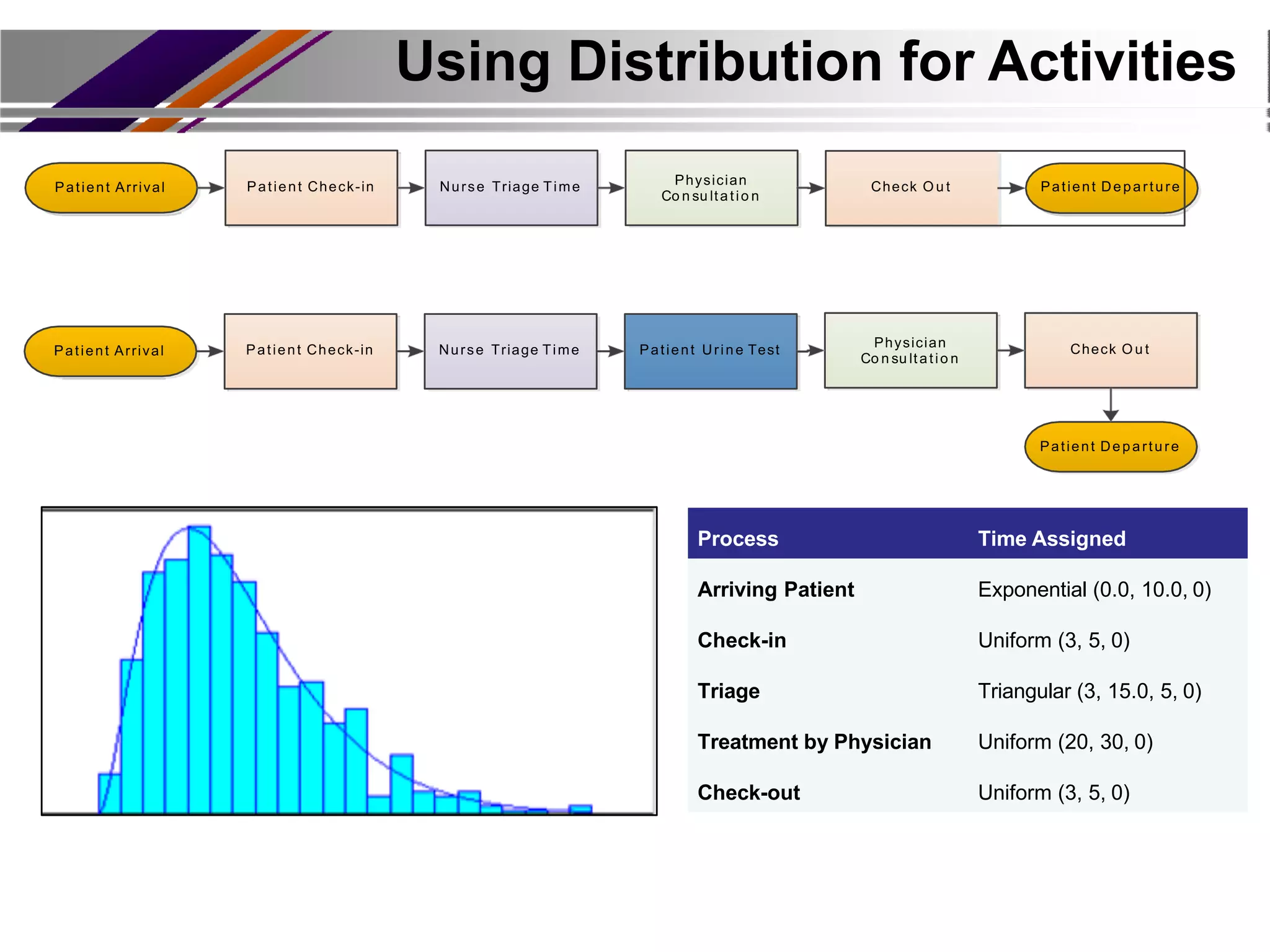
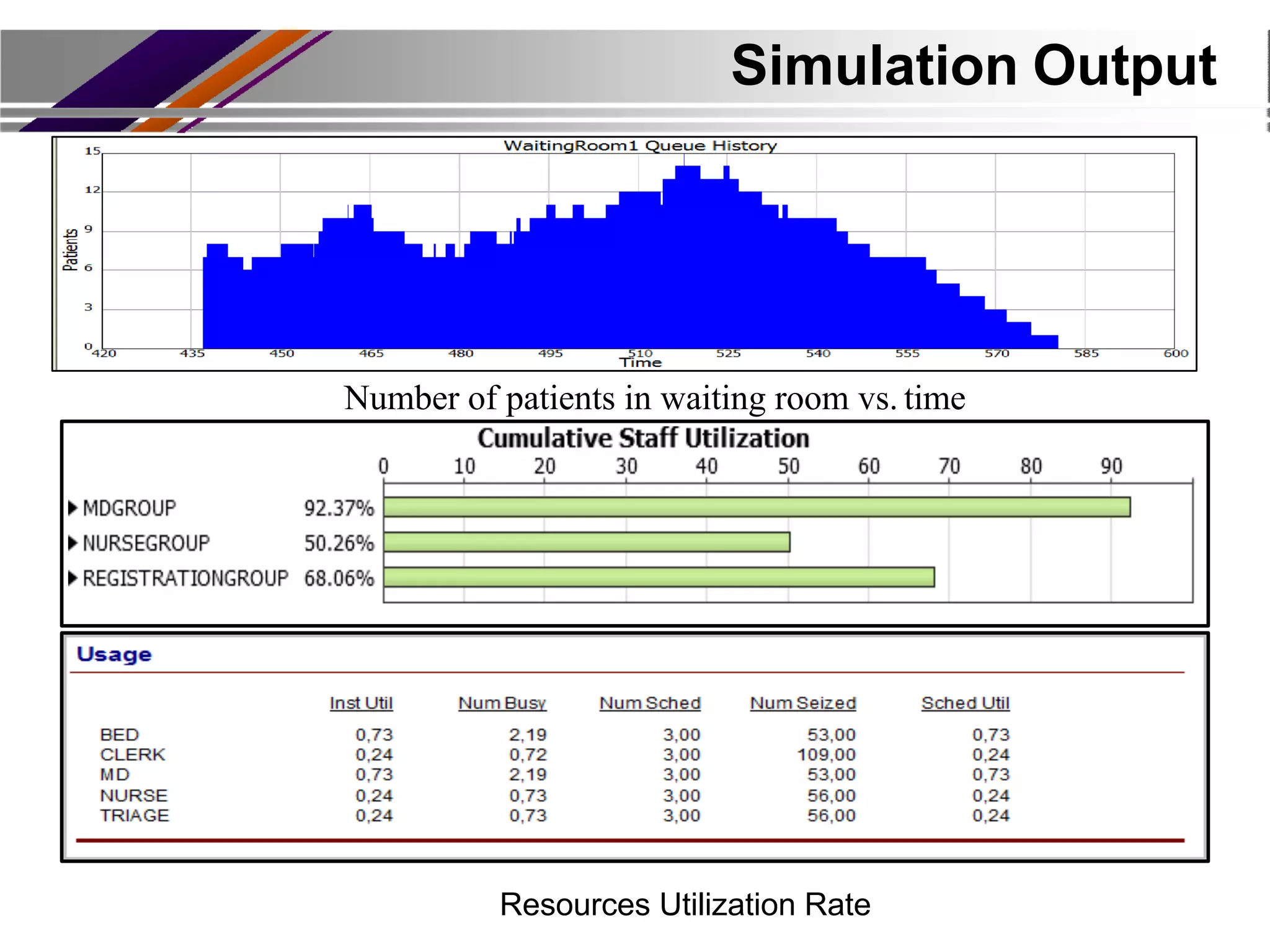
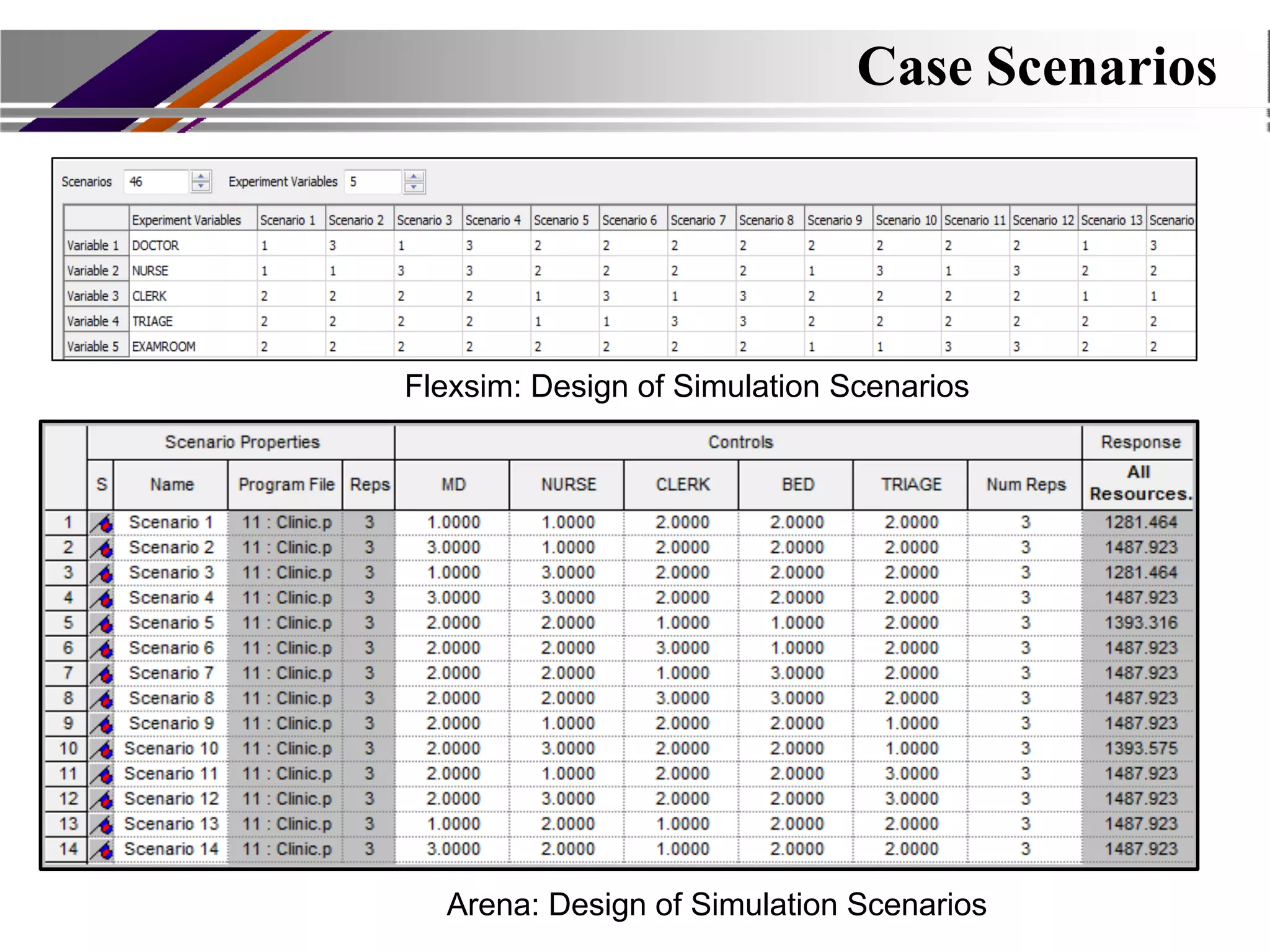
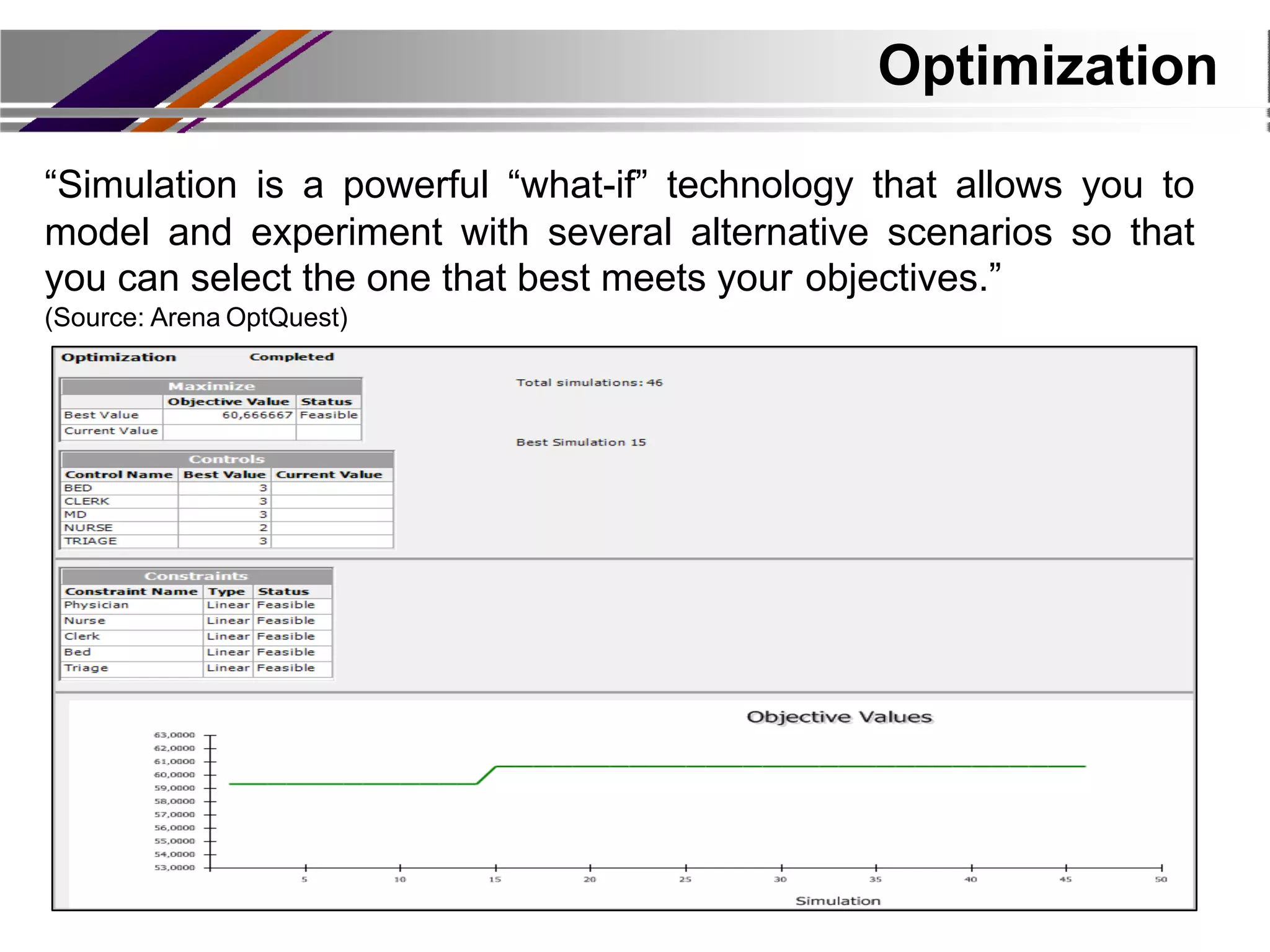
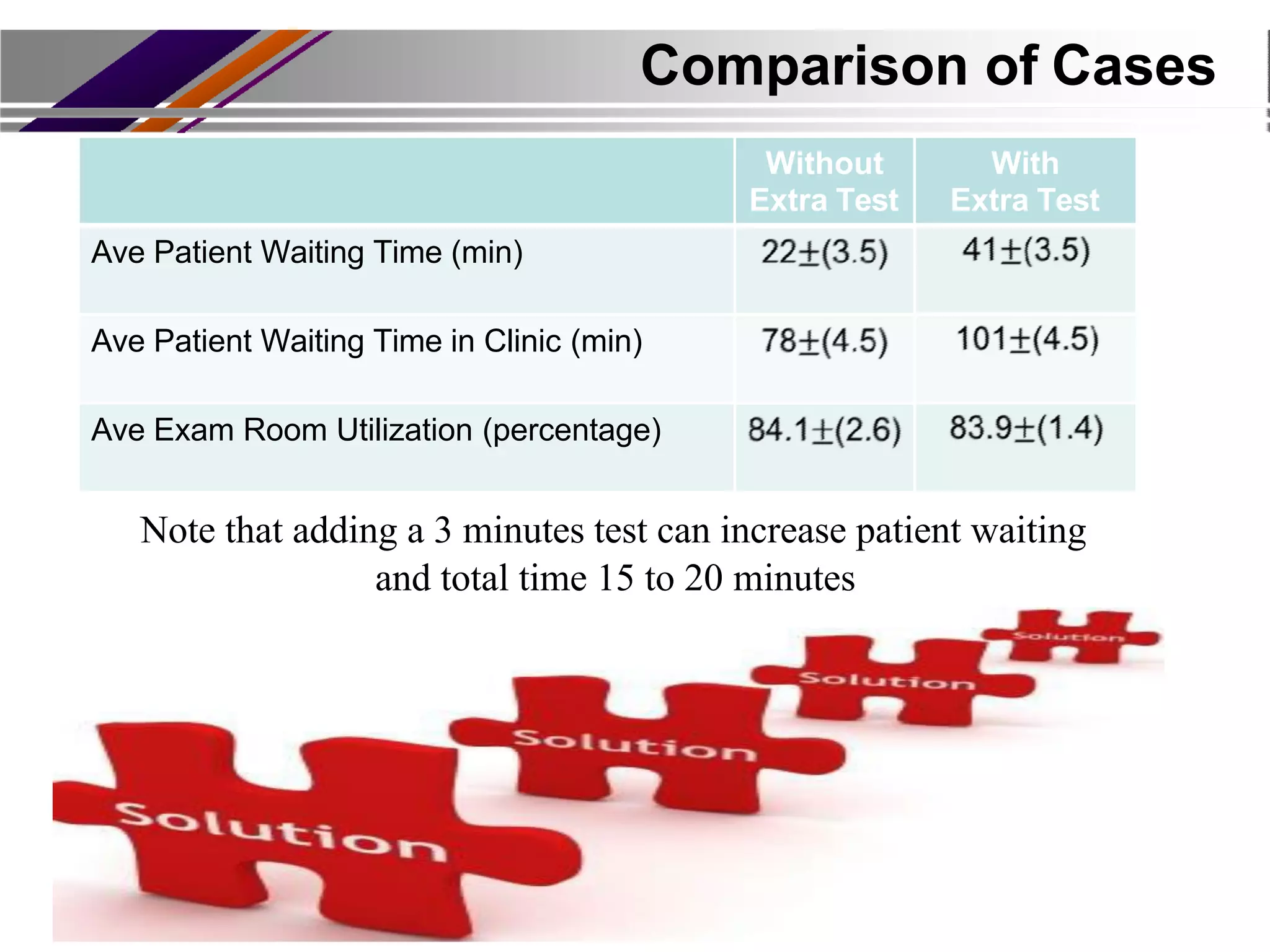
This document discusses discrete event simulation in healthcare. It provides an overview of simulation, including common application areas like manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare. Simulation allows testing of proposed solutions and scenarios in a model without real-world costs or risks. The key steps of simulation include creating workflow charts, collecting data, building a simulation environment, running scenarios, and analyzing results. Common simulation software packages are discussed. An example case study compares performance measures between scenarios with and without an additional medical test to assess impacts. The conclusion emphasizes how simulation can help improve patient flow, decrease wait times, and increase efficiency in healthcare.