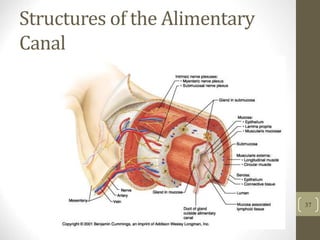
The document provides an overview of the human digestive system, including:
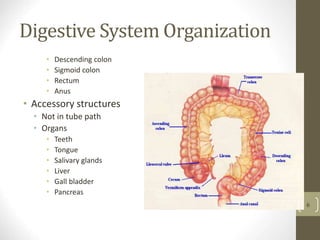
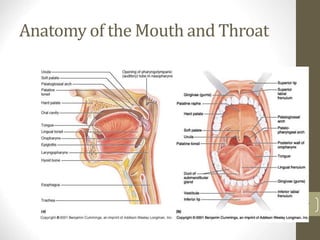
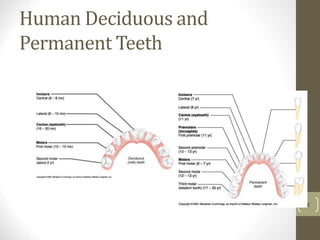
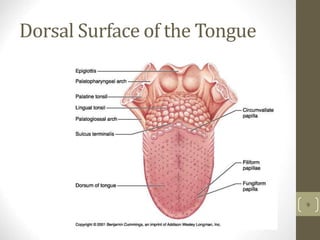
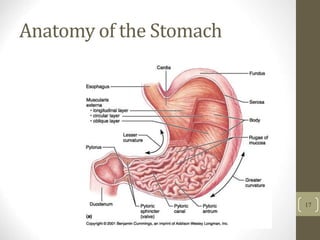
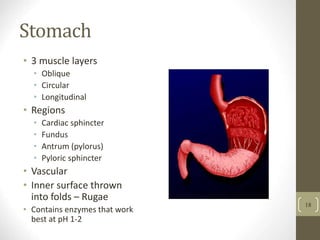
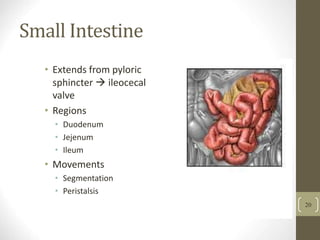
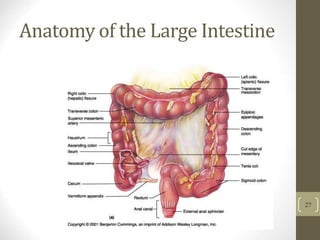
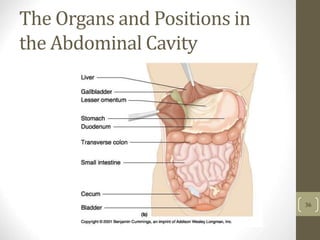
1) It describes the main organs and structures that make up the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth through the esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines.
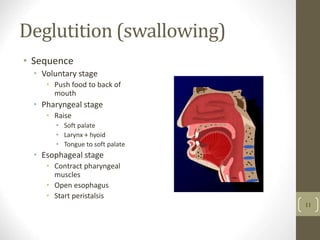
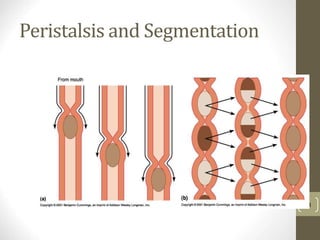
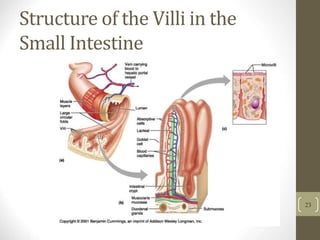
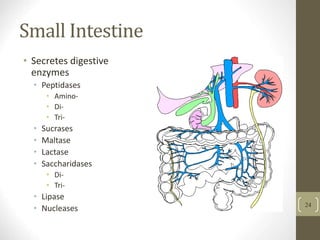
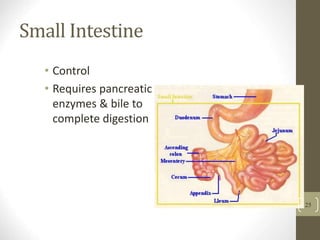
2) It explains the key functions of digestion like mechanical and chemical breakdown of food, as well as absorption of nutrients and water in the small intestine.
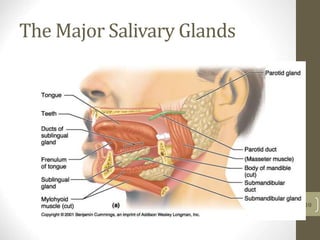
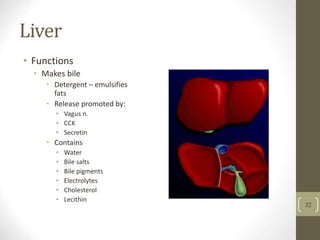
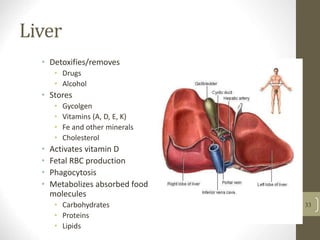
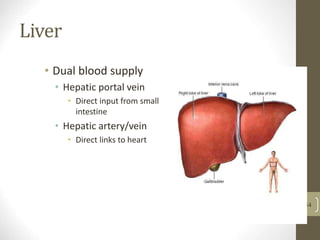
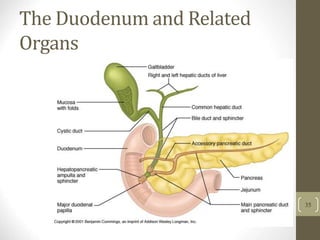
3) It discusses accessory organs that contribute to digestion like the liver, gallbladder and pancreas, and their roles in producing bile and digestive enzymes.