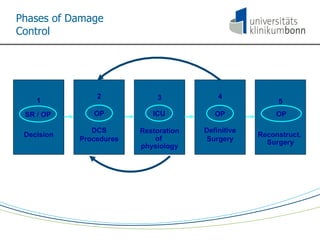
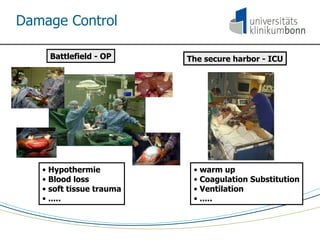
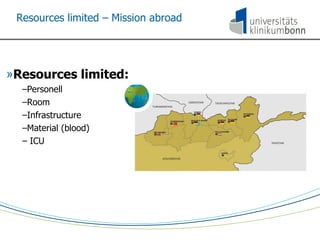
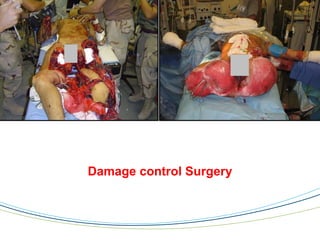
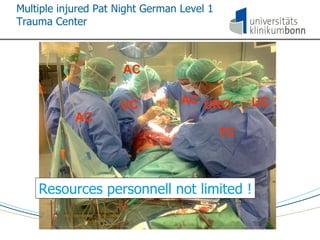
The document discusses the principles and procedures of damage control surgery (DCS) in trauma care, highlighting its origins in abdominal trauma and its application in military and civilian contexts. It emphasizes the importance of rapid action to control bleeding and manage complex injuries, particularly under resource-limited conditions during disaster missions. The text also references various studies and statistics related to the factors influencing survival rates following traumatic injuries.