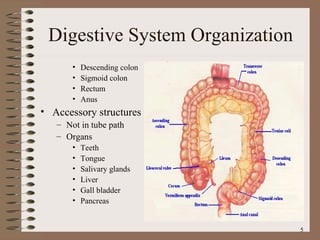
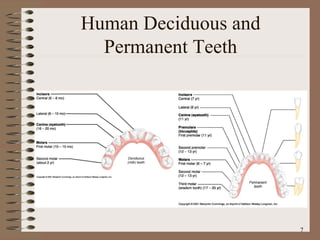
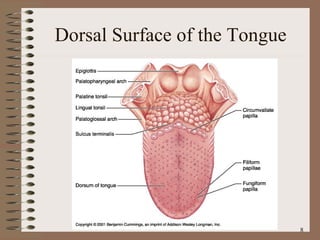
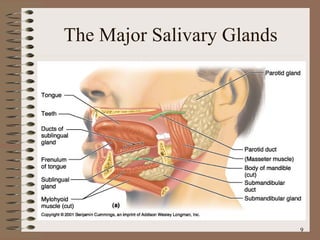
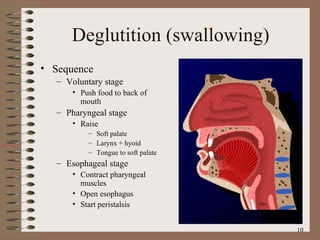
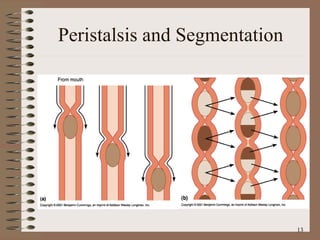
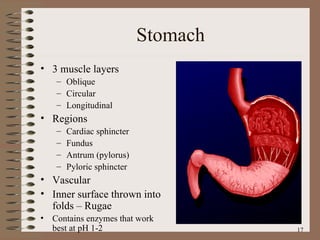
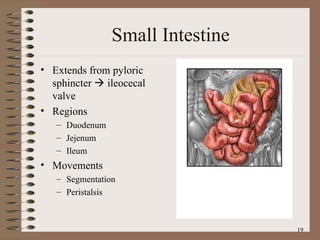
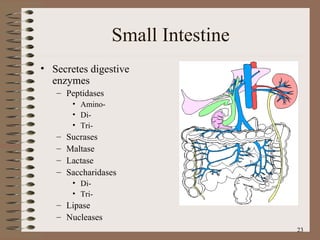
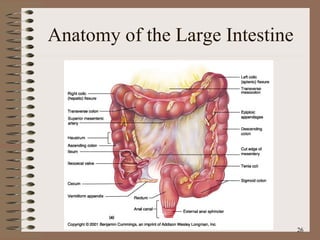
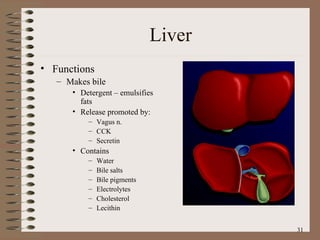
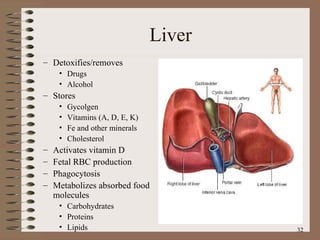
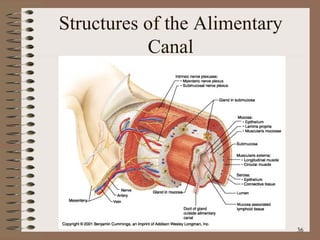
The document summarizes the key structures and functions of the digestive system. It describes the digestive system as a tube within a tube made up of the gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs. It outlines the main phases and locations of digestion, from ingestion through the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines. It also briefly describes the liver and its role in bile production and detoxification.