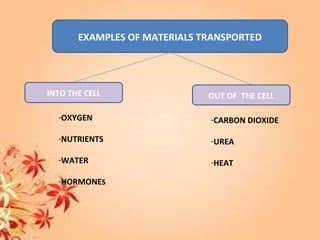
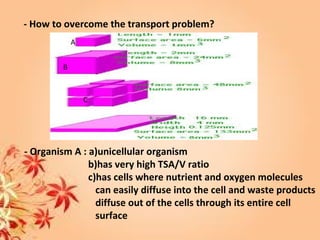
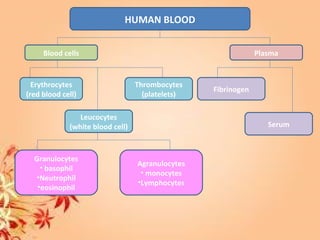
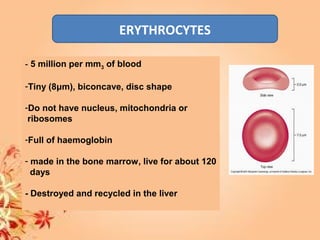
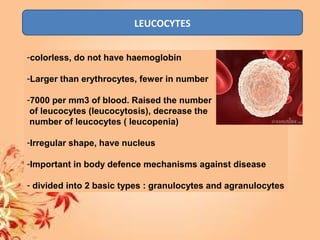
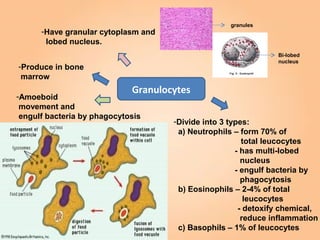
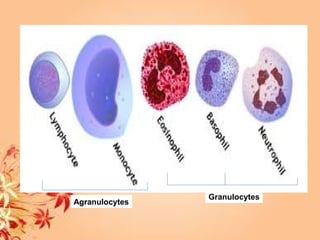
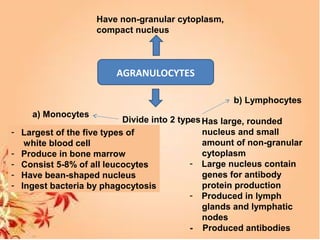
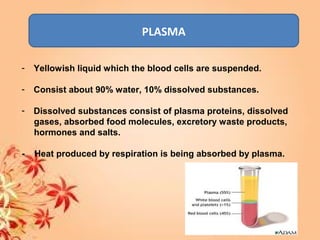
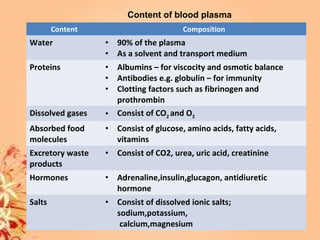
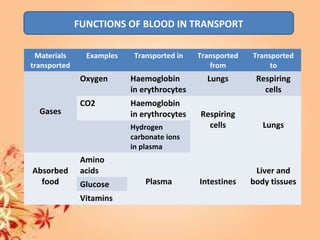
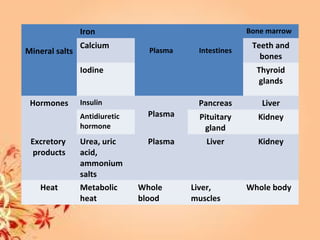
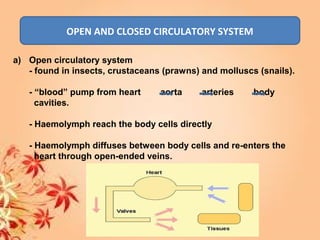
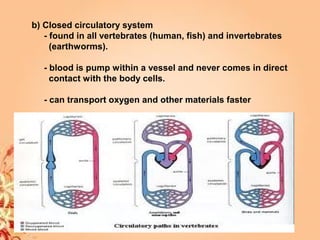
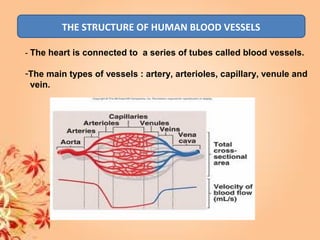
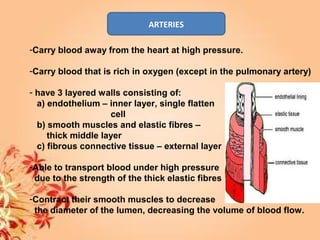
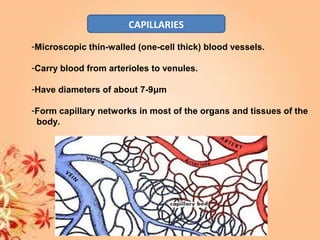
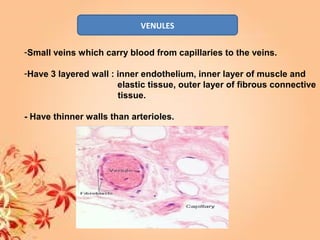
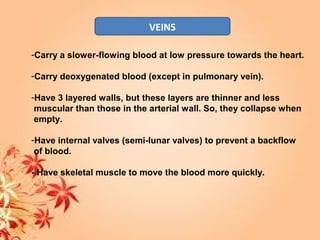
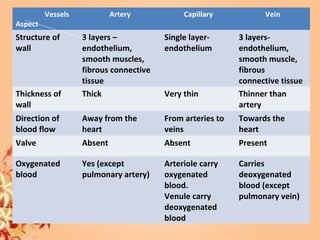
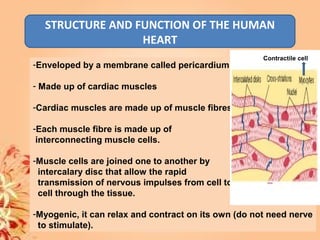
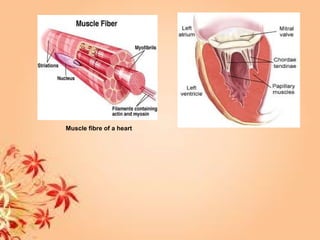
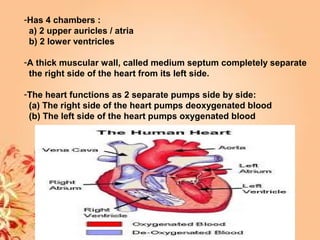
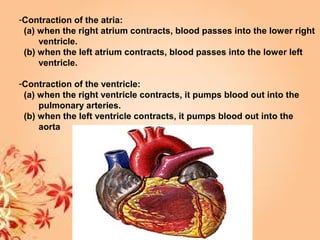
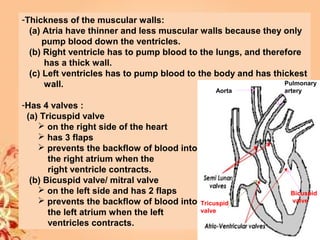
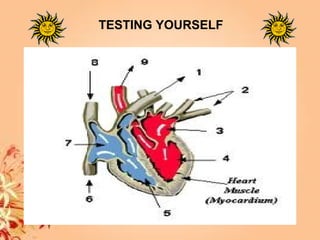
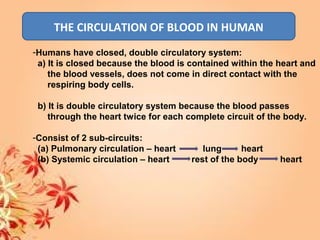
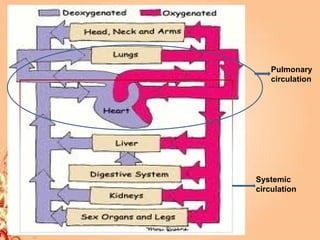
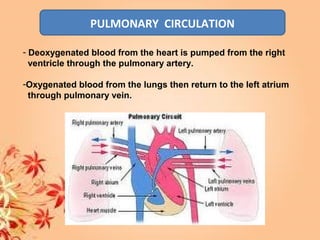
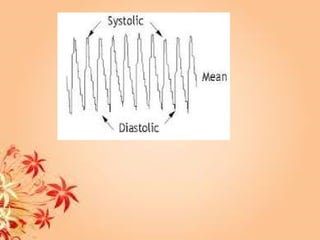
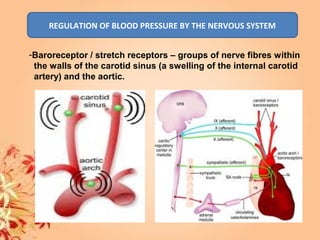
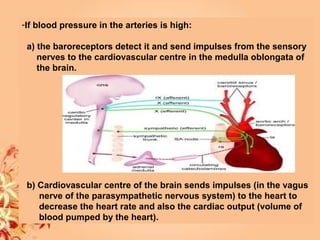
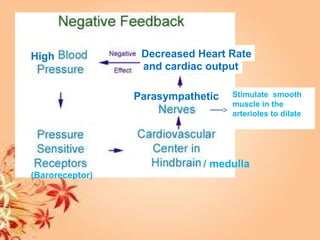
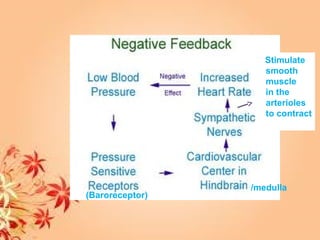
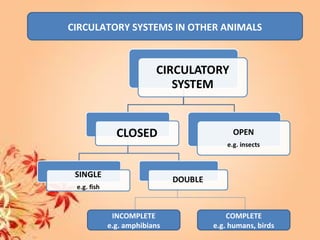
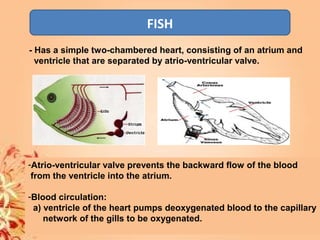
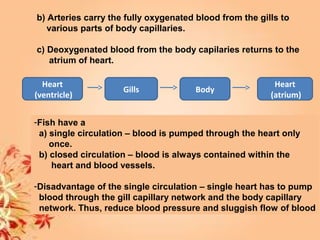
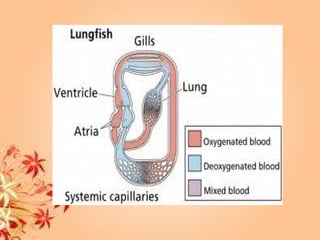
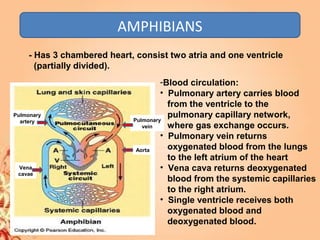
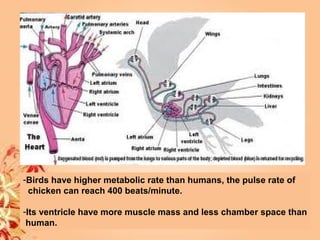
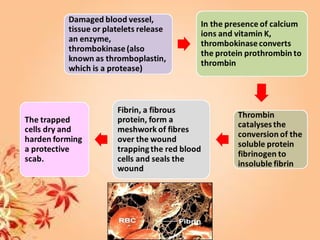
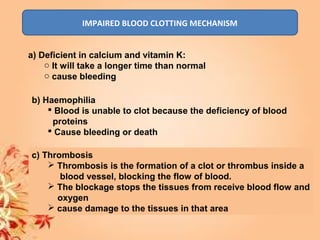
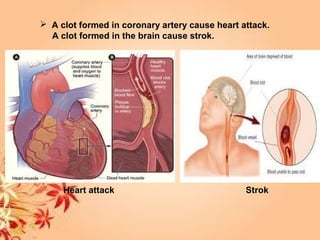
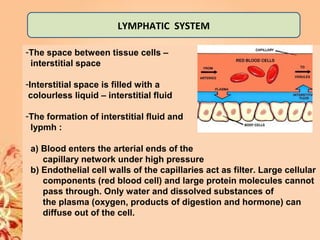
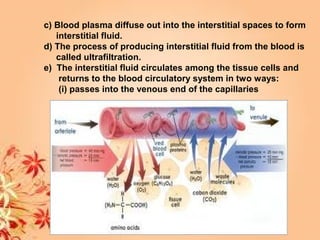
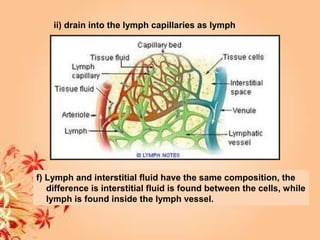
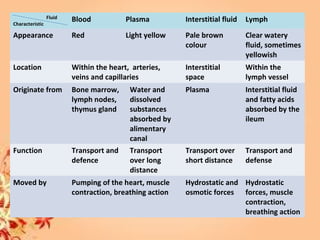
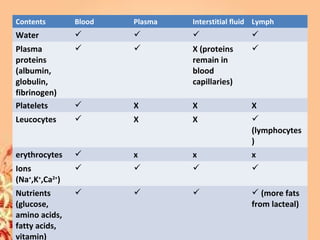
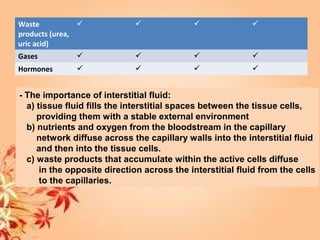
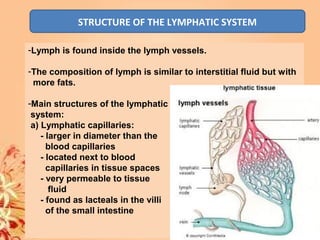
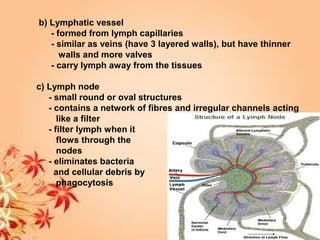
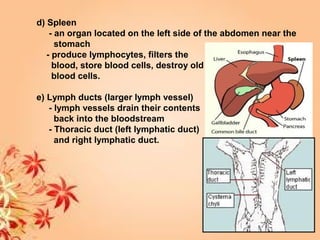
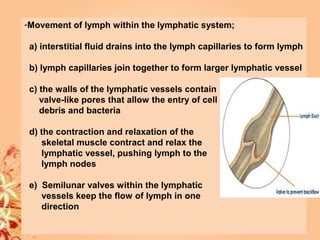
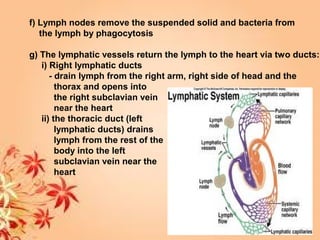
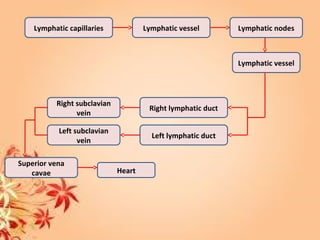
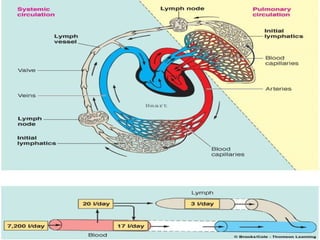
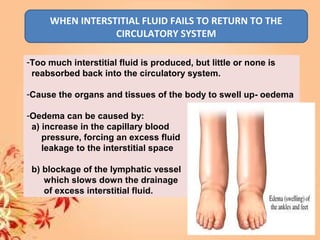
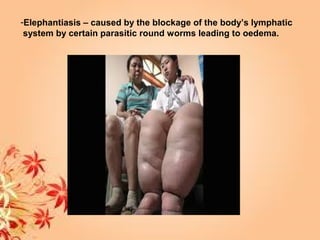
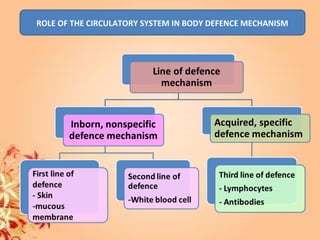
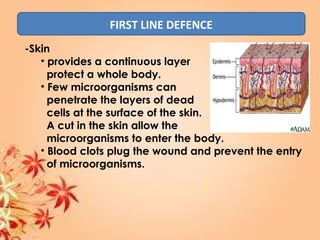
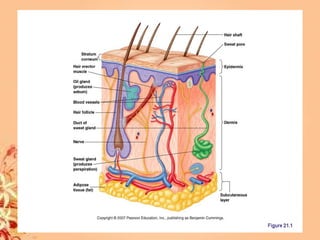
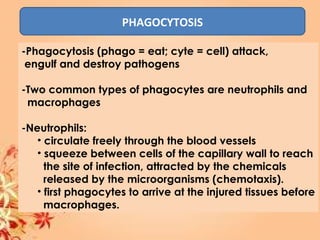
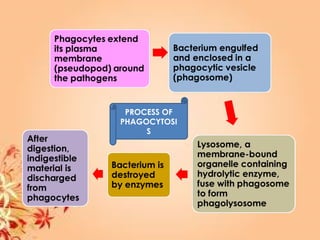
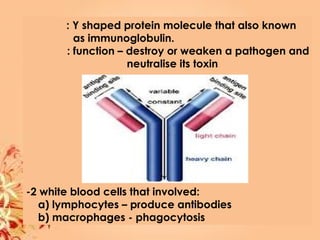
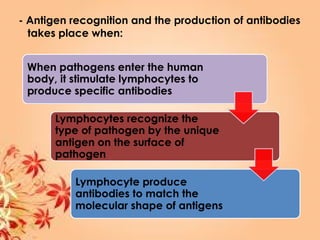
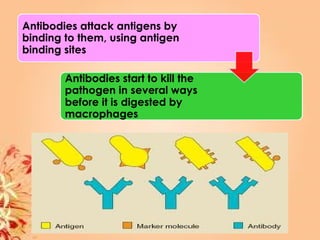
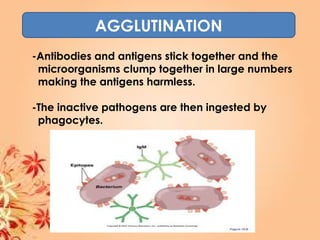
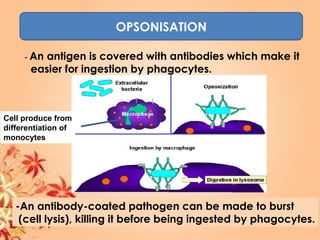
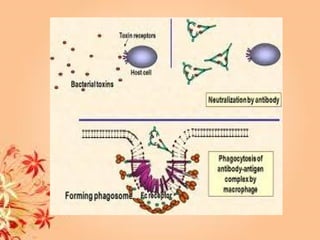
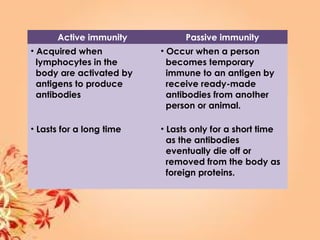
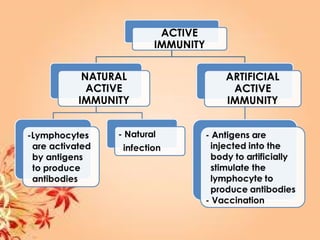
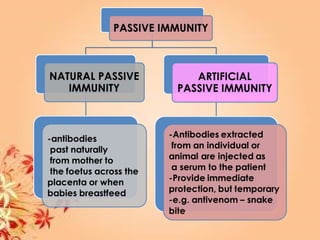
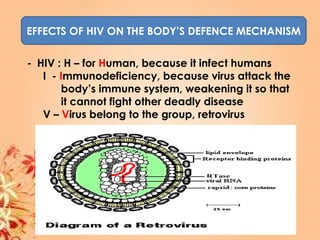
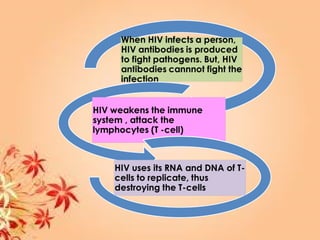
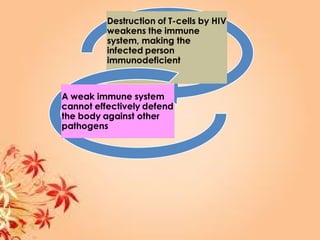
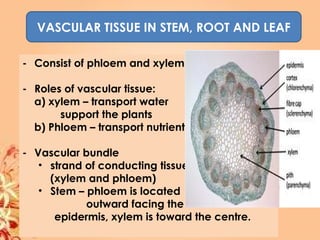
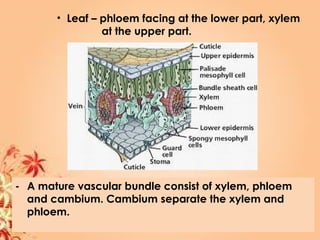
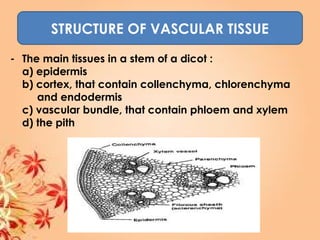
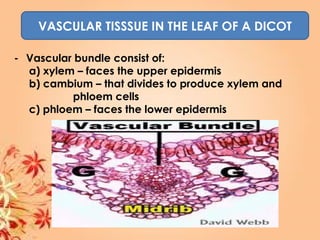
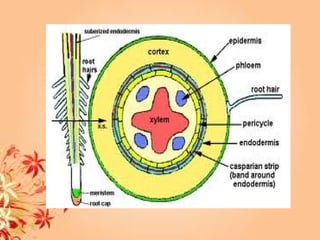
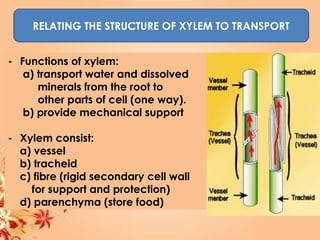
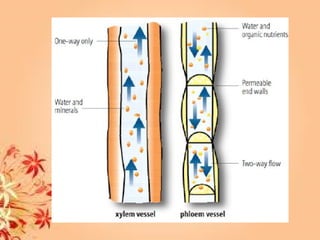
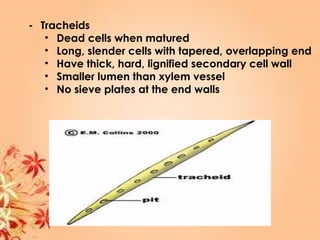
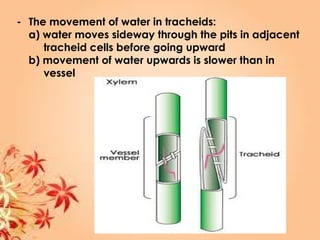
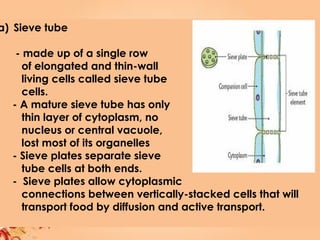
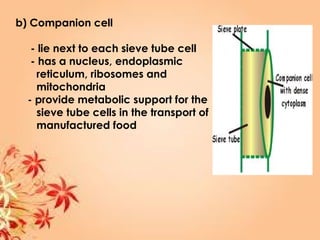
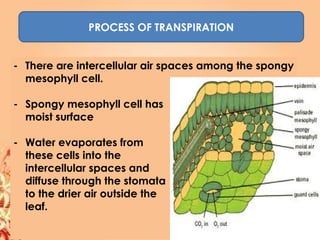
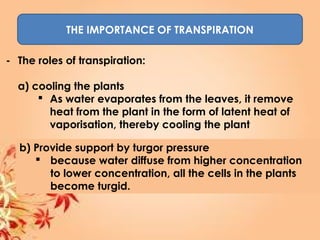
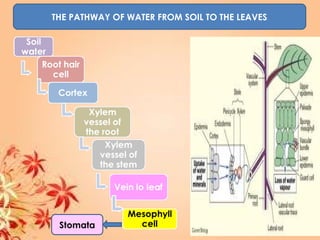
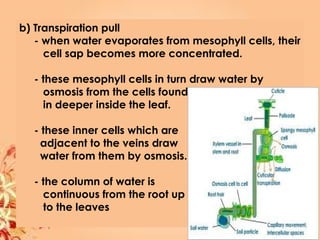
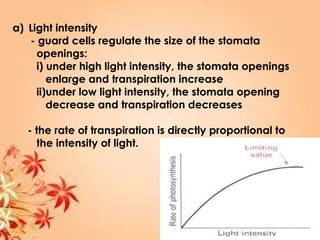
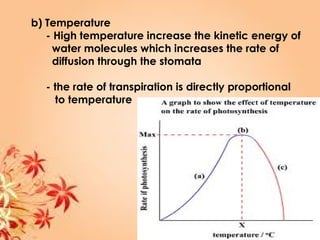
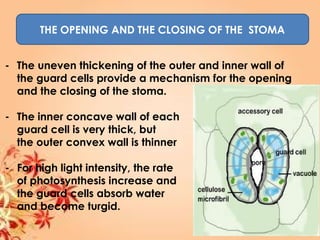
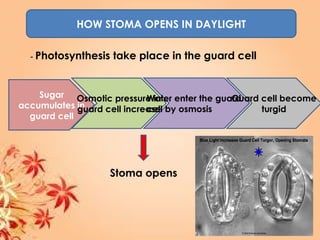
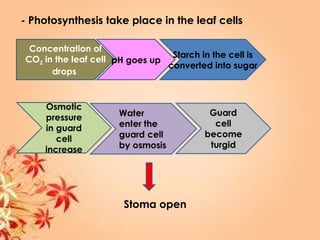
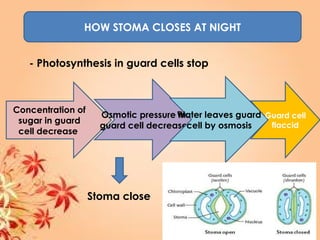
This document summarizes transport in unicellular and multicellular organisms. In unicellular organisms, transport occurs over short distances by simple diffusion, osmosis, or active transport since the cell membrane is in direct contact with the environment. In multicellular organisms, transport must occur over longer distances since interior cells are not in direct contact with the environment. This requires the development of transport systems like circulatory systems to distribute oxygen, nutrients and remove wastes. The human circulatory system uses blood and blood vessels to transport these materials between organs and tissues via processes like diffusion and active transport.