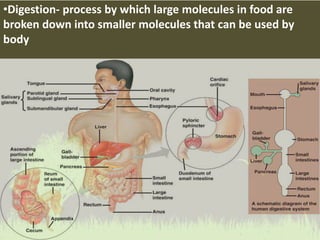
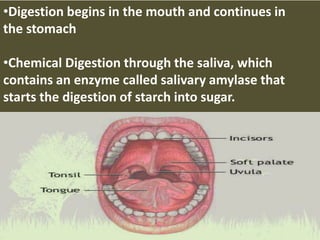
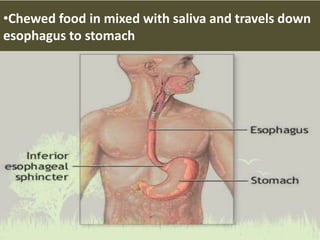
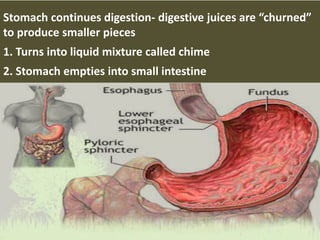
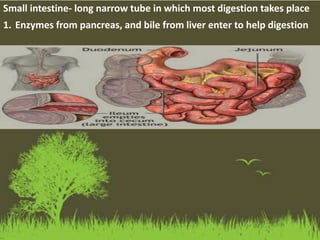
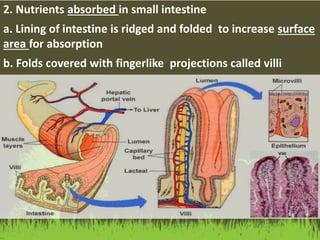
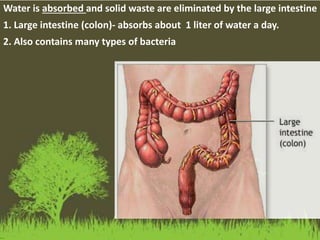
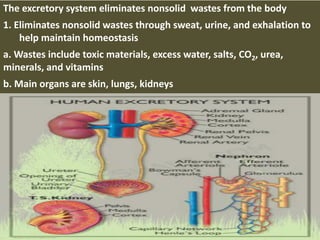
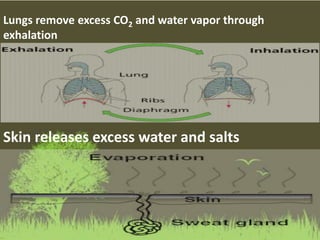
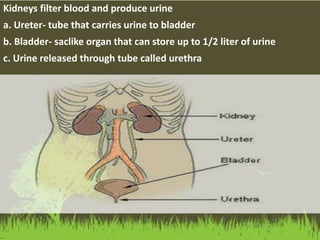
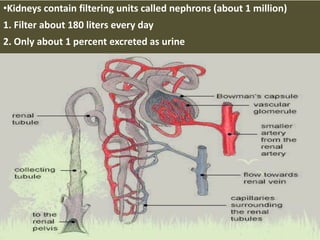
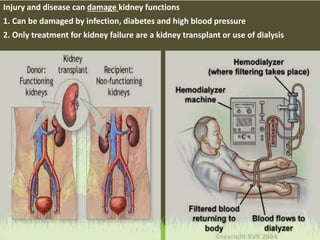
This document summarizes the key functions of the digestive and excretory systems. It explains that digestion breaks down food into smaller molecules that can be used by the body, starting in the mouth and continuing in the stomach and small intestine. The kidneys, lungs and skin are involved in excretion, with the kidneys removing waste from blood to produce urine for excretion. The kidneys also help maintain electrolyte and fluid balance, and release hormones to regulate bones, blood cells and pressure.