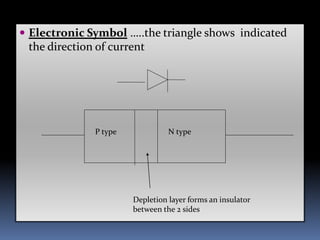
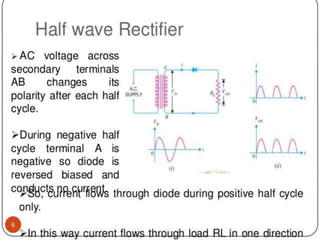
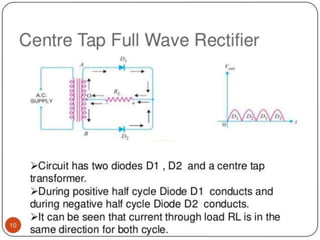
The document summarizes the basics of a p-n junction diode. When a p-type and n-type semiconductor are joined, a depletion layer forms at the junction due to the diffusion of charge carriers. This layer acts as an insulator containing no free charges. When forward biased, the depletion layer narrows allowing current to flow. When reverse biased, the layer widens blocking current. Diodes can be used as rectifiers, switches, detectors and in LEDs.