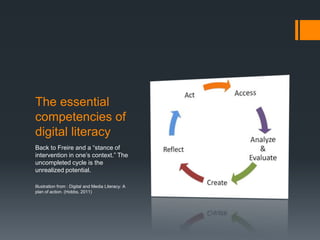
The document discusses the evolving nature of digital and media literacy, emphasizing the importance of new competencies necessary for effective participation in a democratic society. It highlights critical thinking, creativity, and ethical engagement as essential skills, while also addressing the challenges of transferring digital skills across different contexts. The text advocates for a balanced approach that respects both global interconnectedness and local contexts in literacy education.