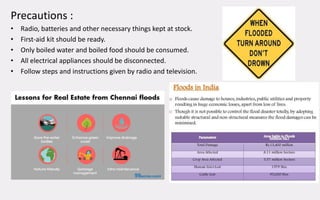
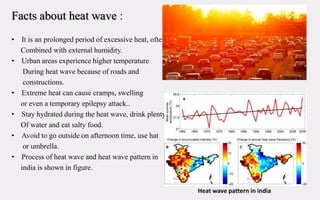
This document provides an overview of various types of hydro-meteorological disasters including floods, cyclones, avalanches, lightning, heat waves, cold waves, droughts, and thunderstorms. It describes the causes and effects of each type of disaster, highlighting that hydro-meteorological disasters result from the interaction of atmospheric and hydrological systems and can threaten lives and property. Precautions are outlined for many of the disasters to help people protect themselves during events.