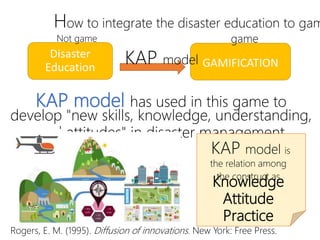
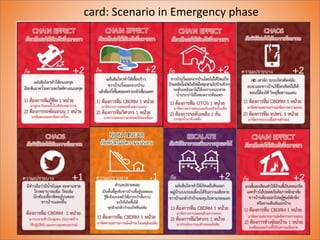
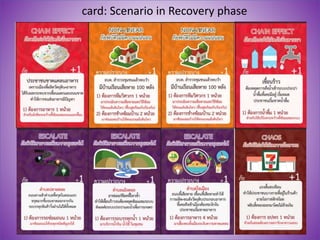
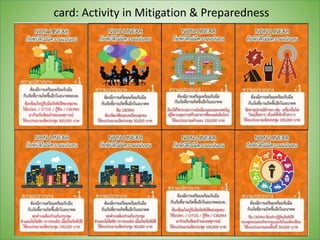
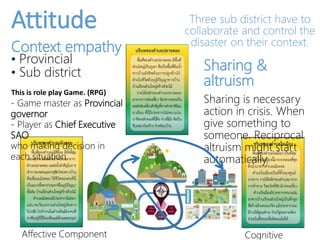
This document discusses using gamification to improve disaster education. It presents two games called FloodQuest and AlarmSlide that aim to increase players' knowledge, attitudes, and practices around risk management, safety, and monitoring hazards. The document also notes some limitations of current disaster education in Thailand, such as a lack of local context and hands-on tools. Gamification is proposed as a way to boost engagement by integrating game mechanics into existing disaster-related content. An example role-playing game is described where players collaborate as local leaders to control disasters and allocate resources. The document concludes that games are effective learning tools but require careful design and facilitation to change attitudes and link lessons to player behavior.