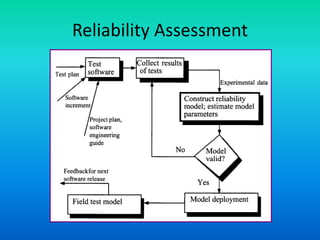
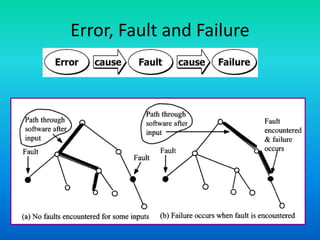
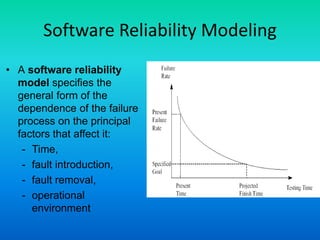
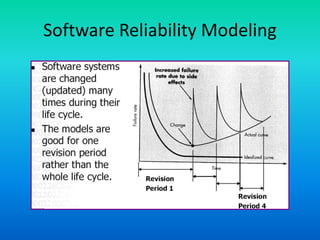
The document discusses software reliability, emphasizing its importance in ensuring fault-free performance and its link to software verification. It outlines key concepts such as errors, faults, failures, and their definitions, as well as the classical definition of reliability expressed as a probability measure. Additionally, it highlights that reliability is not time-dependent and is affected by design faults and internal environmental conditions.