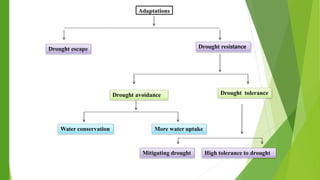
Drought is defined as a prolonged period with less than normal rainfall that can cause crop failure and water shortage. The document discusses various types of drought and their effects on plants. It then outlines several mitigation techniques to reduce drought impacts, including adopting drought-resistant crop varieties, soil and water conservation methods, and long-term strategies like integrated water basin planning and long-range rainfall forecasting. Key mitigation practices involve crop management, water harvesting, mulching, drip irrigation, and in-situ soil moisture conservation.