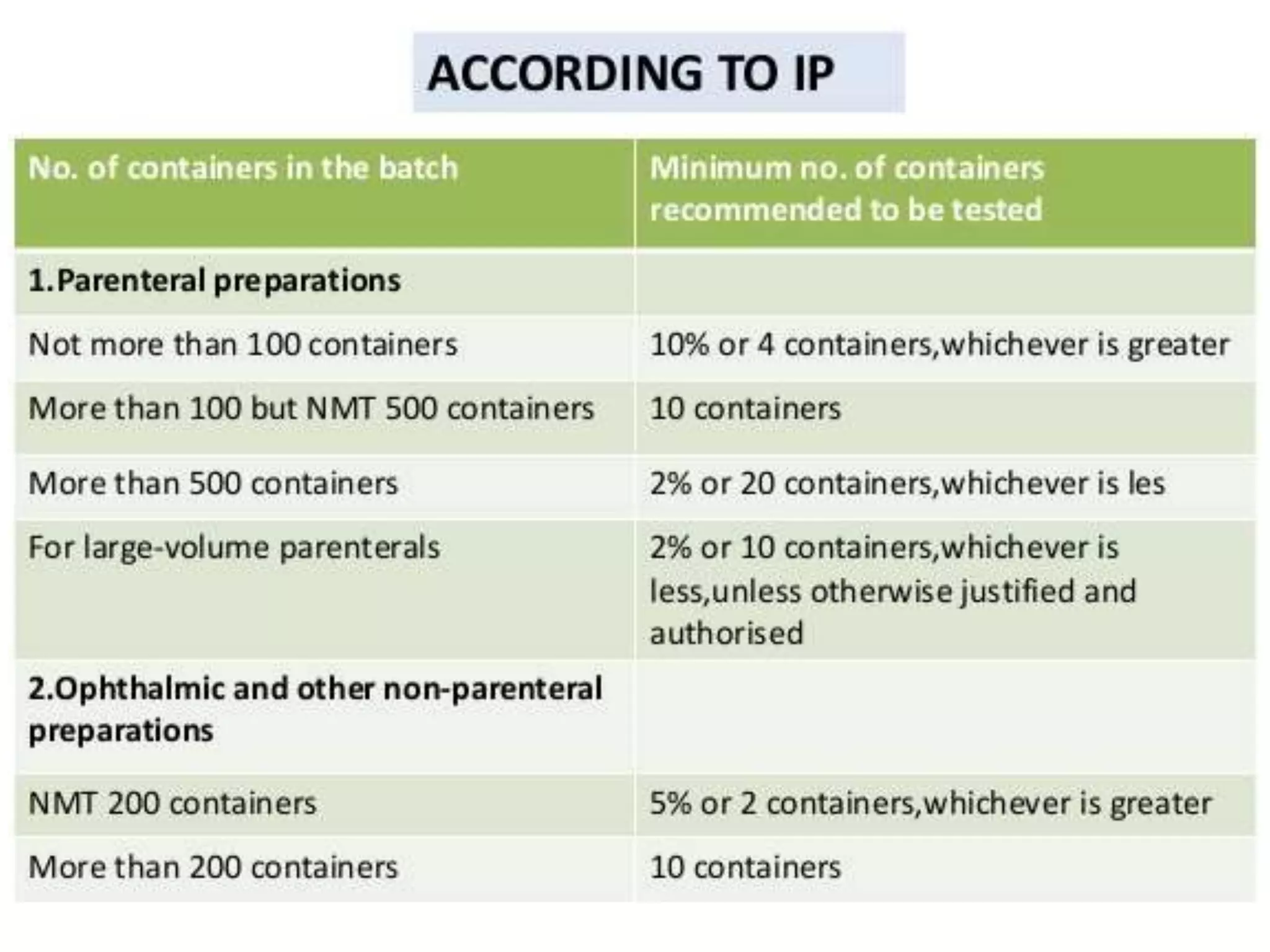
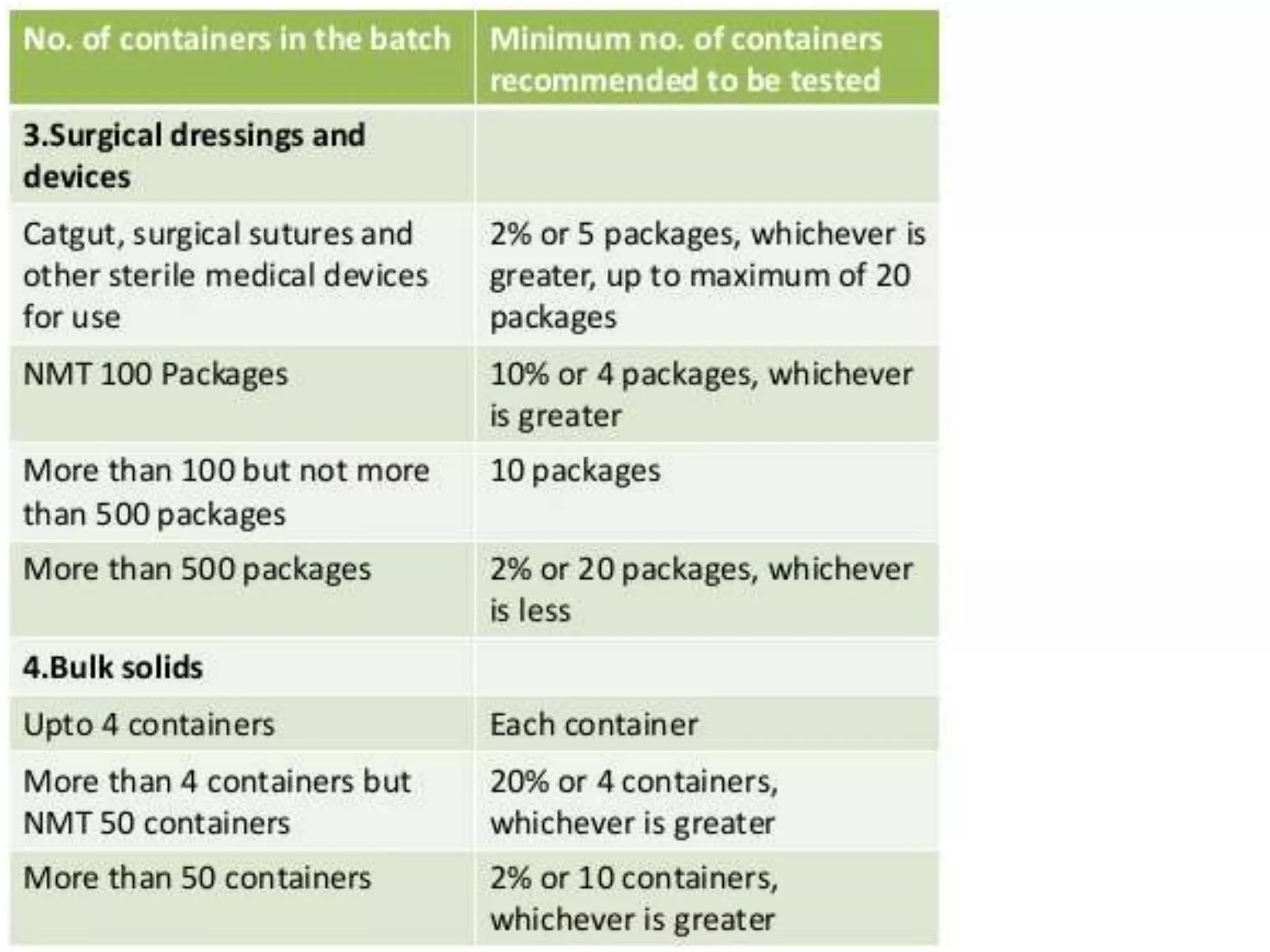
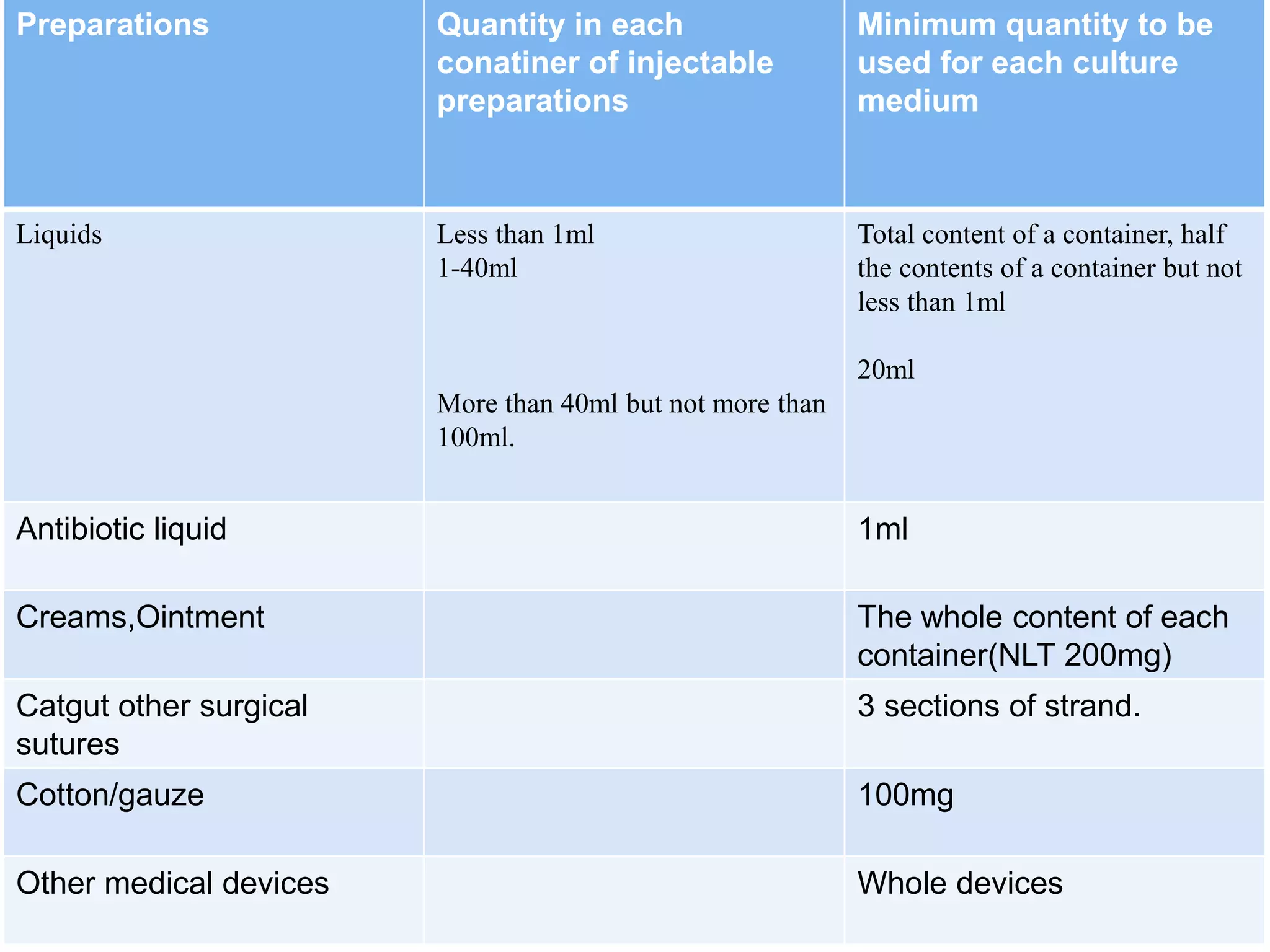
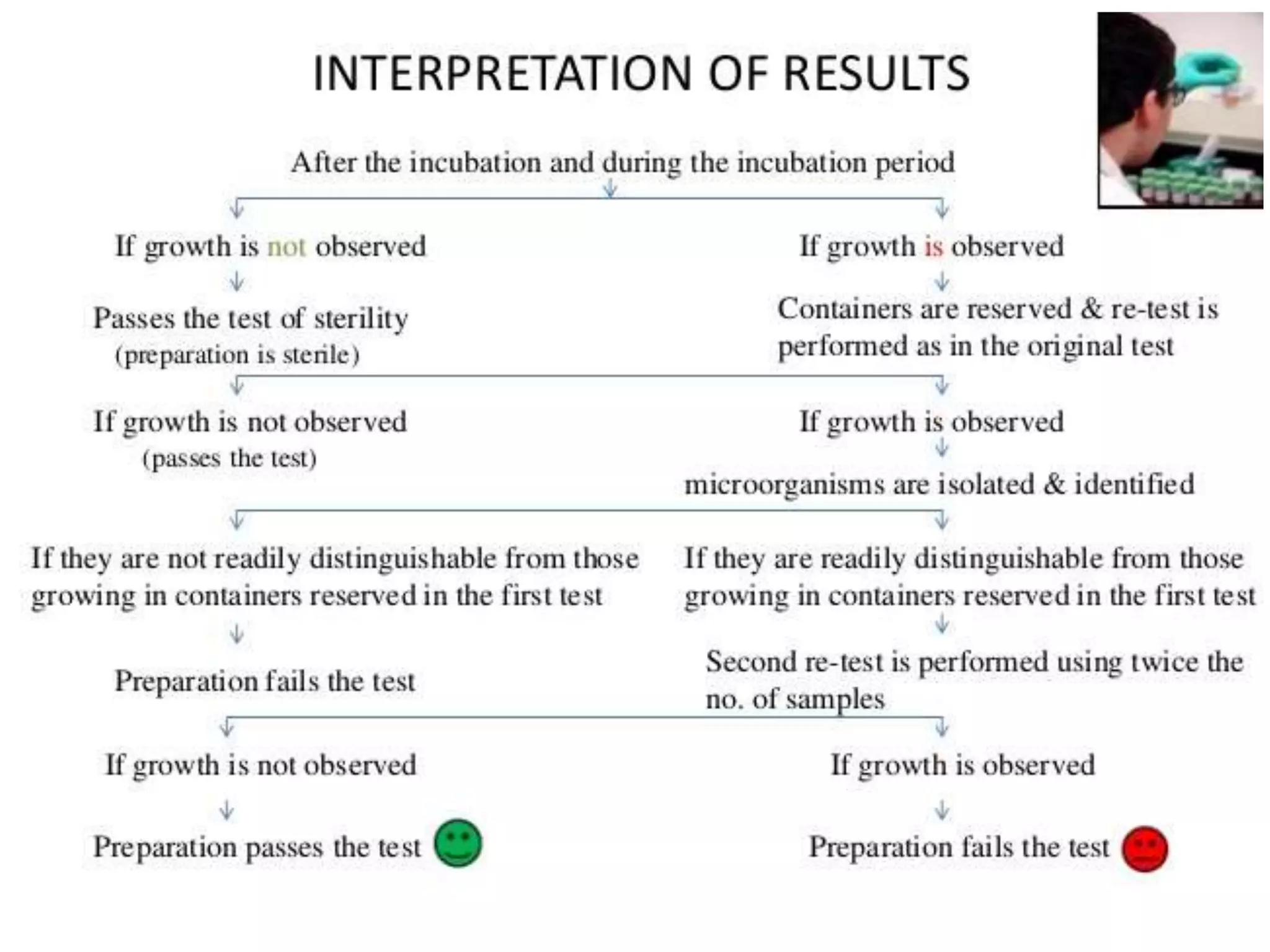
This document discusses sterility testing protocols for pharmaceutical products as per Indian Pharmacopeia guidelines. It defines sterility testing as testing to confirm absence of viable microorganisms. Sterility testing is important for medical devices and preparations like ophthalmic, injections, implants etc. The test is based on principle that microorganisms will grow in nutritive media at favorable temperature. There are two methods for sterility test - membrane filtration method suitable for liquids and direct inoculation method where samples are directly inoculated to culture media. The document discusses the different culture media and quantities of samples used based on product type.