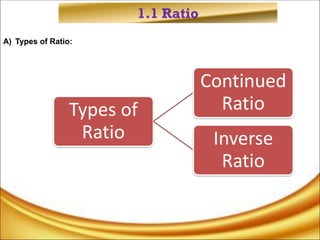
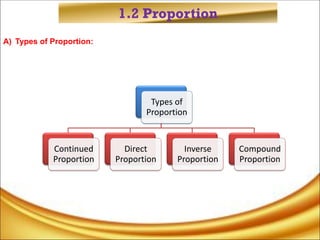
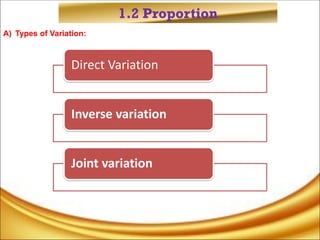
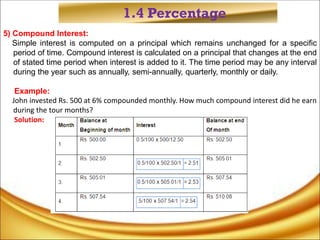
The document discusses the concepts of ratios, proportions, and percentages, explaining their definitions, types, and applications in mathematical problems. It provides examples to illustrate the usage of ratios in real-world scenarios, such as dividing resources and calculating values based on given ratios. Additionally, it covers the methods for calculating percentages, including sales tax and discounts.