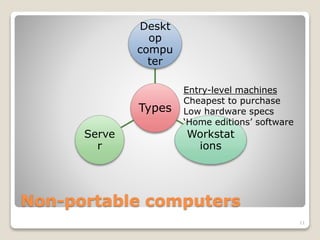
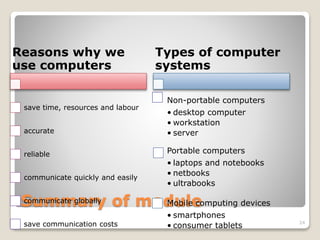
Computers have become an integral part of our everyday lives for several reasons: they improve efficiency by saving time, resources, and labor; they provide accurate and reliable results; and they enable communication across distances and sharing of information globally. There are different types of computer systems - non-portable computers like desktops, workstations, and servers which are generally larger and not meant to be moved, as well as portable computers like laptops, notebooks, netbooks, and ultrabooks, and mobile computing devices like smartphones and tablets. Users can be categorized as casual users, SOHO (Small Office Home Office) users, power users, or mobile users, and there has been a trend of convergence where separate technologies are combined into single