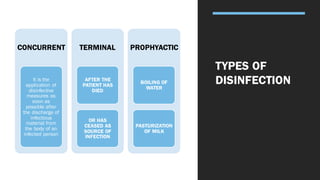
The document outlines various methods and agents used for disinfection, including physical, chemical, and natural approaches. It details the processes of disinfection, sterilization, and the importance of maintaining hygienic practices in medical settings. Key agents mentioned include autoclaves, chlorine, and formaldehyde, along with their applications and effectiveness in killing microorganisms.