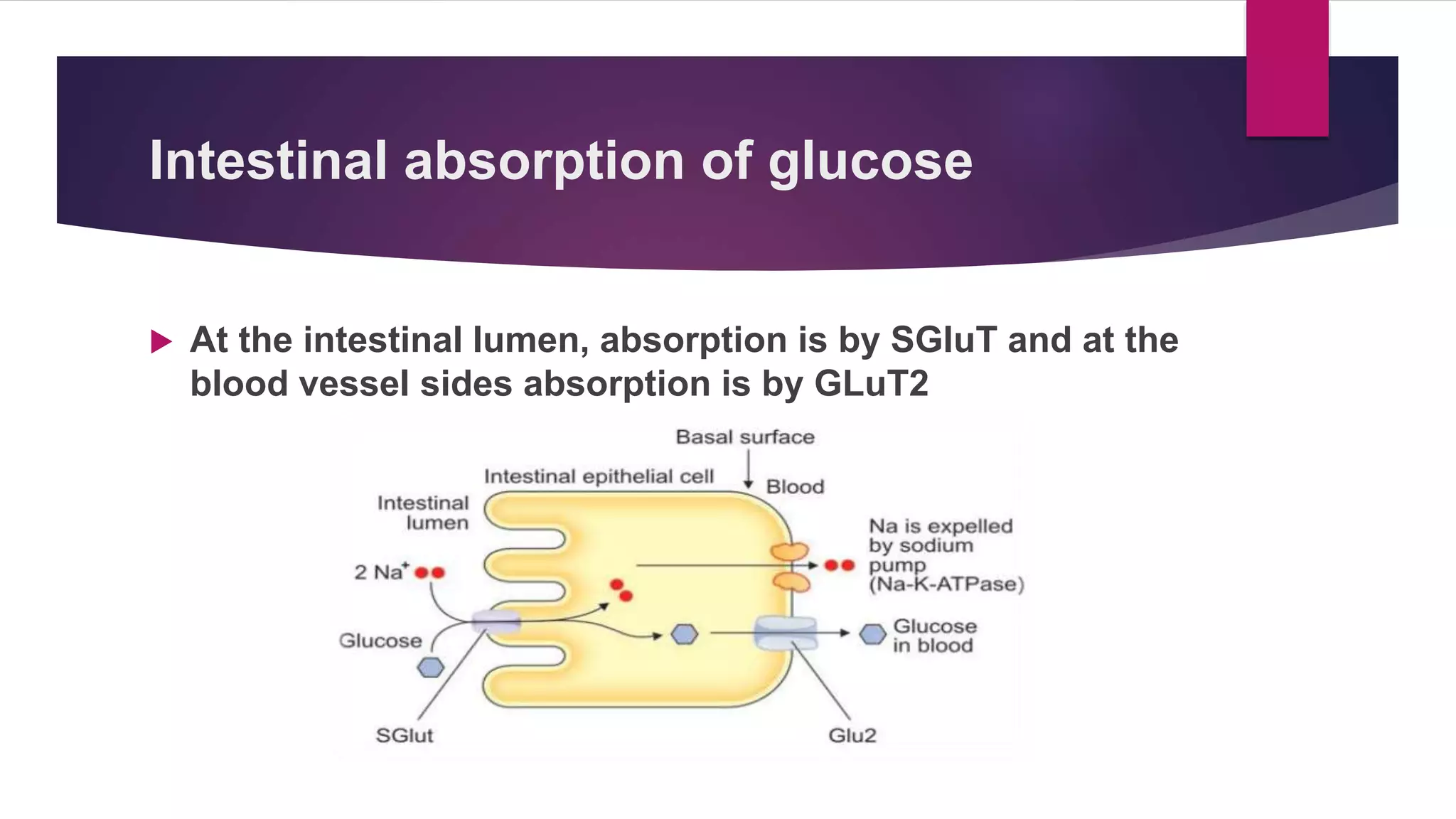
This document summarizes the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. It notes that carbohydrates are broken down into monosaccharides like glucose, fructose, and galactose by enzymes in the mouth and small intestine. These monosaccharides are then absorbed actively through the small intestine. Glucose absorption uses active transport involving sodium-glucose transporters, while fructose absorption occurs through facilitated diffusion. Factors like thyroid hormones can affect carbohydrate absorption rates. Conditions like lactose intolerance can also impact digestion if digestive enzymes are absent.