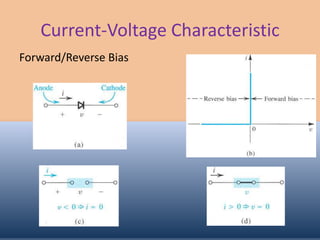
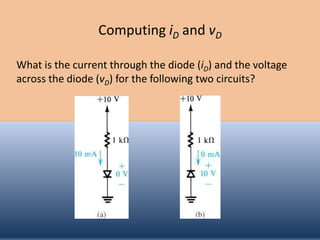
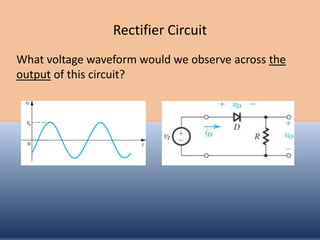
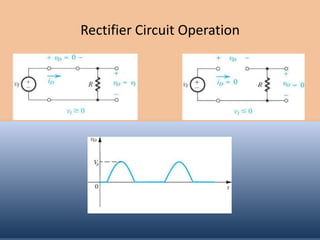
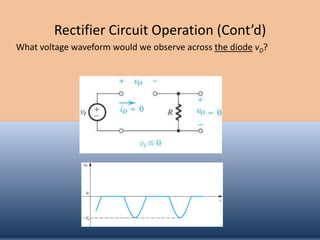
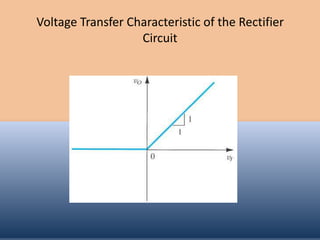
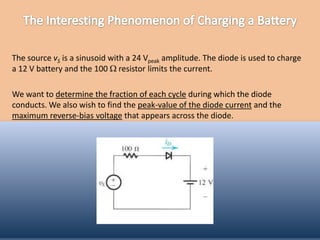
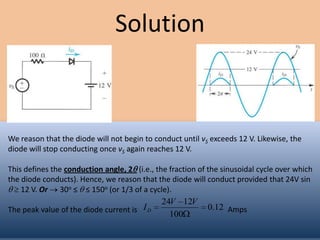
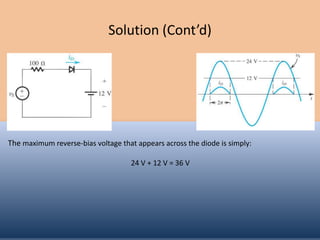
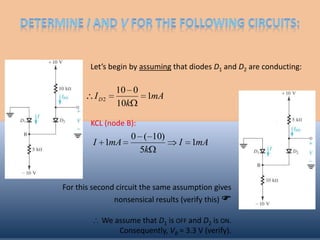
The document discusses the characteristics and operation of an ideal diode, including analyzing simple circuits involving diodes. It examines the current-voltage relationship of diodes and how rectifier circuits use diodes to produce a voltage waveform from a sinusoidal input. Examples are provided to determine the conduction angle, peak diode current, and maximum reverse bias voltage for a rectifier circuit charging a battery from a sinusoidal source.