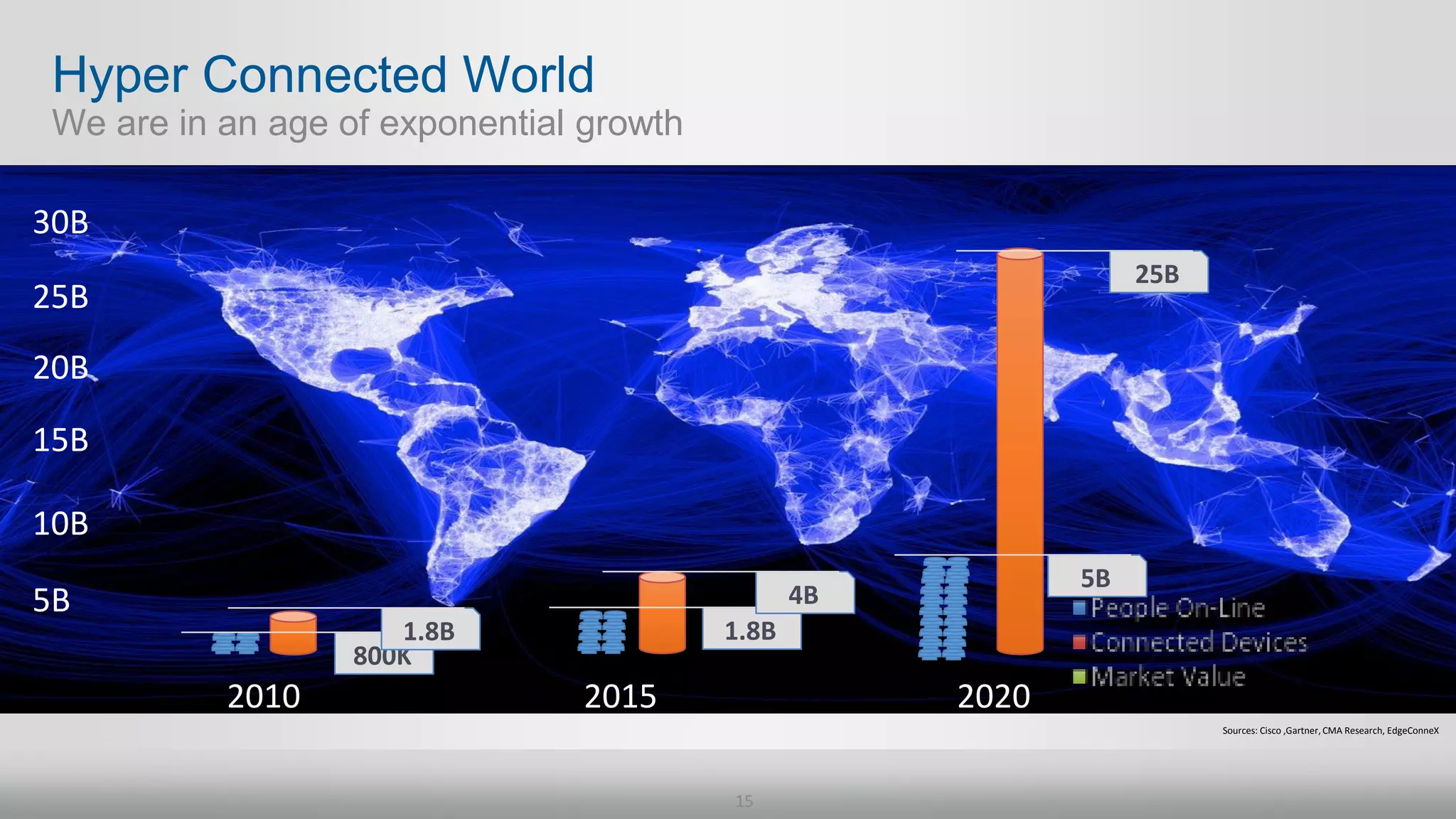
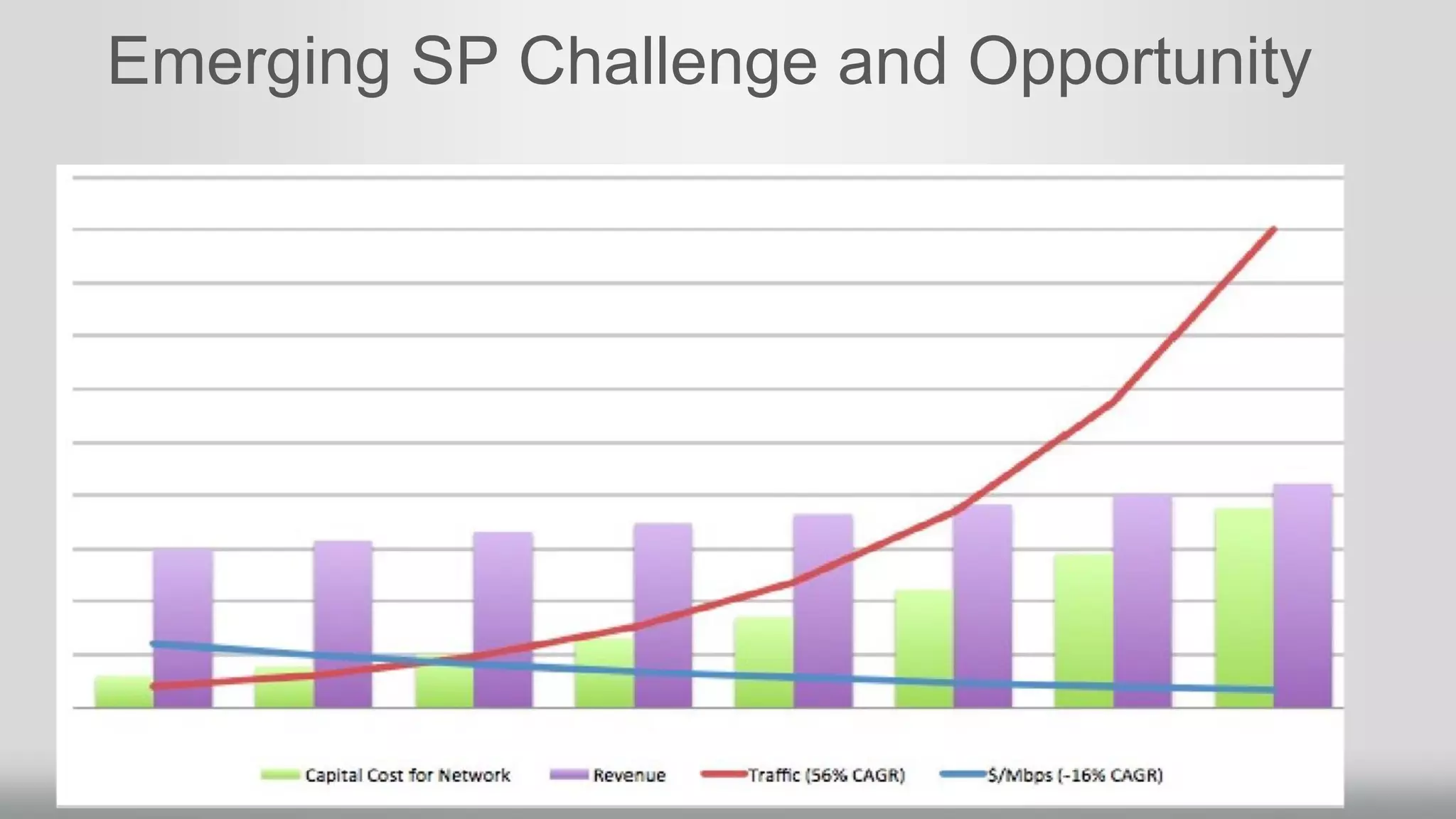
2. Networking performance has not kept up with Moore's Law like CPU performance has. Network ASICs have increased 10x over 12 years while CPUs increased 64x.
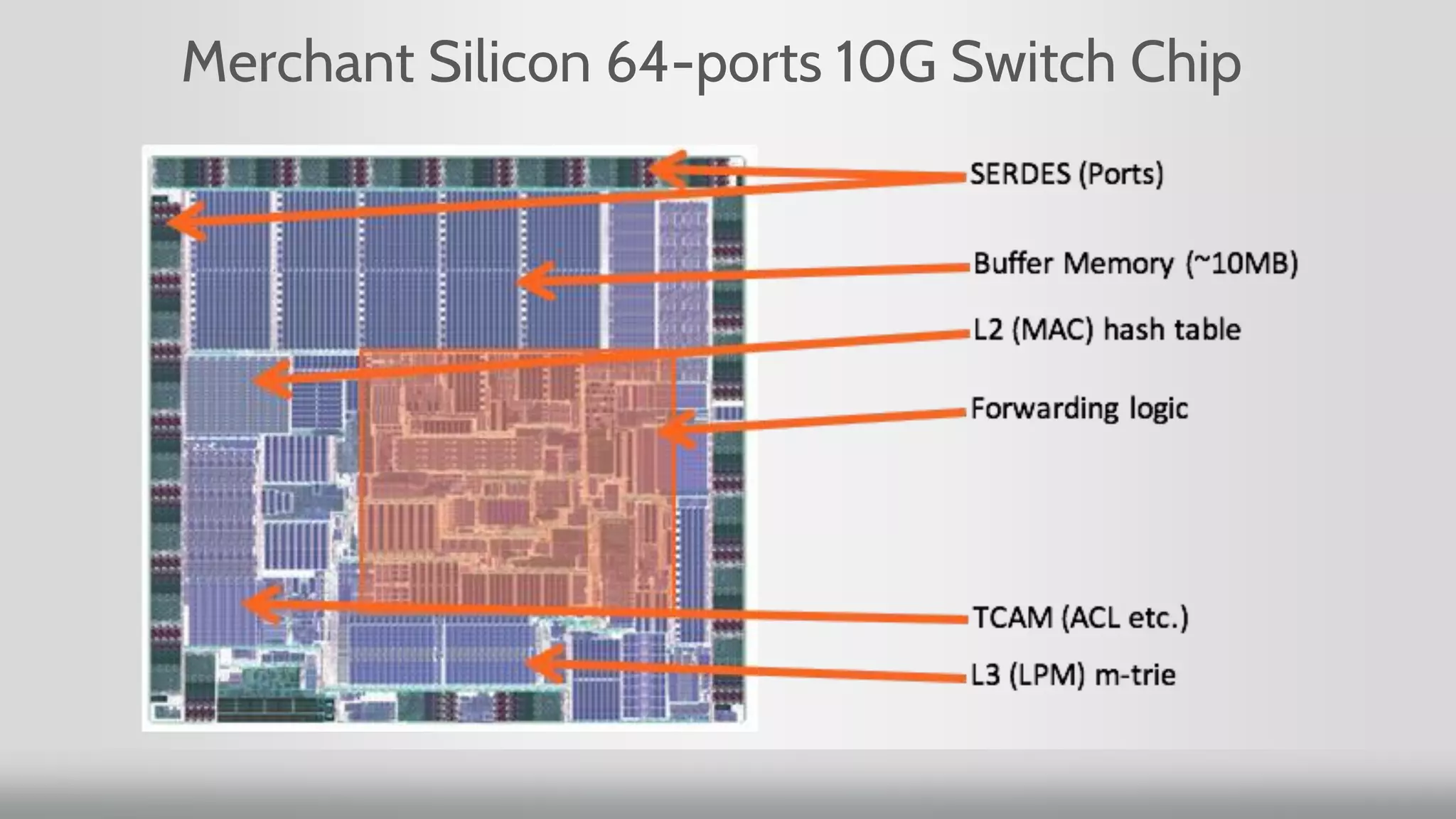
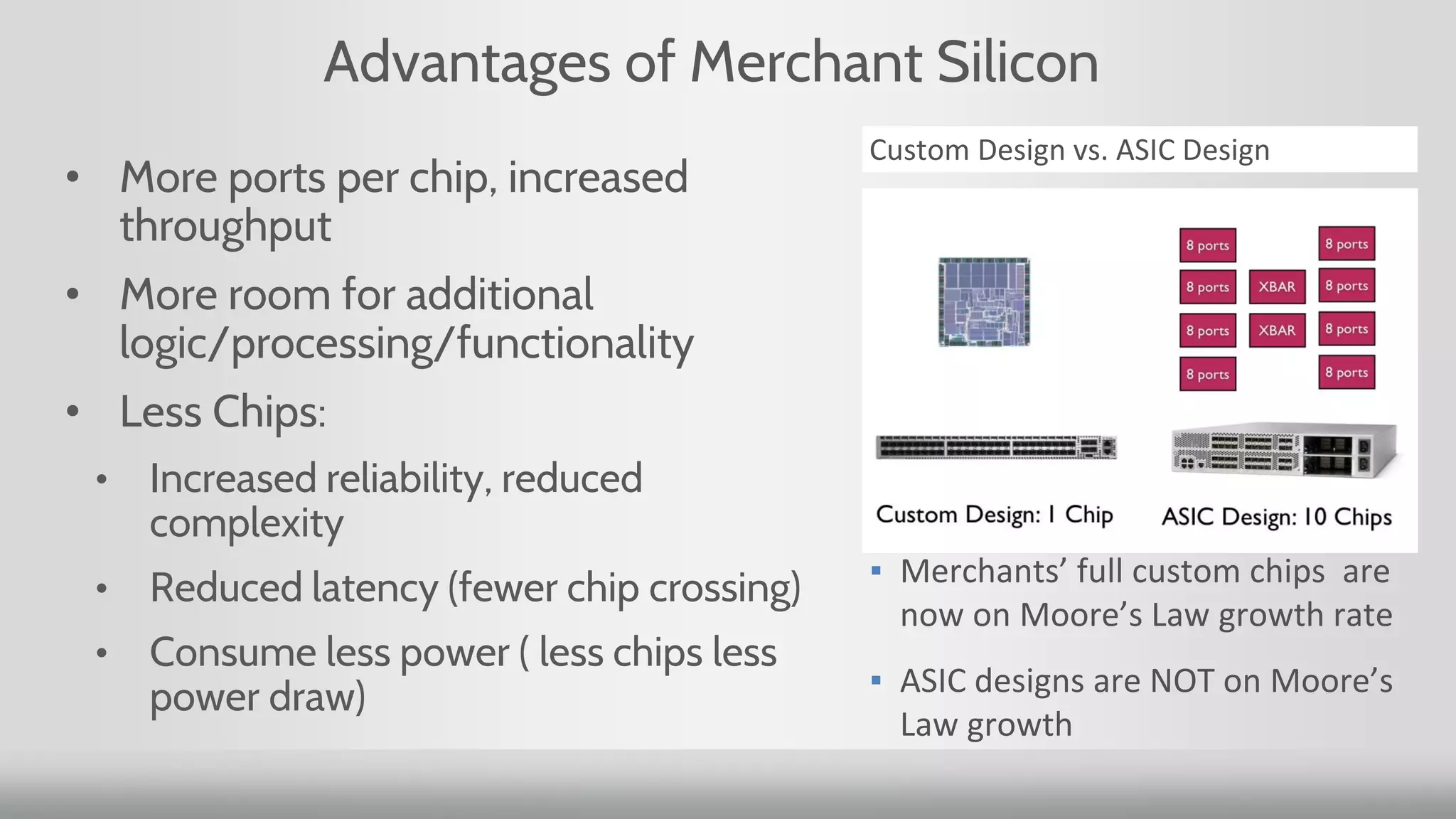
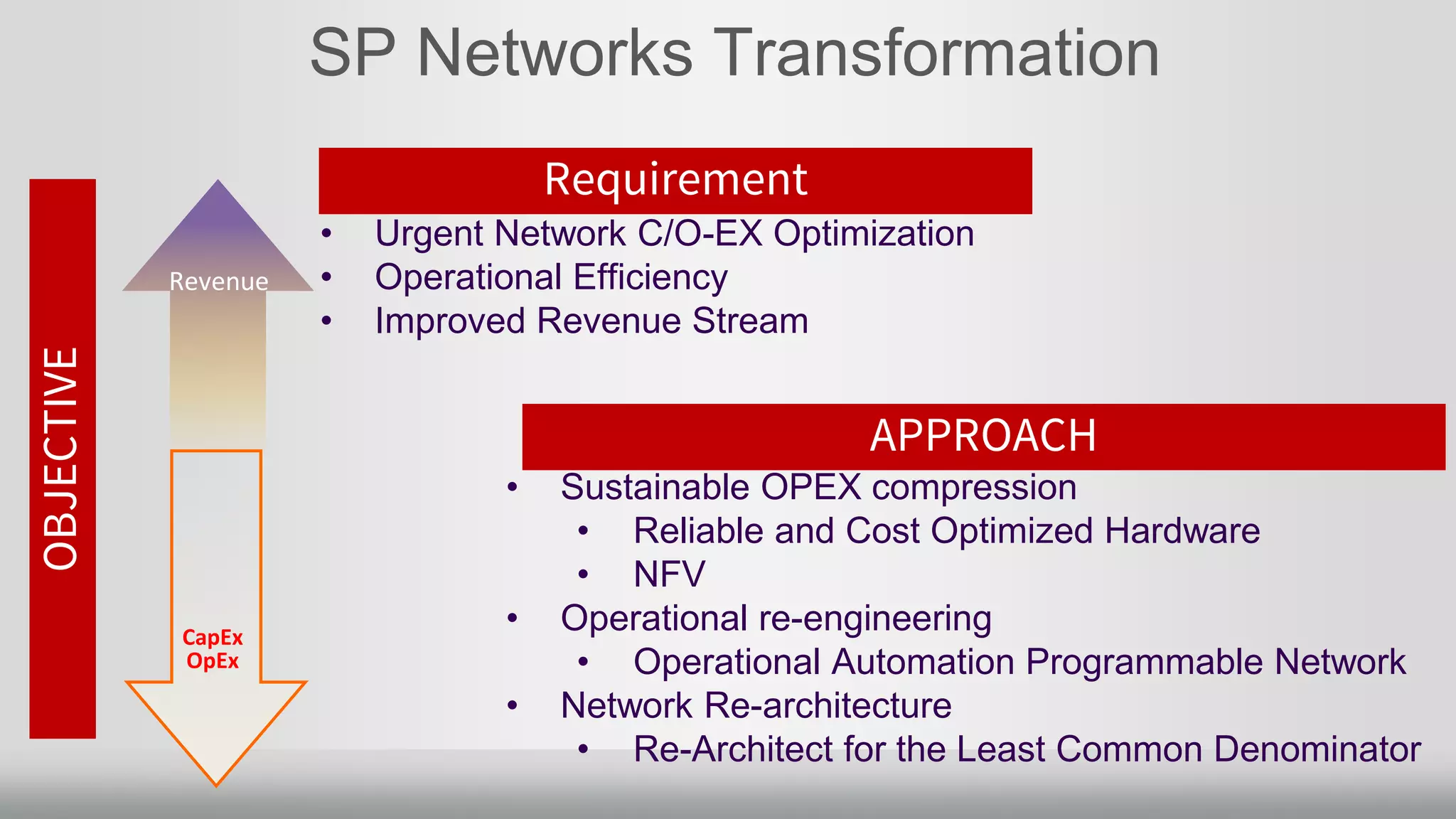
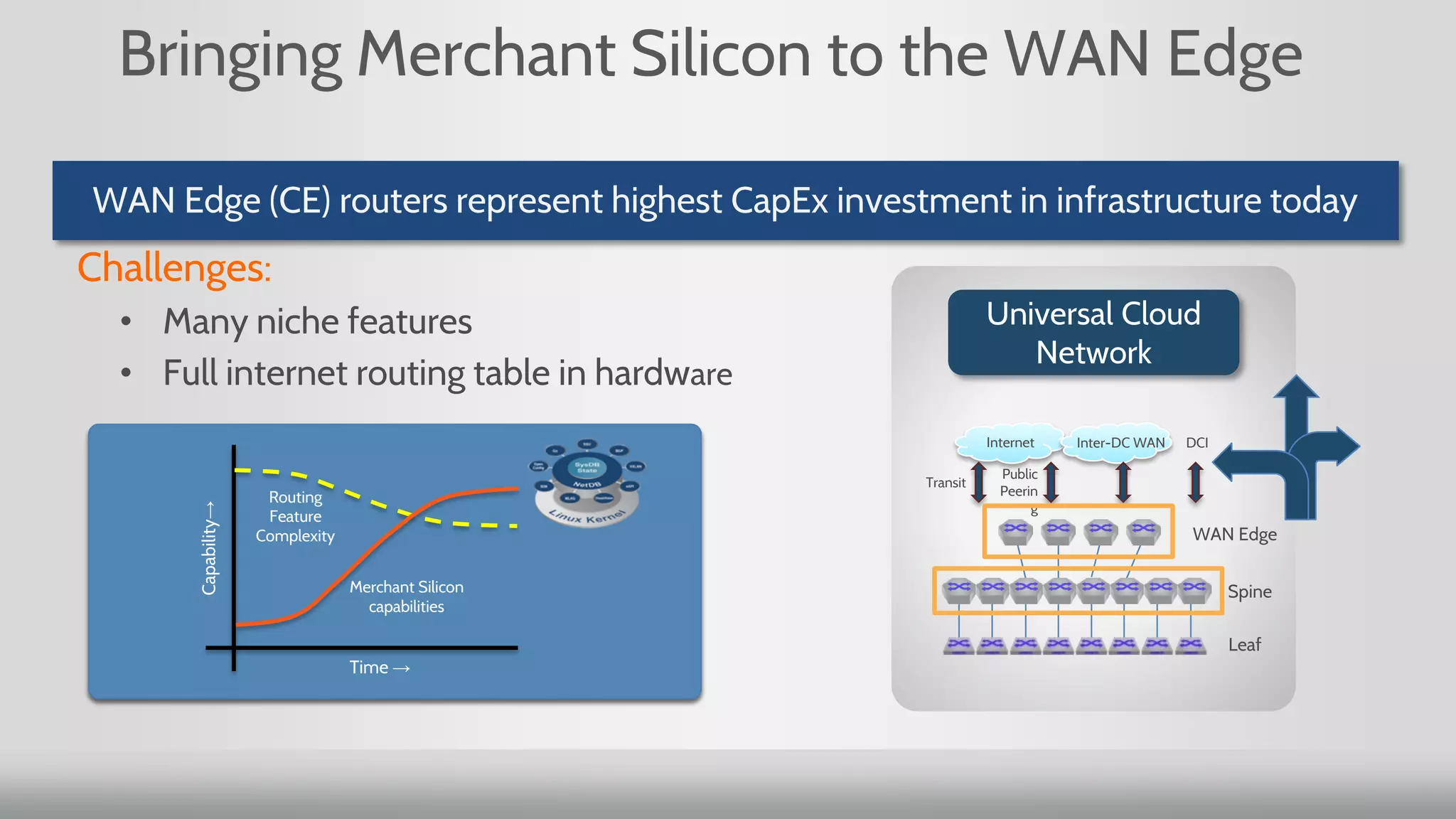
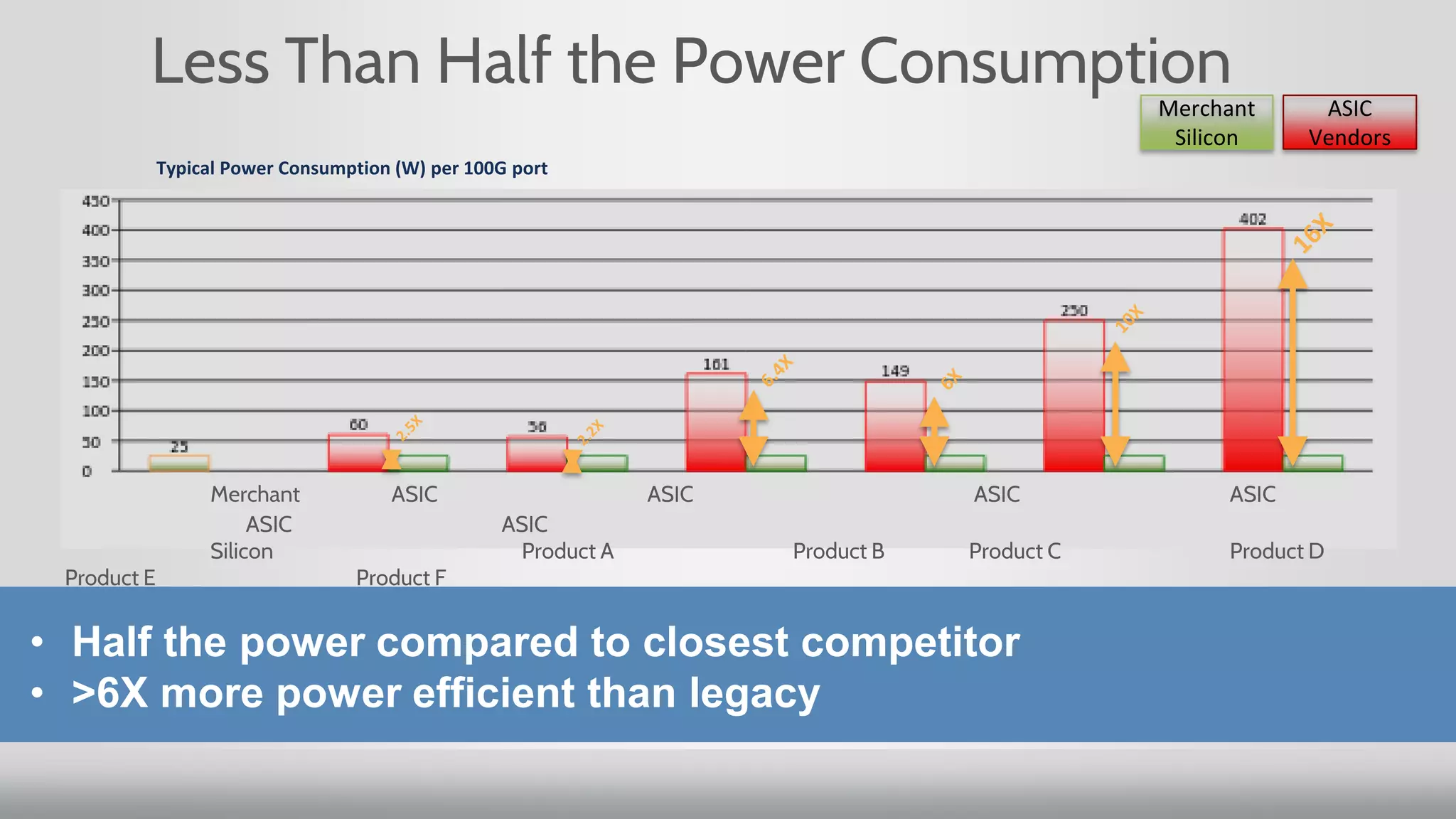
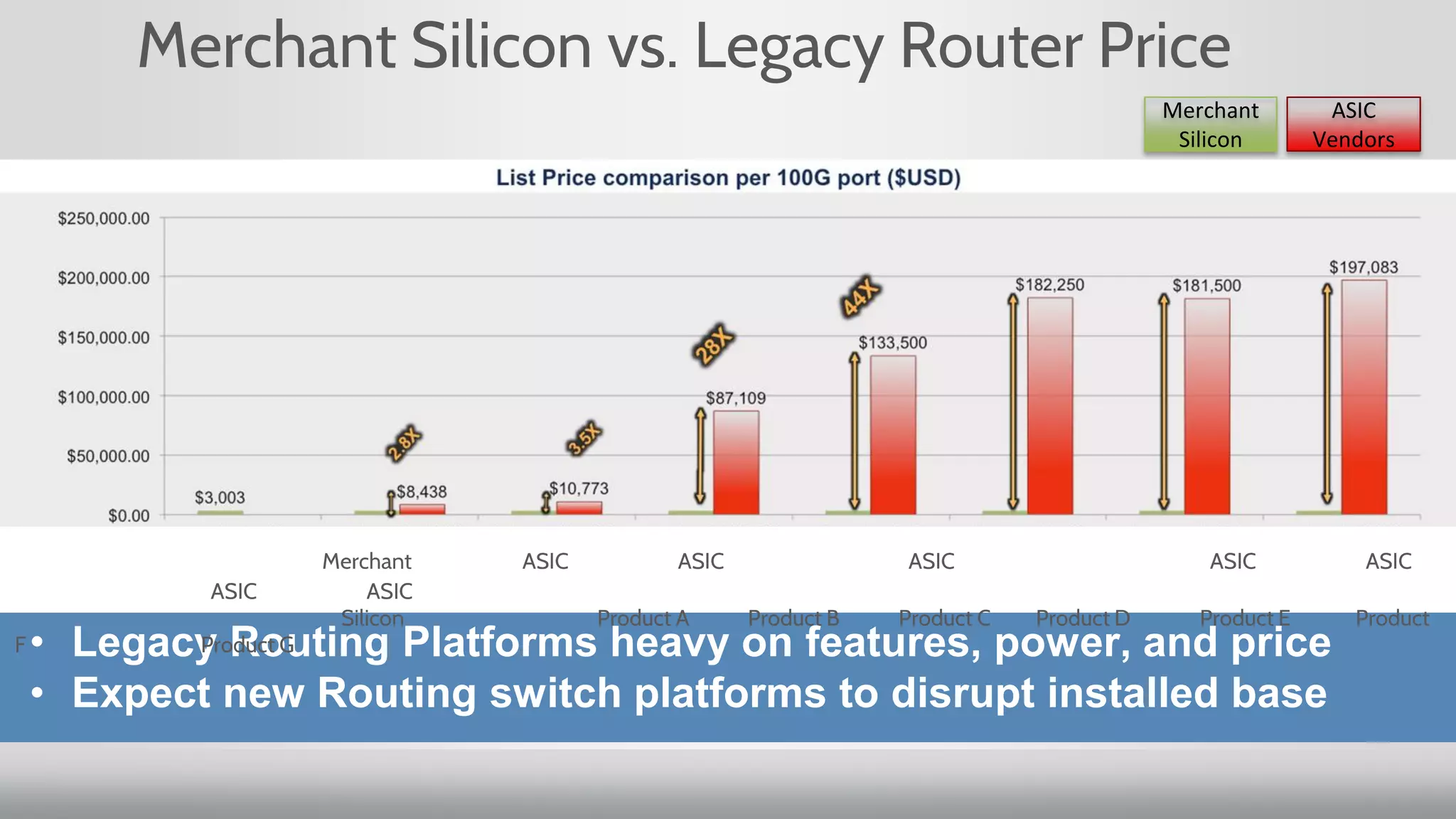
3. Merchant silicon using full custom chip designs has allowed networking to scale at Moore's Law growth rates, providing higher port density, lower price per port, and lower power consumption