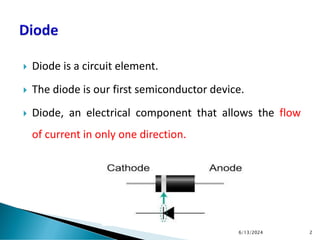
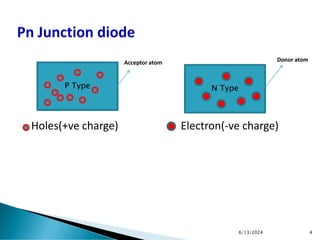
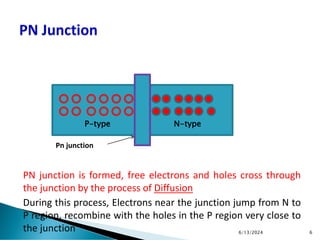
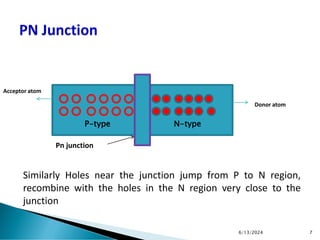
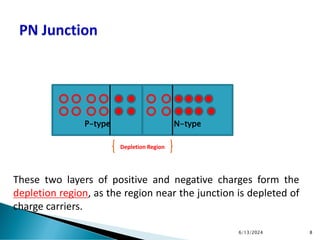
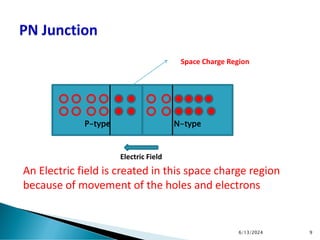
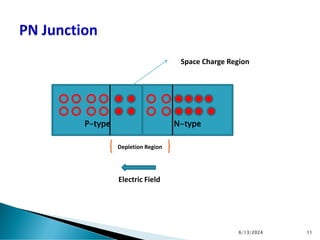
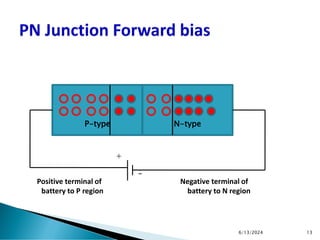
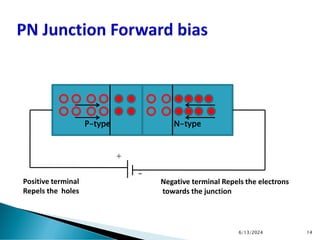
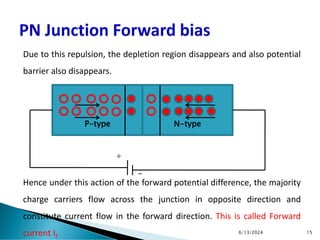
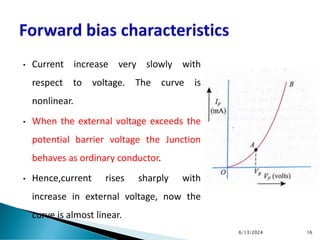
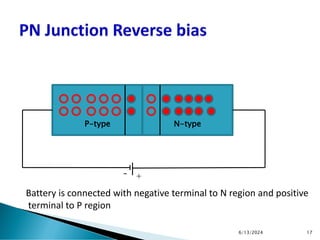
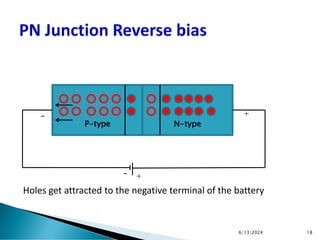
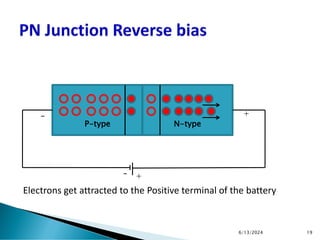
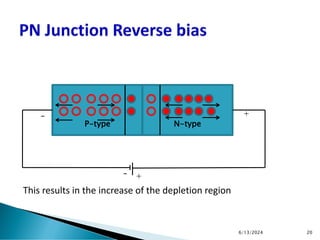
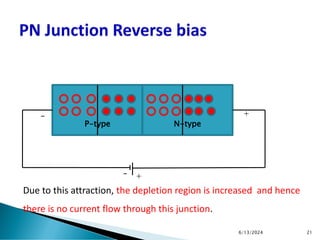
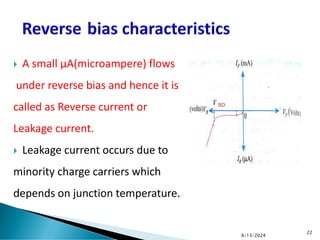
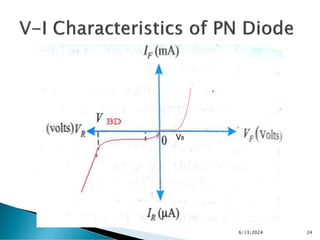
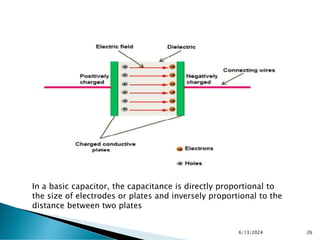
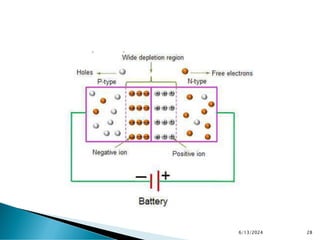
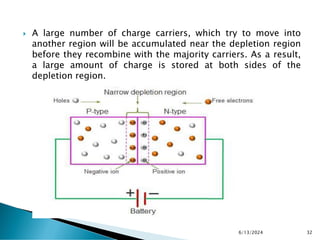
The document explains the fundamental principles of diodes, particularly the pn junction diode, which allows current to flow in one direction due to the formation of a depletion region and electric field. Additionally, it discusses the concepts of transition and diffusion capacitance in diode operation, highlighting how capacitance is affected by bias and the structure of the diode. The document emphasizes the non-linear current-voltage relationship and the impact of external voltage on current flow and capacitance.