Digestive System 8.pptkjvjhvjhvhvhkvkvkvk
- 2. Food and Energy • Energy available in food is measured by burning food • calorie = amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius • Dietary calories are referred to as C C = 1000 calories or 1 kilocalorie
- 3. Calories • Average teen needs 2200 Calories/day for females 2800 Calories/day for males
- 4. Nutrients 1. Water 2. Carbohydrates 3. Fats 4. Proteins 5. Vitamins 6. Minerals
- 5. Water • Water is most important nutrient • Every cell in the human body needs water – Many body processes and chemical reactions take place in water • Makes up bulk of blood, lymph and other bodily fluids • Drink at least 1-2 liters of water each day (6-8 cups) – Not enough = dehydration causes problems in circulatory, respiratory, and nervous systems
- 6. Caloric Nutrients • Carbohydrates: Nutrients that are the main source of energy for the body • Protein: Nutrients that are the main source of building blocks for the body • Fats/Lipids: Used for cellular components, such as cell membranes, also used for storage of energy.
- 7. Fats/Lipids Saturated or Unsaturated? solids at room temp = saturated (butter and animal fat) liquids at room temp = unsaturated (vegetable oils) -Saturated fats are the “bad” fats, and unsaturated are the “good” fats
- 8. Proteins • 8 amino acids the body cannot make are called “essential amino acids” – Must be obtained from food that you eat • meat, fish, eggs and milk, legumes • Trytophan, Lysine, Methionine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Threonine, and Phenylalanine
- 9. Vitamins • Organic molecules that help regulate body processes (work with enzymes) • Most vitamins obtained from food – Bacteria in digestive tract synthesize vitamin K – Skin synthesizes vitamin D when exposed to sunlight
- 10. Vitamins • 2 types of vitamins: 1. fat-soluble A,D,E and K can be stored in fatty tissues of body -excessive amounts can be toxic 2. water-soluble C and B vitamins dissolve in water and can’t be stored
- 11. Minerals • Inorganic nutrients that the body needs in small amounts, also called micronutrients ex: calcium major component of bones and teeth iron makes hemoglobin magnesium, sodium and potassium
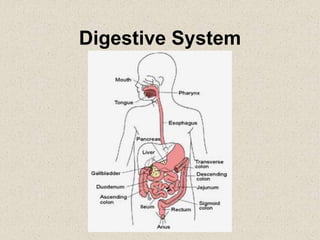
- 13. Digestive System • Includes: – Mouth – Pharynx – Esophagus – Stomach – Small intestine – Large intestine – Accessory structures: salivary glands, pancreas, liver add secretions
- 14. Function • Function of the digestive system is to help convert large food molecules into simpler molecules (monomers) that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body
- 15. Mouth • Teeth – Mechanical work of digestion by cutting, tearing, and crushing – 1st step in digestion and increases surface area of food • Saliva – salivary glands – Helps to moisten food and make it easier to chew – Begins chemical digestion enzyme amylase breaks down bonds in starches and releases sugars – Also contains lysozyme enzyme that fights infection by breaking down cell walls of many bacteria
- 16. Esophagus • Long tube of smooth muscle that connects the pharynx with the stomach • Chewed clump of food = bolus • Tongue and muscles push bolus down throat • Epiglottis closes over trachea to keep food out
- 17. Esophagus • Esophagus carries food to stomach • Contractions of smooth muscles (peristalsis) – Peristalsis-Squeeze food thru esophagus into stomach – Reverse peristalsis = vomiting – Cardiac sphincter (thick ring of muscle) closes and prevents stomach contents from moving back up esophagus
- 18. Stomach • Large sac of smooth muscle • Chemical digestion – Gastric glands secrete substances – Mucus lubricates and protects stomach wall – Hydrochloric acid/pepsin (breaks down proteins) • Mechanical digestion (smooth muscle contractions) – Mixture called chyme – After an hour or two, pyloric valve opens and chyme begins to flow into small intestine
- 19. Small Intestine • Enters the duodenum (first of 3 parts of small intestine) – Almost all of digestive enzymes enter the intestine – Most of chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine – Mixes with fluids and enzymes from pancreas and liver
- 20. Small Intestine • Pancreas: 1. Produces hormones that regulate blood sugar levels 2. Produces enzymes that break down carbs, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids 3. Produces sodium bicarbonate (base which neutralizes stomach acid) so enzymes can be effective
- 22. Liver • Liver: – Located above and to the right of the stomach – Produces bile (fluid loaded with lipids and salts) – Bile acts as a detergent, dissolving droplets of fats from food – Bile is stored in gallbladder
- 24. Small Intestine • Duodenum-First part of the small intestine where chemical digestion begins to take place • Jejunum and ileum are remaining parts of small intestine (average about 6 meters long) • Villi are fingerlike projections covering surface of small intestine – Absorption of nutrients occurs here
- 25. Small Intestine Large Intestine • By time it leaves small intestine, food is basically nutrient-free water, cellulose and other undigestible substances • Appendix: in humans does little to promote digestion, but in other mammals it stores cellulose and other materials
- 26. Large Intestine • Also known as the colon • Primary function is to remove water from the undigested material • Water is quickly absorbed across the wall of the large intestine • Concentrated waste material that remains passes through the rectum and is eliminated from the body
- 28. Digestive System Disorders • Peptic ulcer powerful acids in stomach damage stomach wall – Doctors thought that ulcers were caused by too much acid, but scientists have discovered bacteria Helicobacter pylori is cause (now cure rates are as high as 90%)
- 30. Digestive System Disorders • Diarrhea not enough water is absorbed • Constipation too much water is absorbed – Eat plenty of fiber and drink plenty of water!
- 31. Excretory System Function • Function of the excretory system is to maintain homeostasis in the body by eliminating metabolic (cellular) wastes
- 32. Organs of Excretion • skin excretes water and salts, small amount of urea (sweat) • lungs excretes carbon dioxide • liver converts nitrogenous wastes from digestion into urea • kidneys excretes urea and other metabolic wastes
- 33. Kidneys • The kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. • They are located near the middle of the back, just below the rib cage, one on each side of the spine. • Kidneys play important role in maintaining homeostasis -remove waste products from the blood -maintain blood pH -regulate the water content of the blood (regulating blood volume)
- 35. How Do the Kidneys Work? • Remove excess water from the blood • Remove urea from the blood – Urea is a form of ammonia, which is produced by your cells during cellular metabolism
- 36. Kidney Structure • Each kidney is made of many smaller units called nephrons • Nephron – Each nephron has its own blood supply (arteriole, venule, and capillaries) – Each nephron releases fluids to collecting duct which leads to ureter
- 37. Parts of the Excretory System • ureter- tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder • urethra- tube that carries urine from the bladder and releases it from the body • urinary bladder- saclike organ which stores urine before it is excreted
- 38. Urine Formation • In each nephron, urea and water are filtered out of the blood, and some water is reabsorbed. • The remaining material is conducted to the urinary bladder through the ureters, where it becomes urine.
- 39. Disorders of the Excretory System • Kidney failure- Can be caused by a number of things; treatment is dialysis – Dialysis is when the urine collection is done by a machine, rather than by a kidney • Kidney Stones- made of solidified calcium, magnesium or salts – cause is unknown, but drinking too few liquids could be a cause. – Can back up the urine flow in the kidney – VERY painful