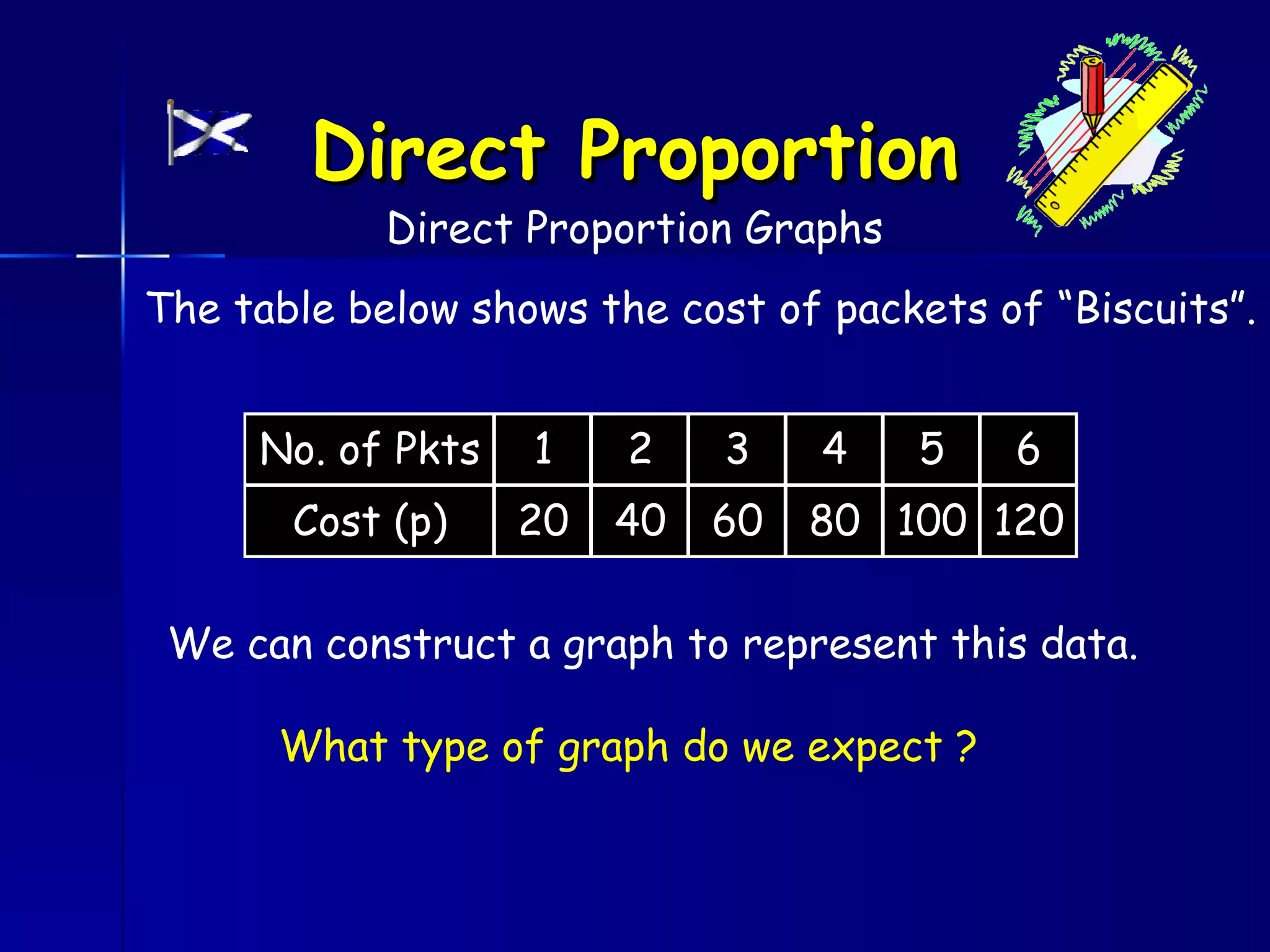
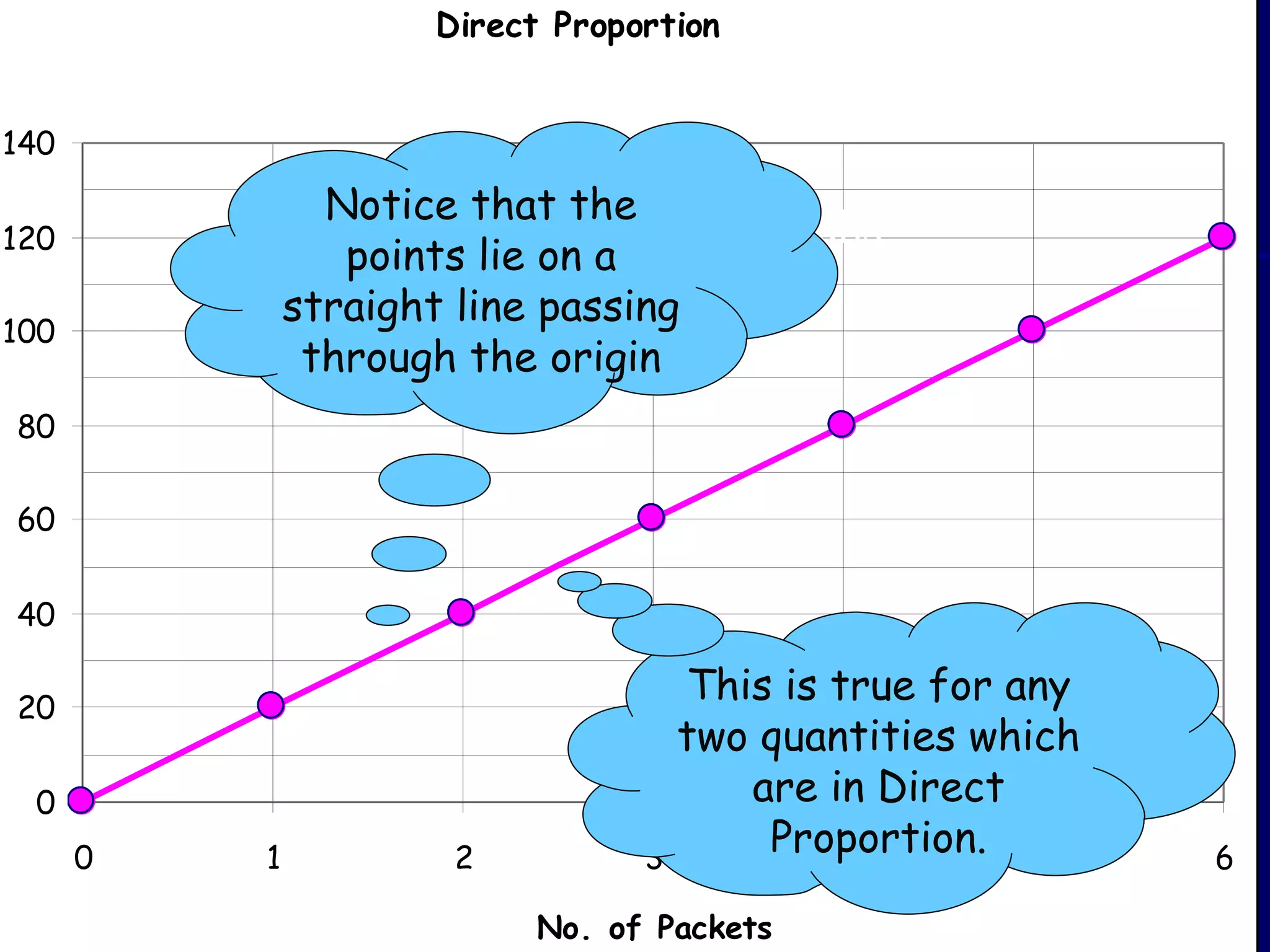
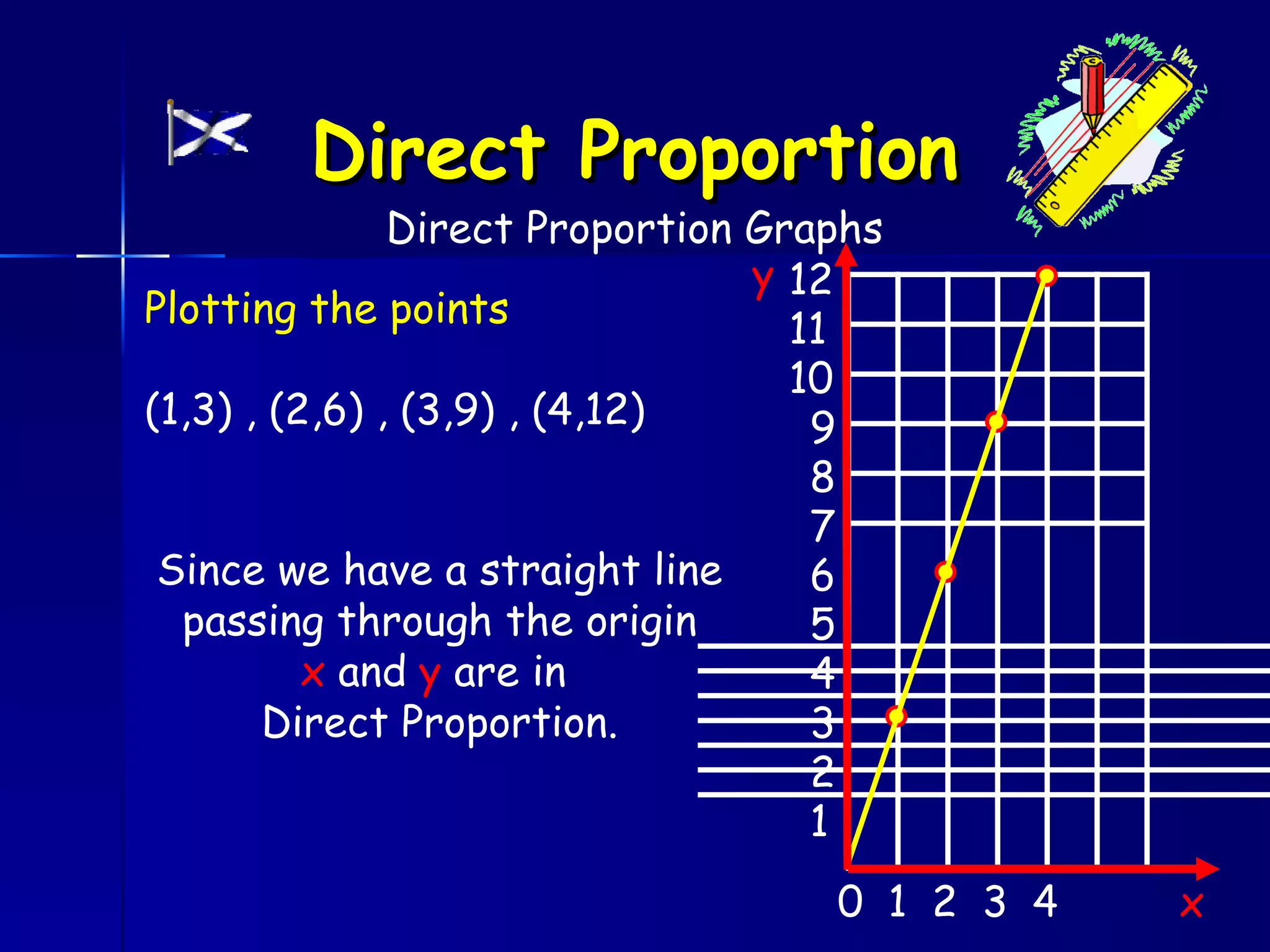
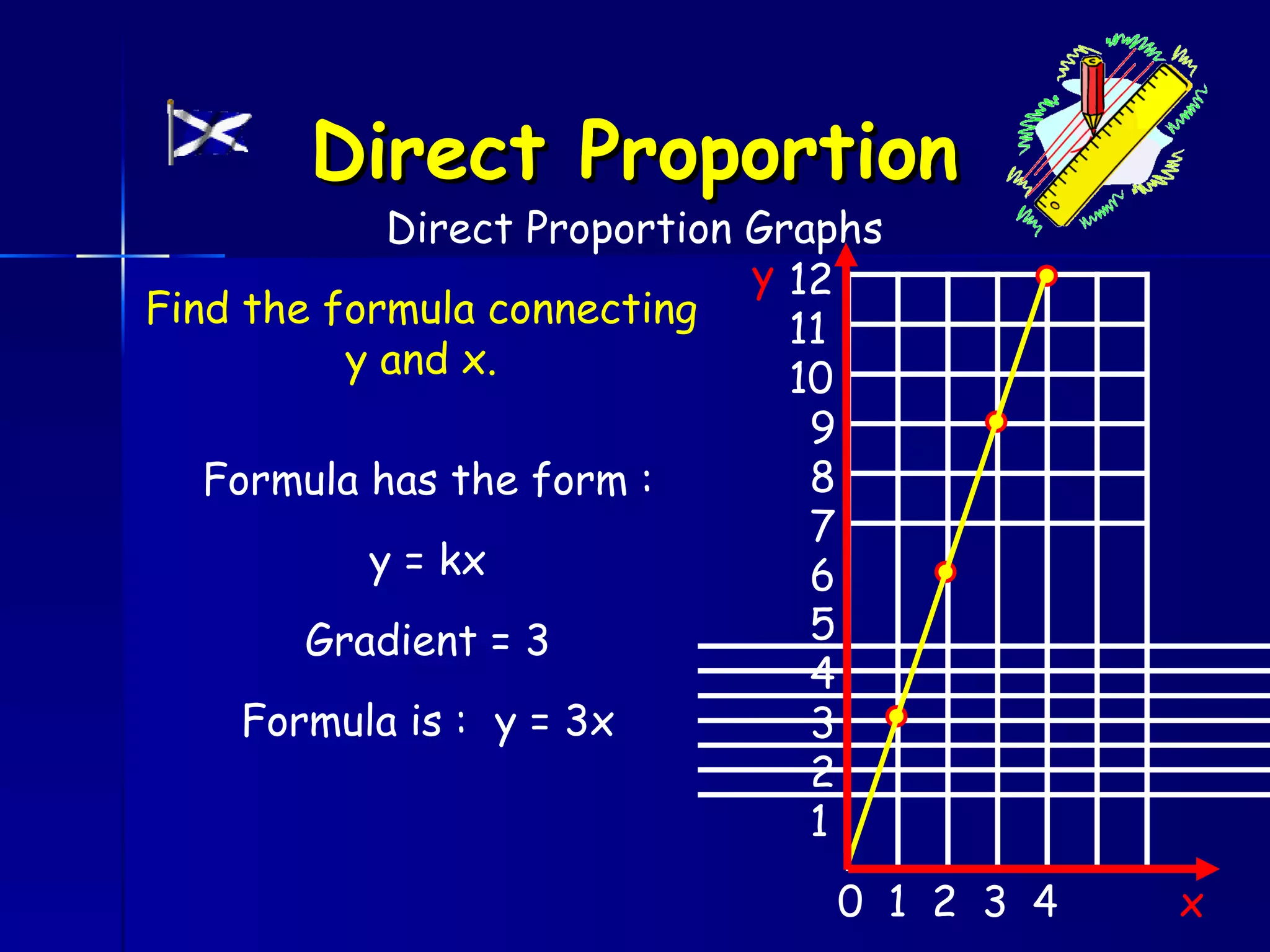
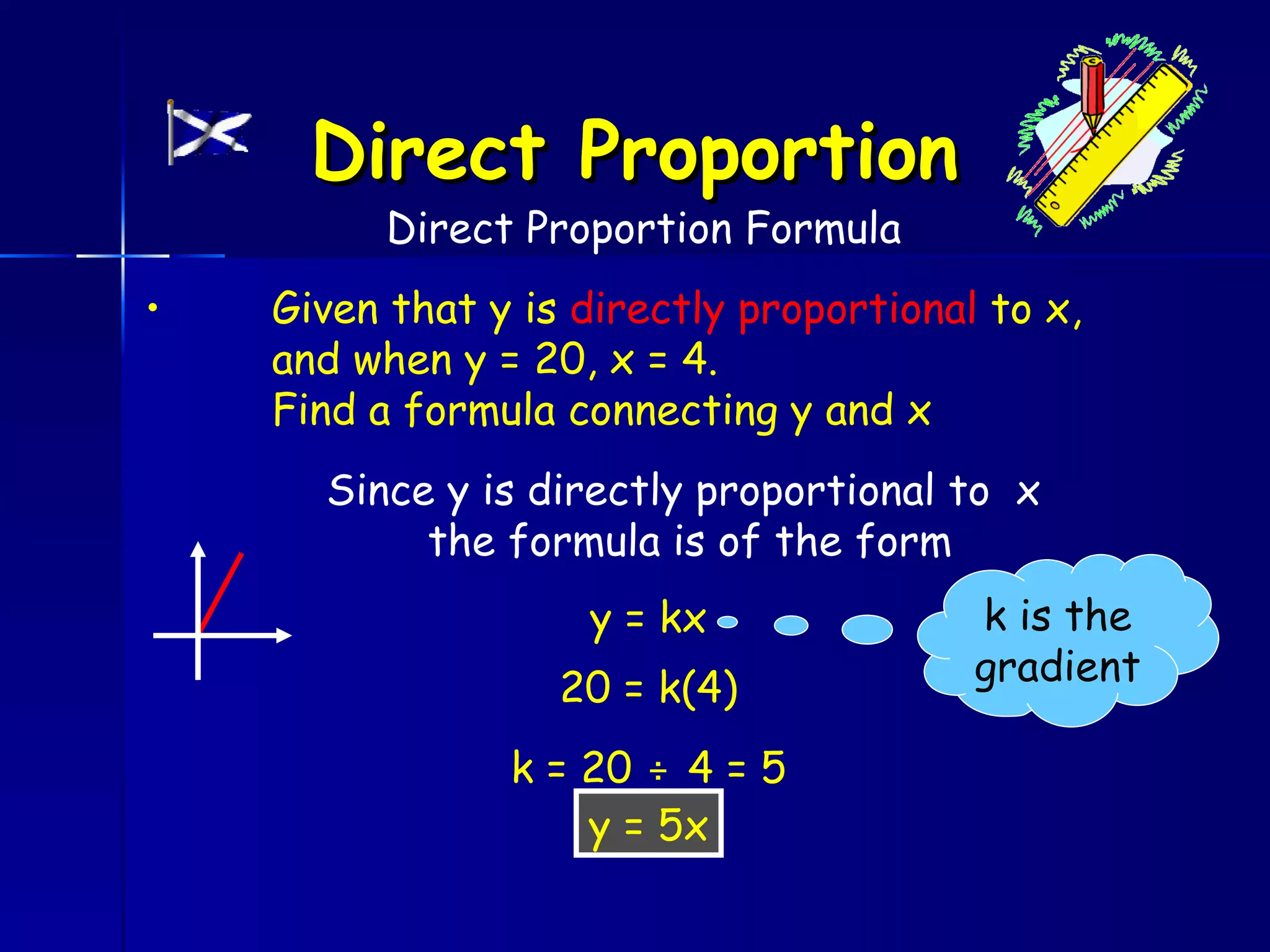
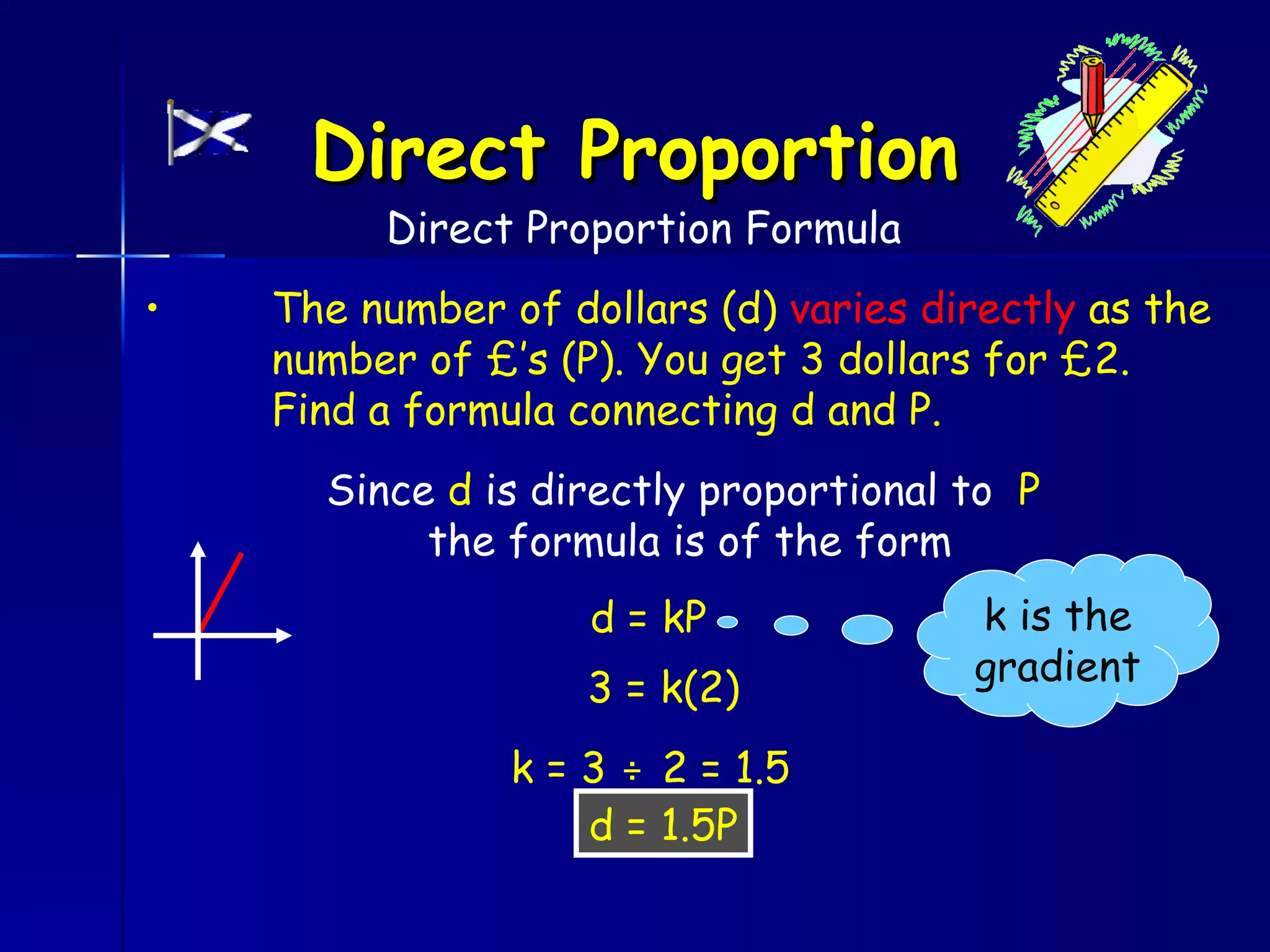
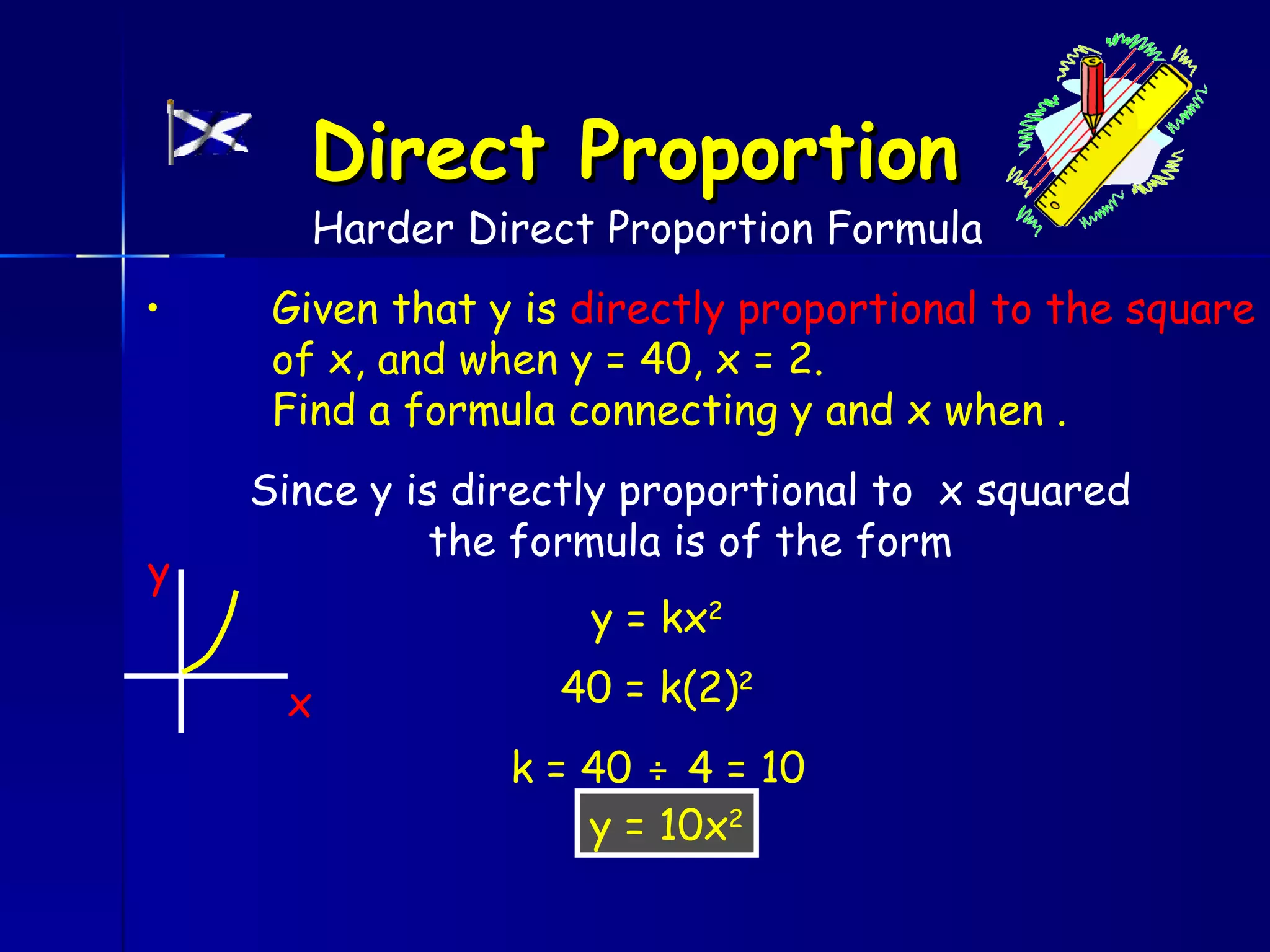
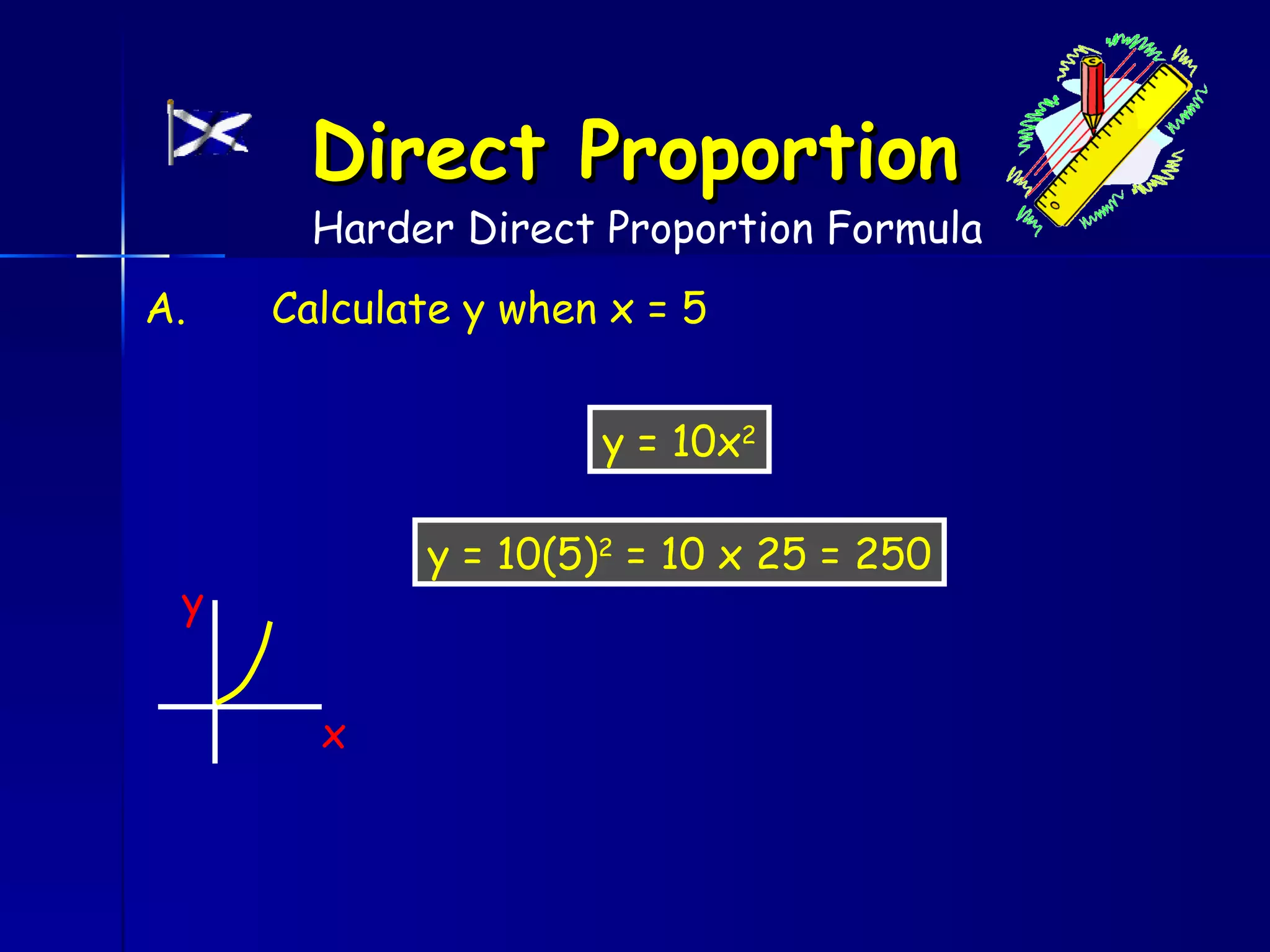
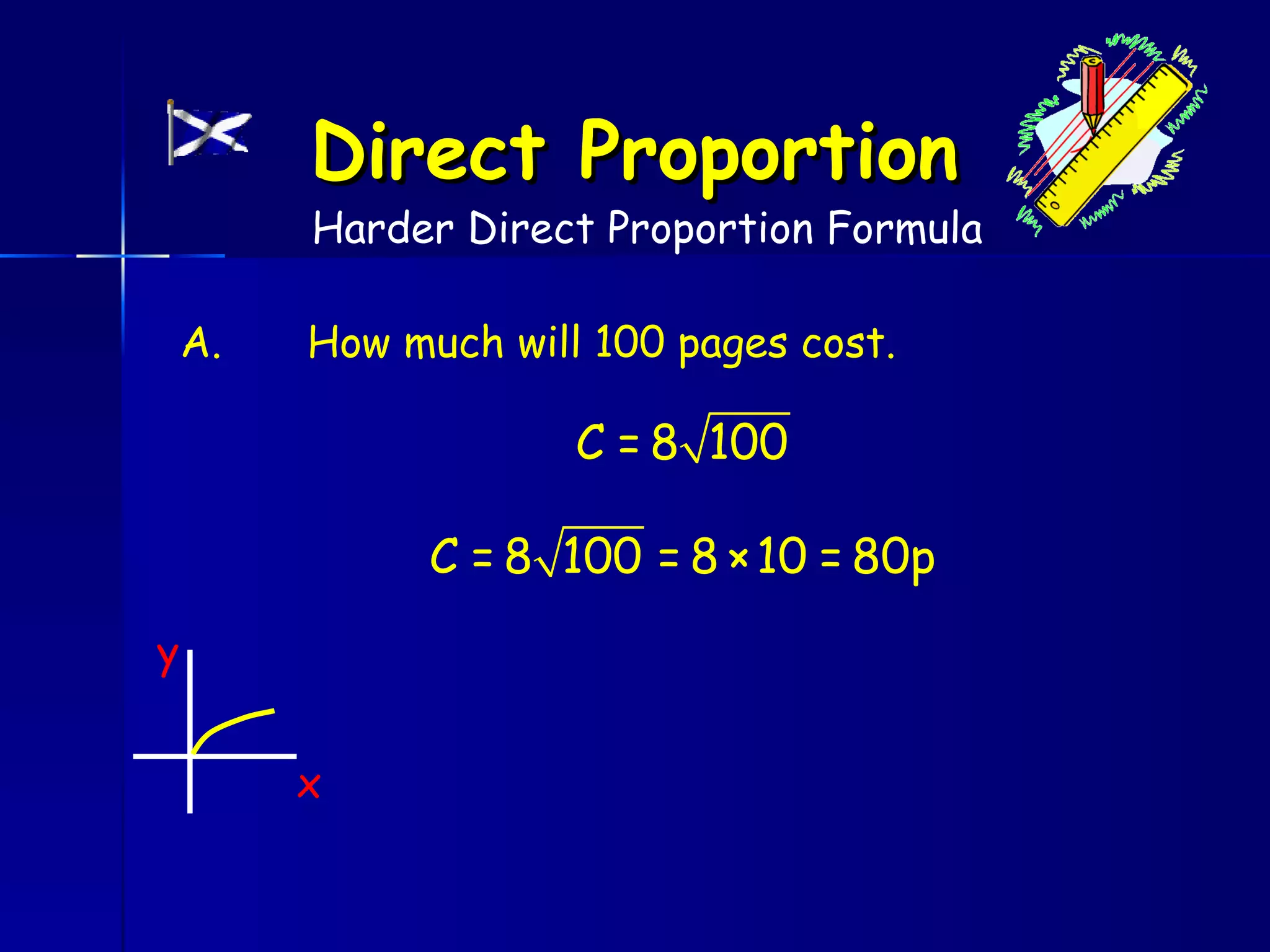
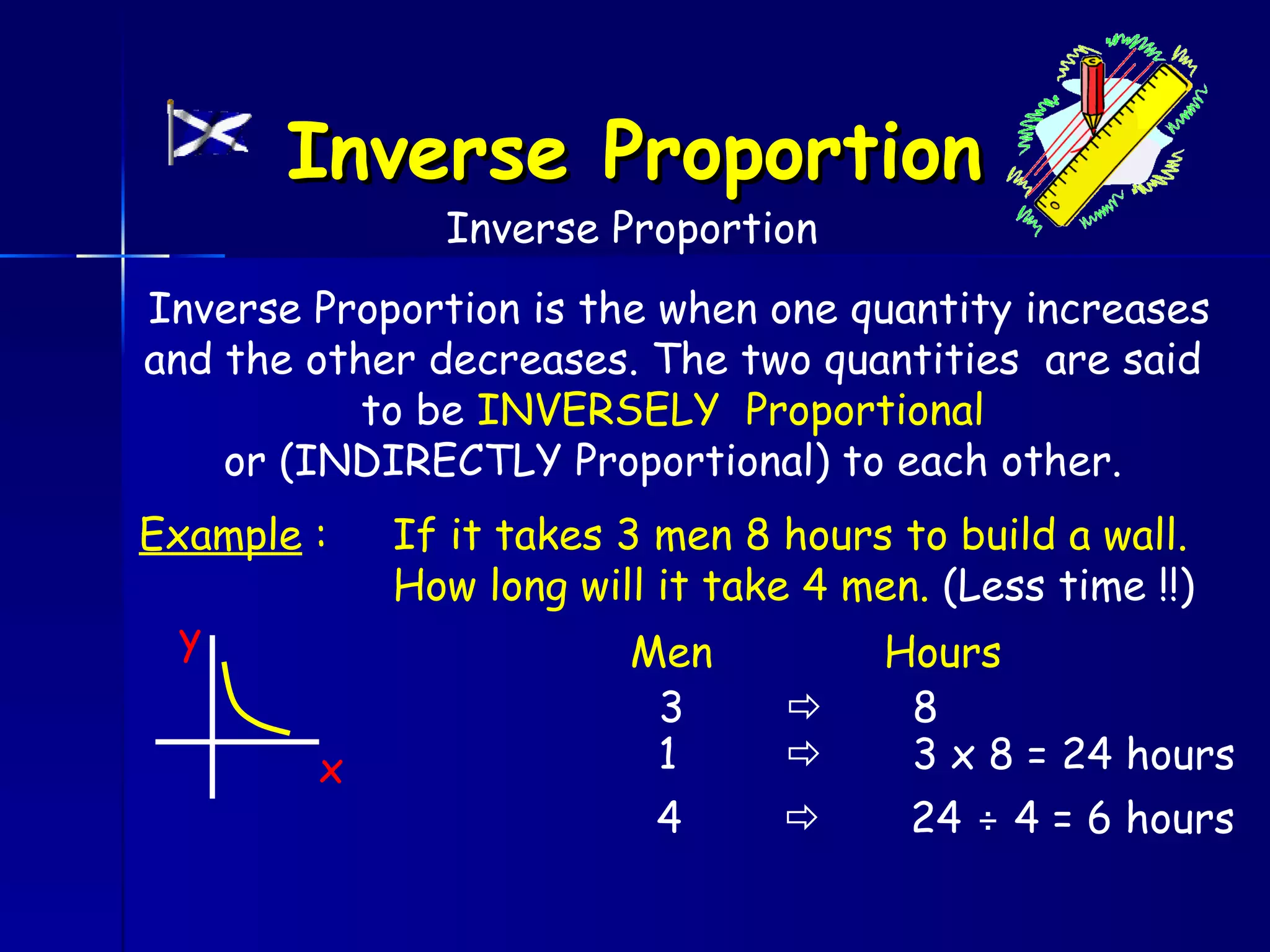
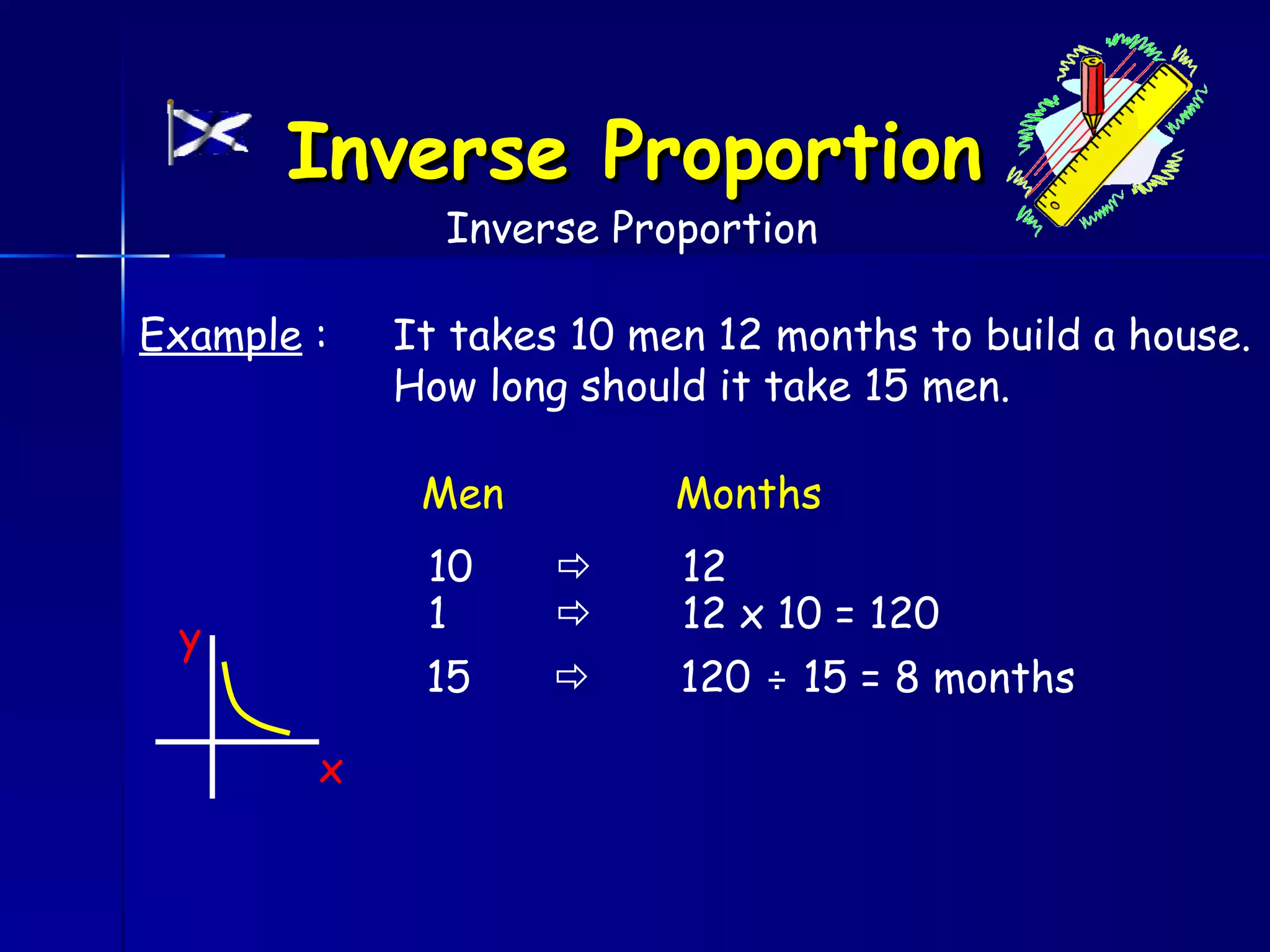
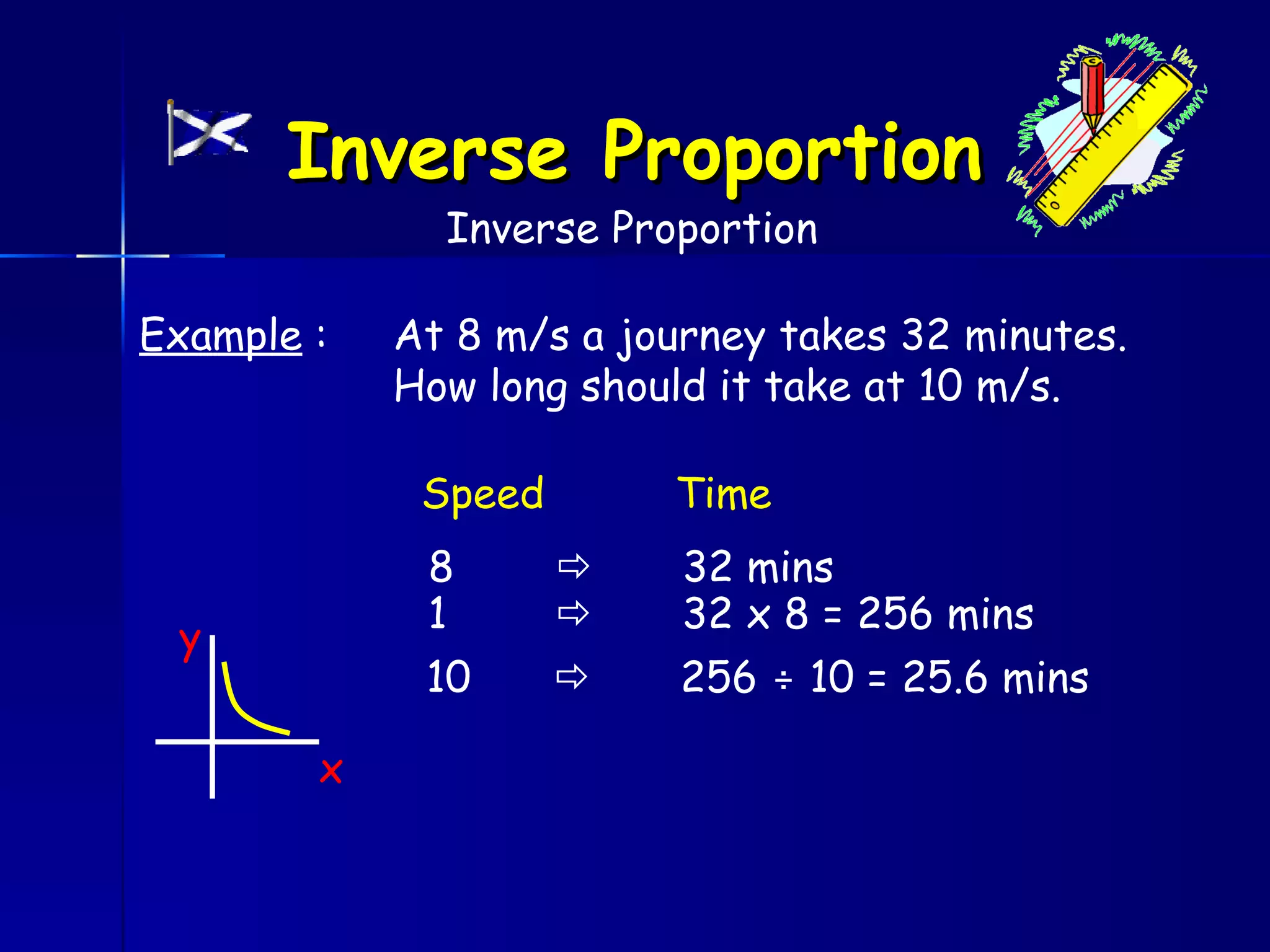
The document discusses direct and inverse proportions. It provides examples of quantities that are directly proportional, such as cost and number of items. Directly proportional quantities follow the relationship that if one quantity doubles, the other will double as well. They form a straight line passing through the origin on a graph. Inverse proportions occur when one quantity increases as the other decreases, such as time taken to complete a task with more workers. Formulas are provided to represent direct and inverse proportional relationships between variables.