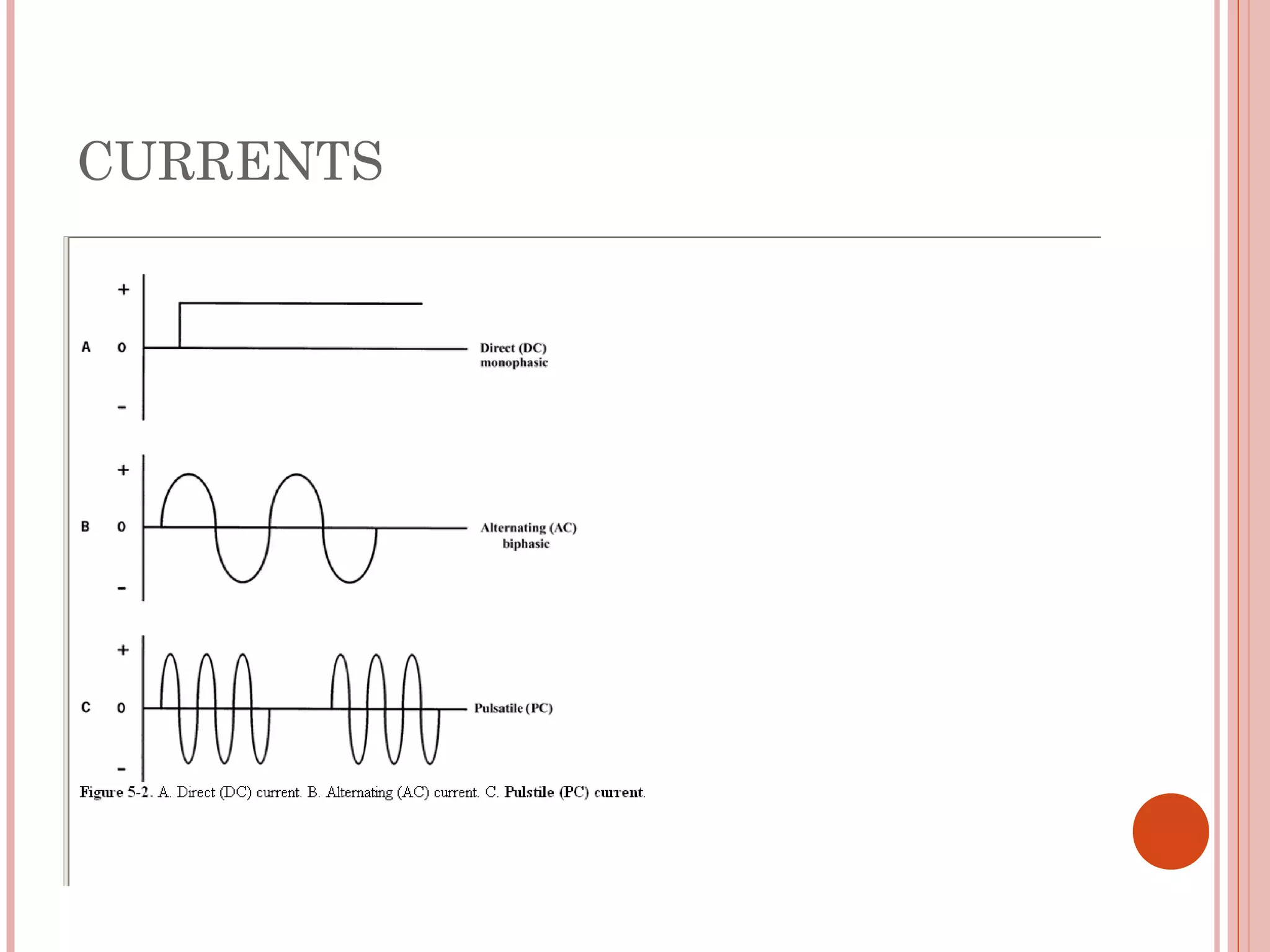
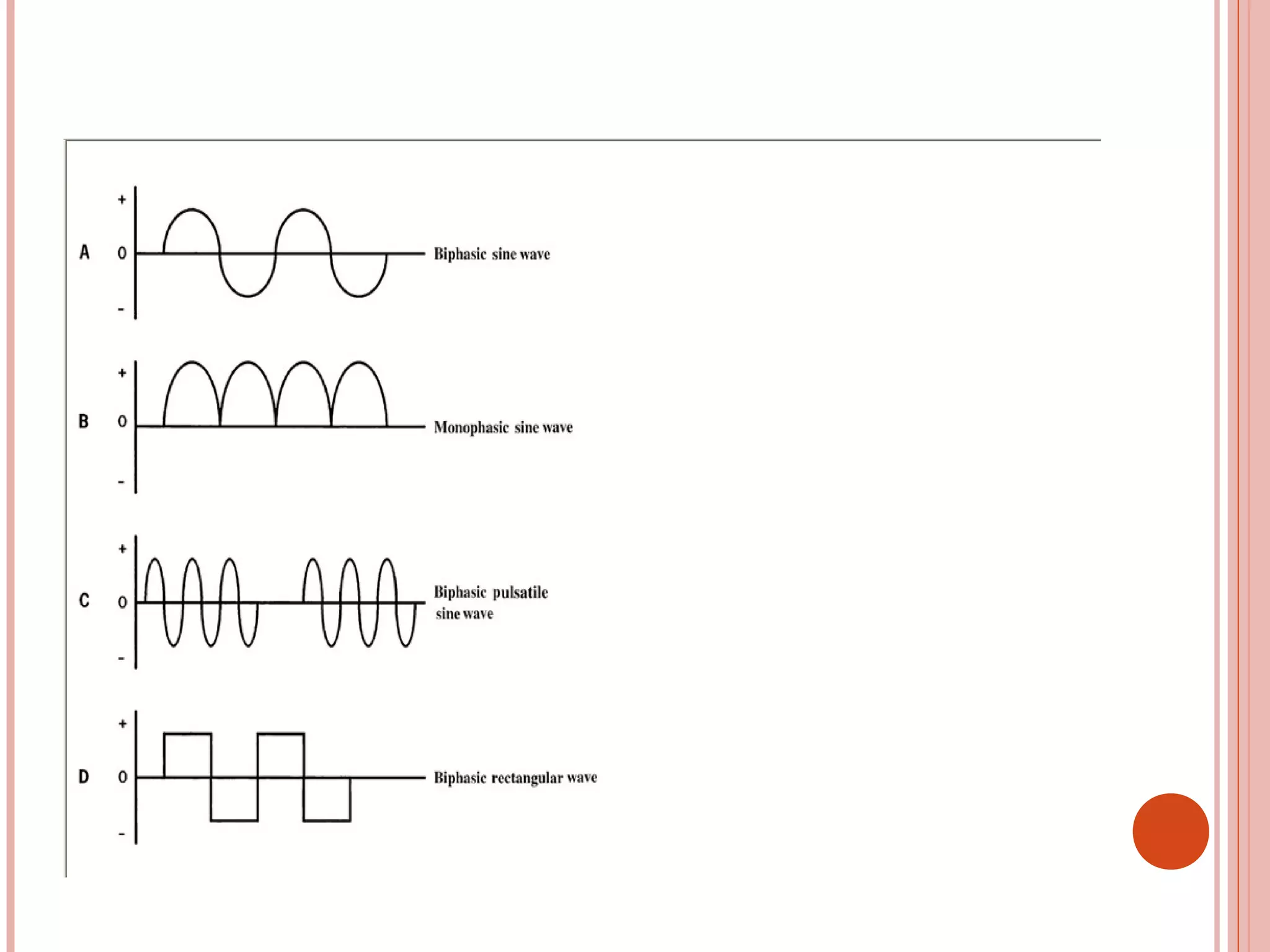
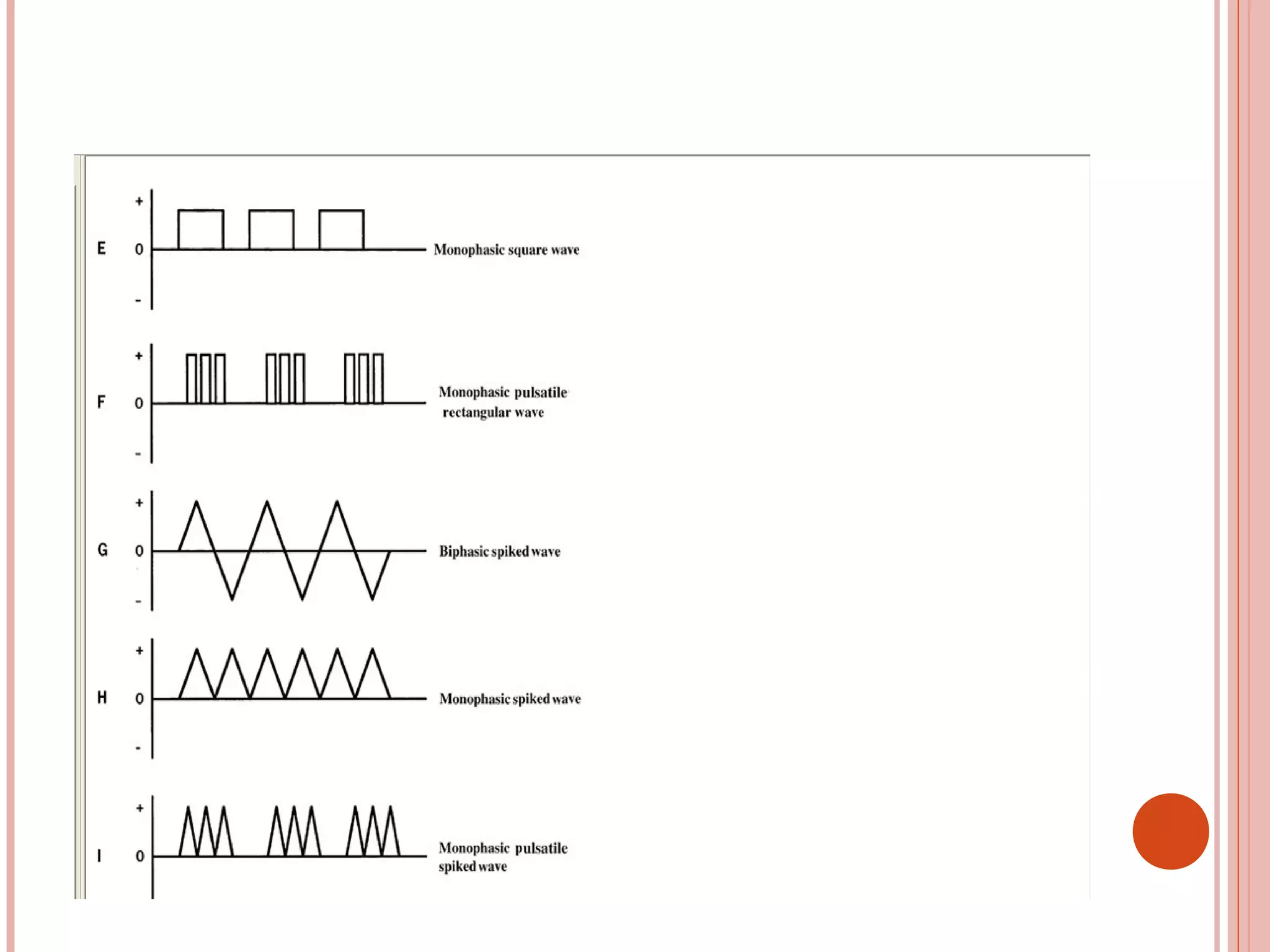
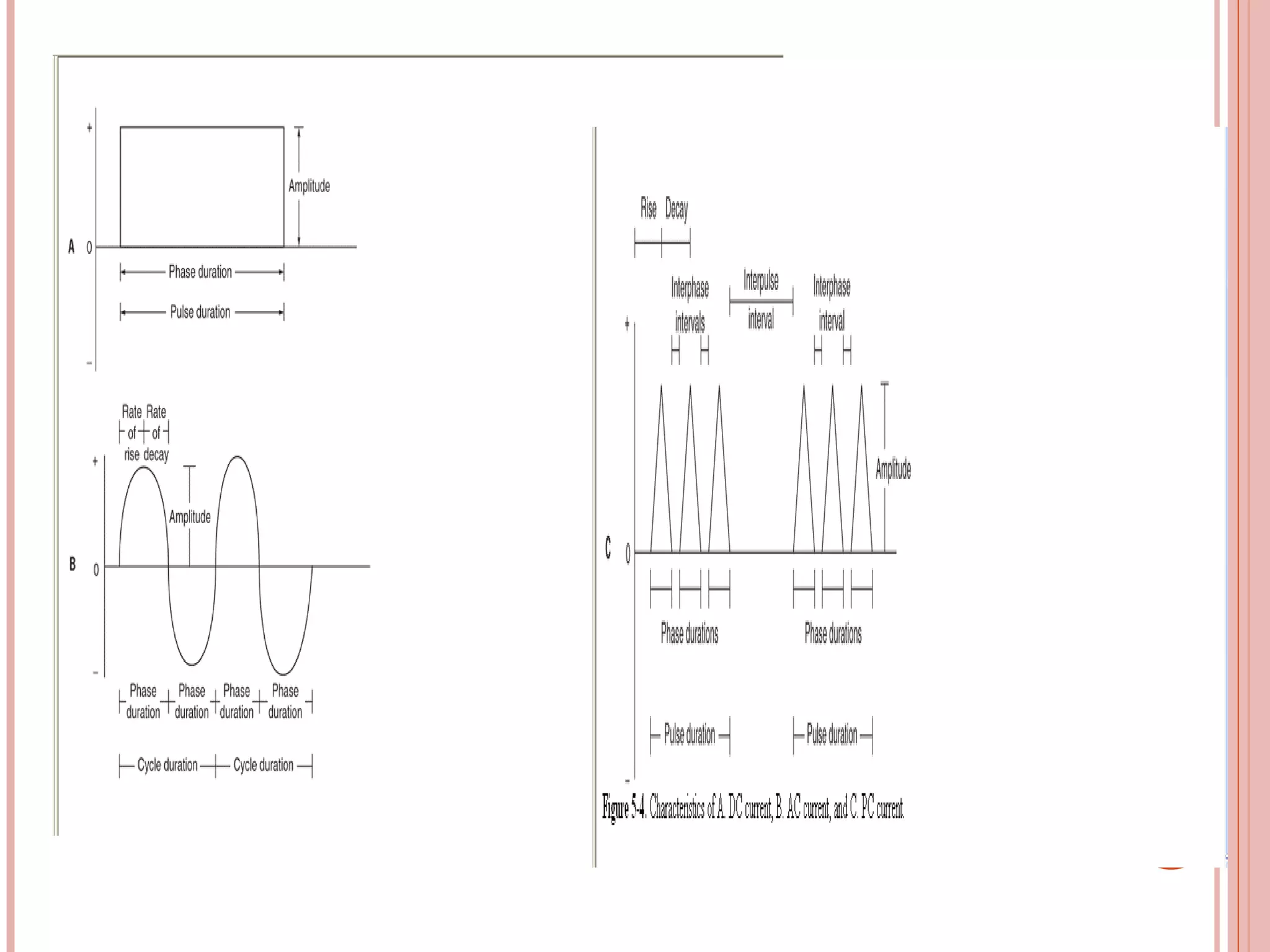
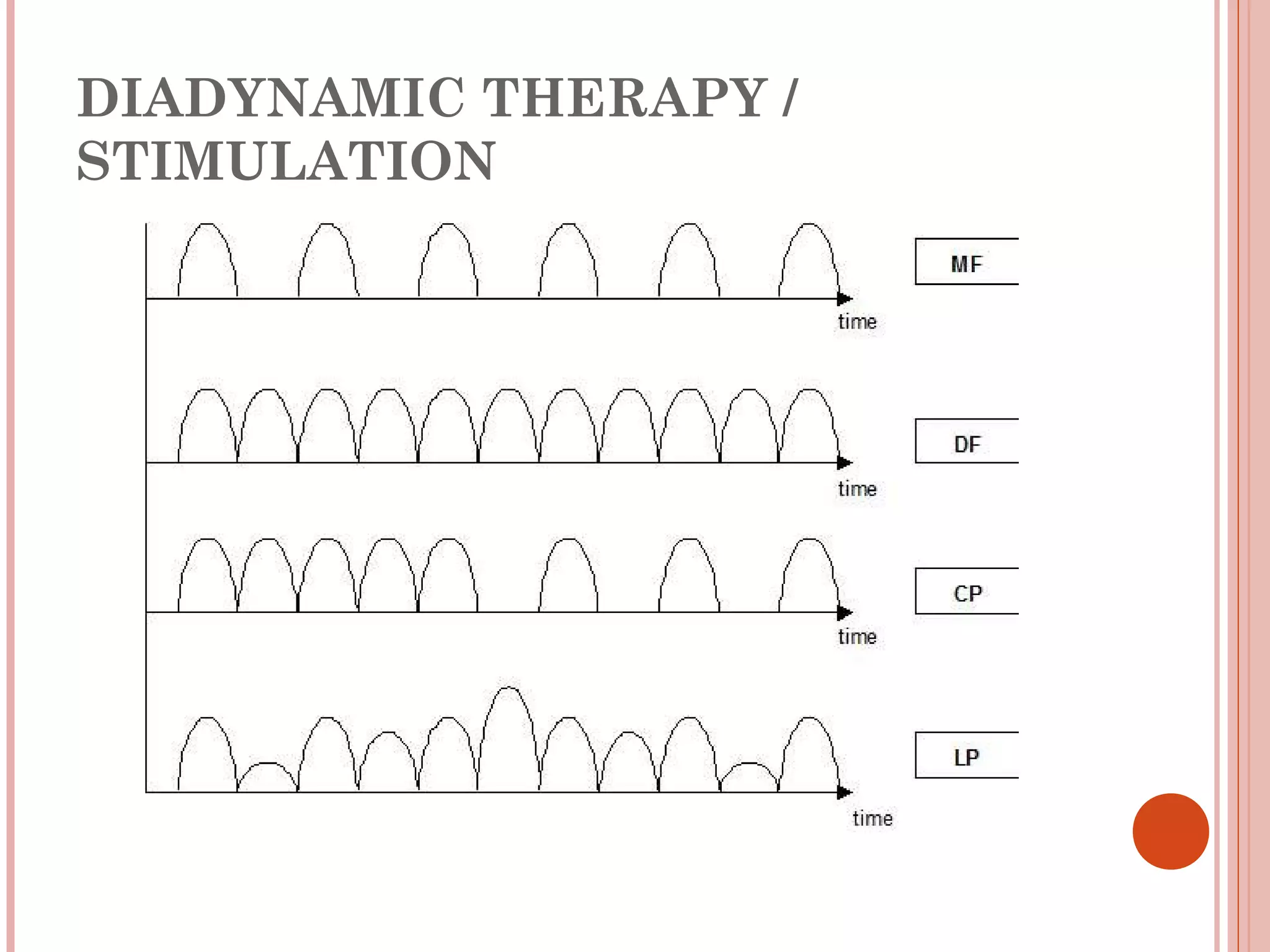
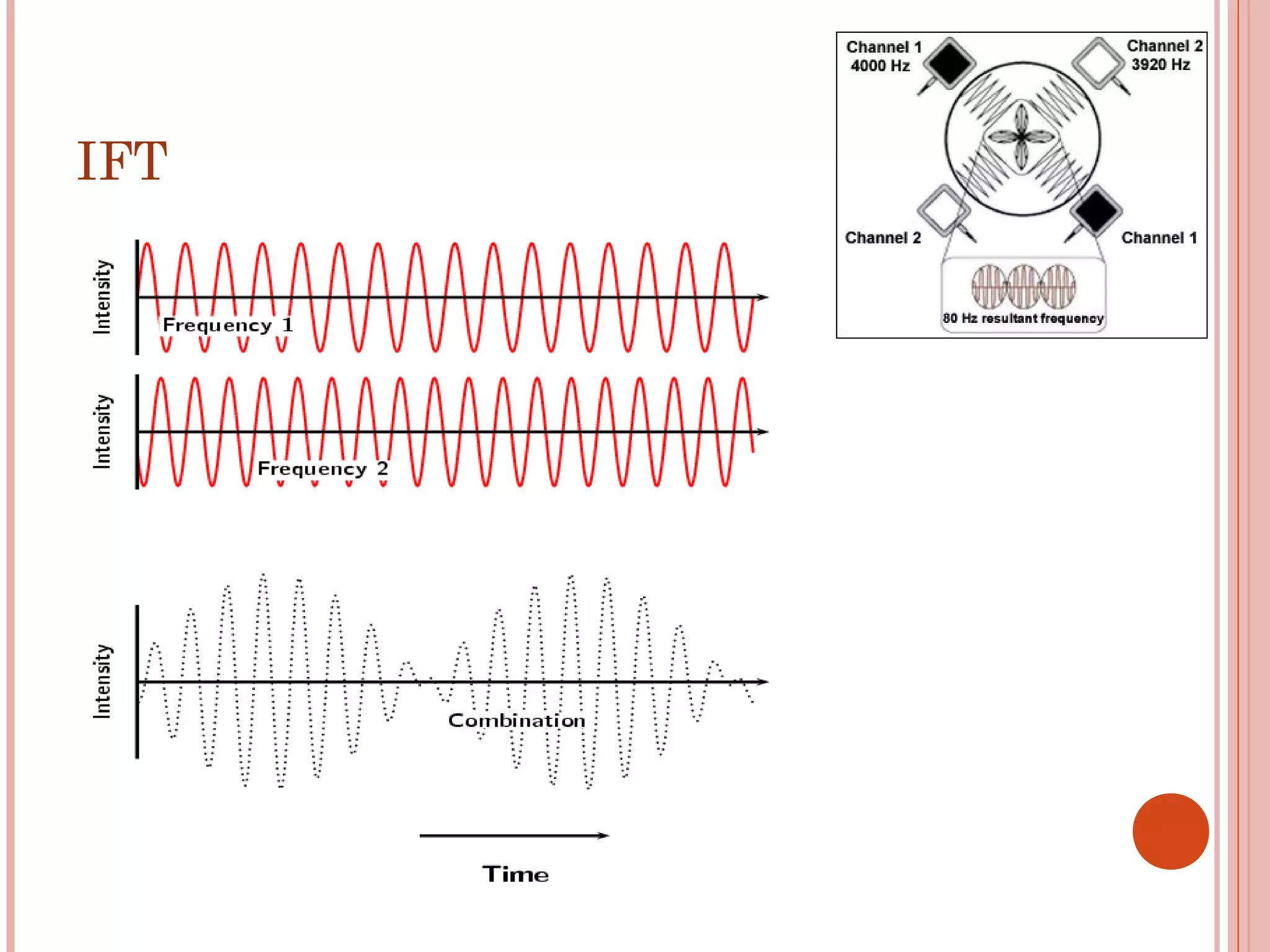
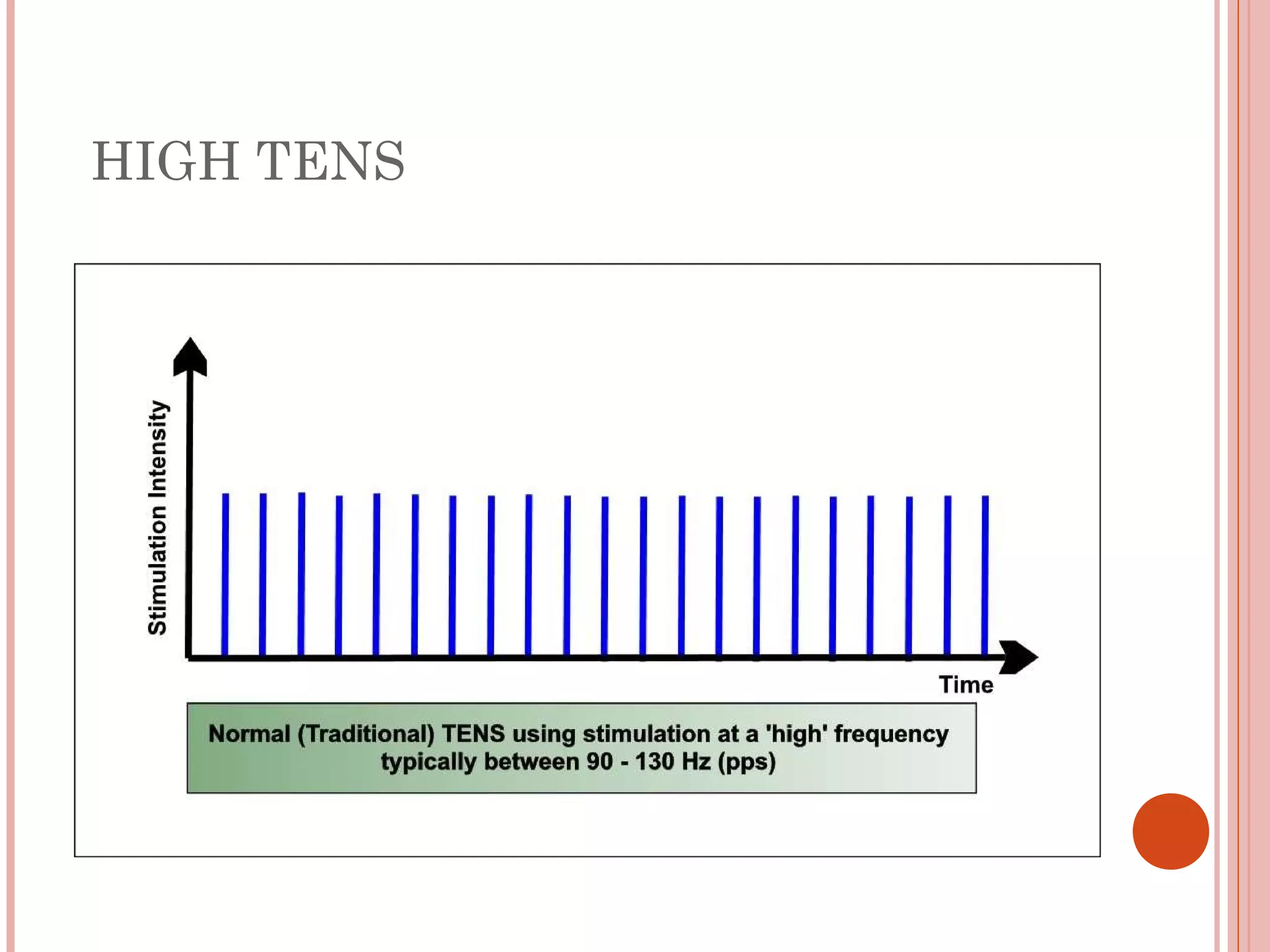
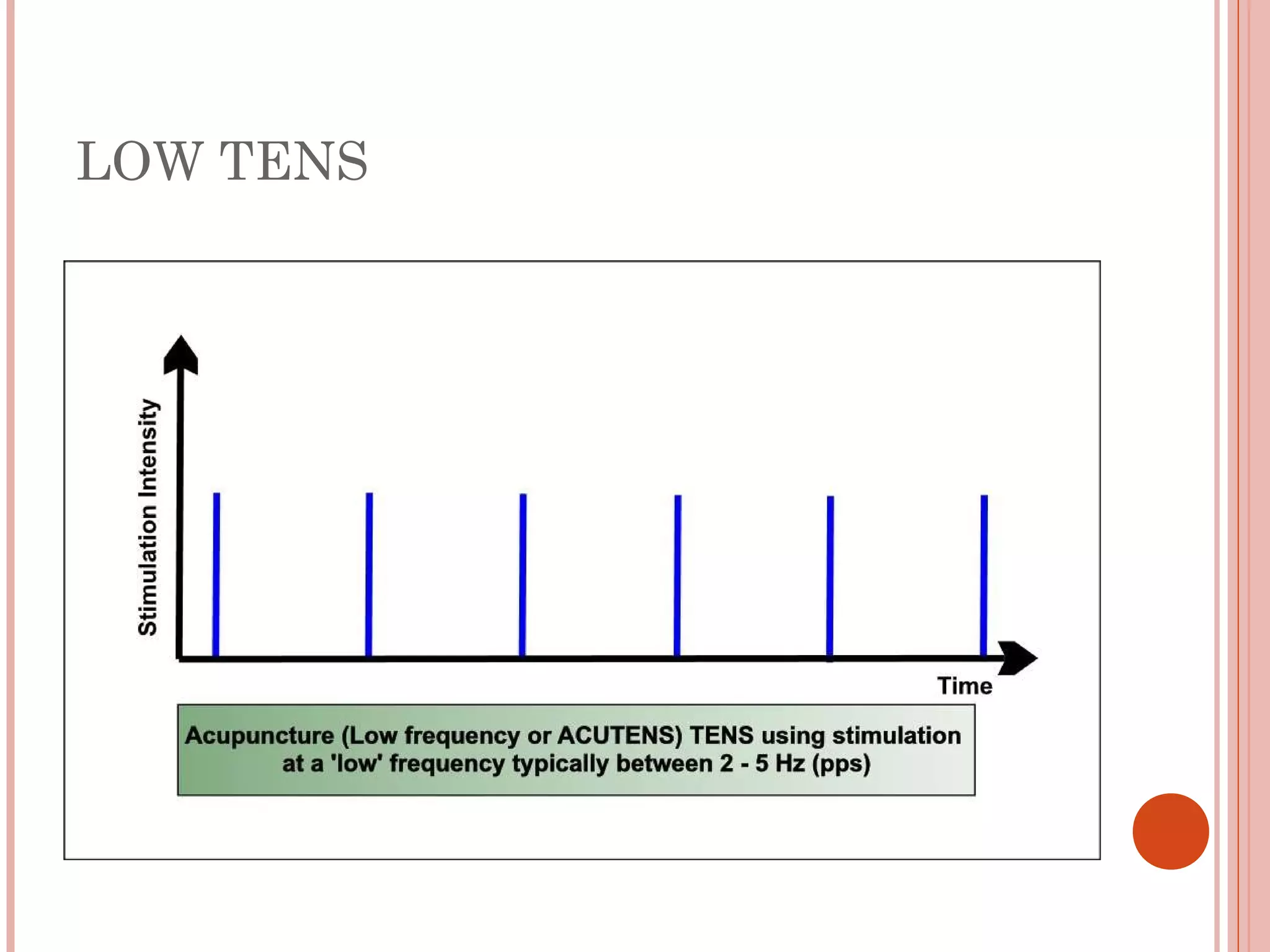
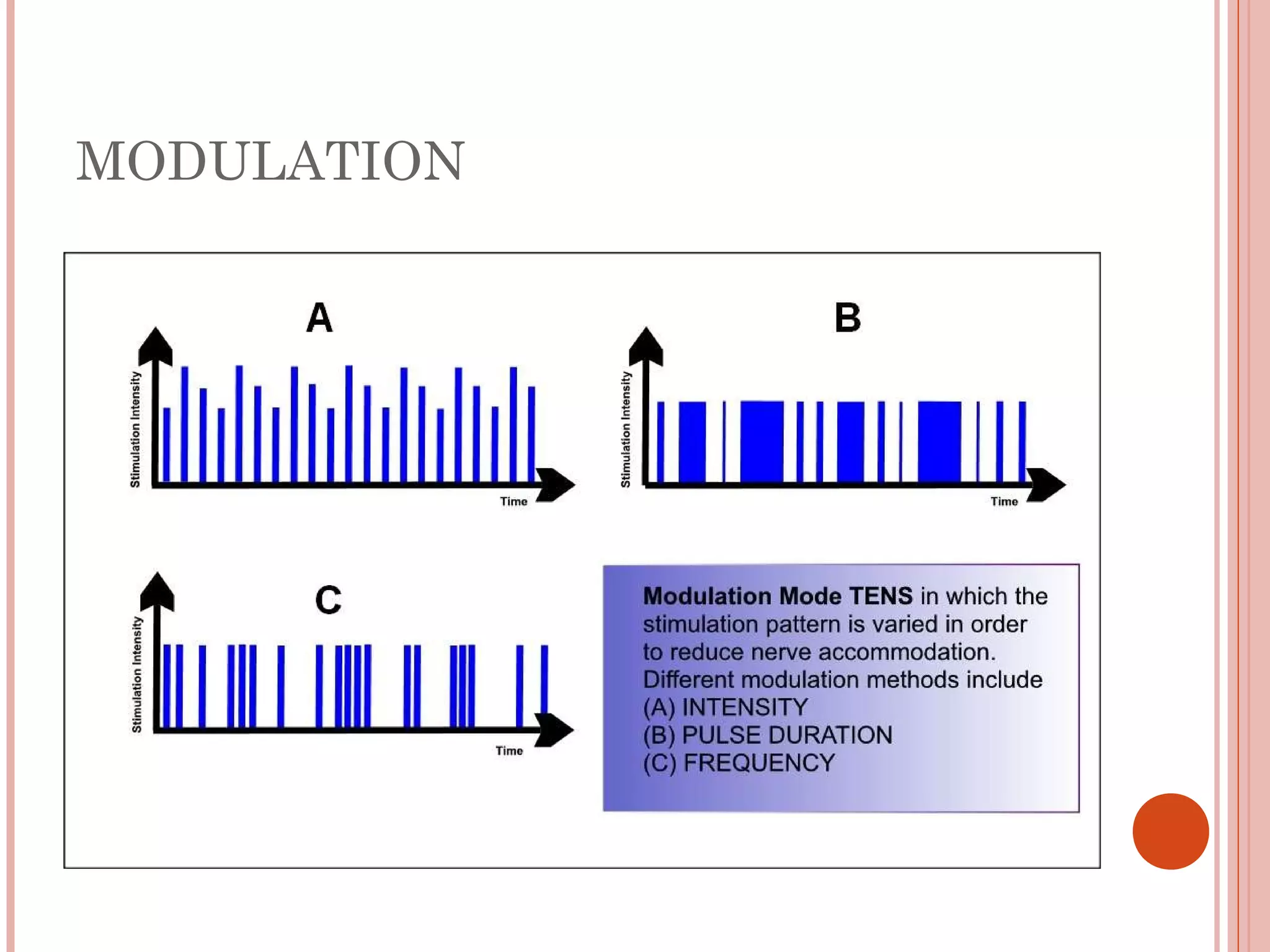
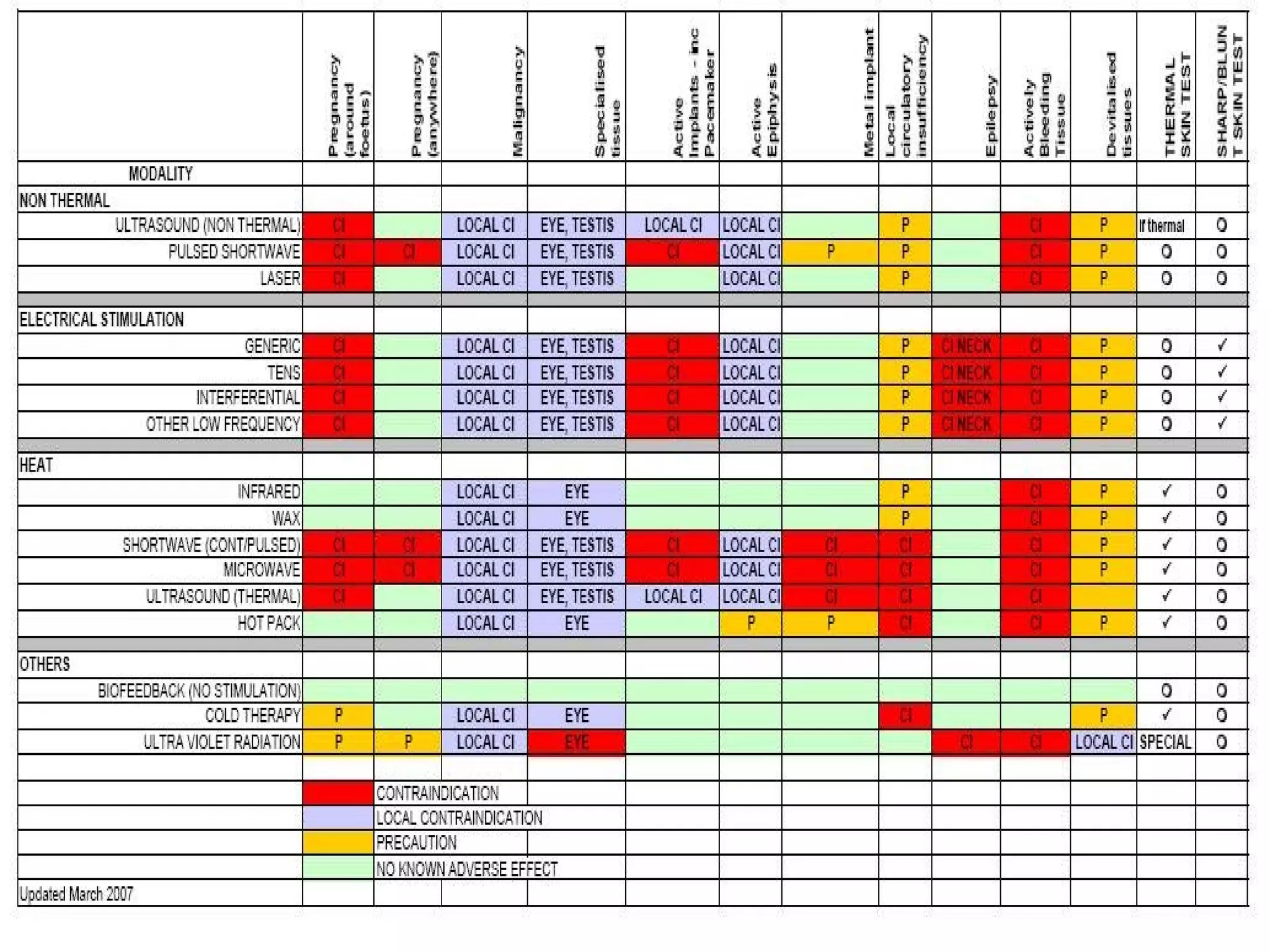
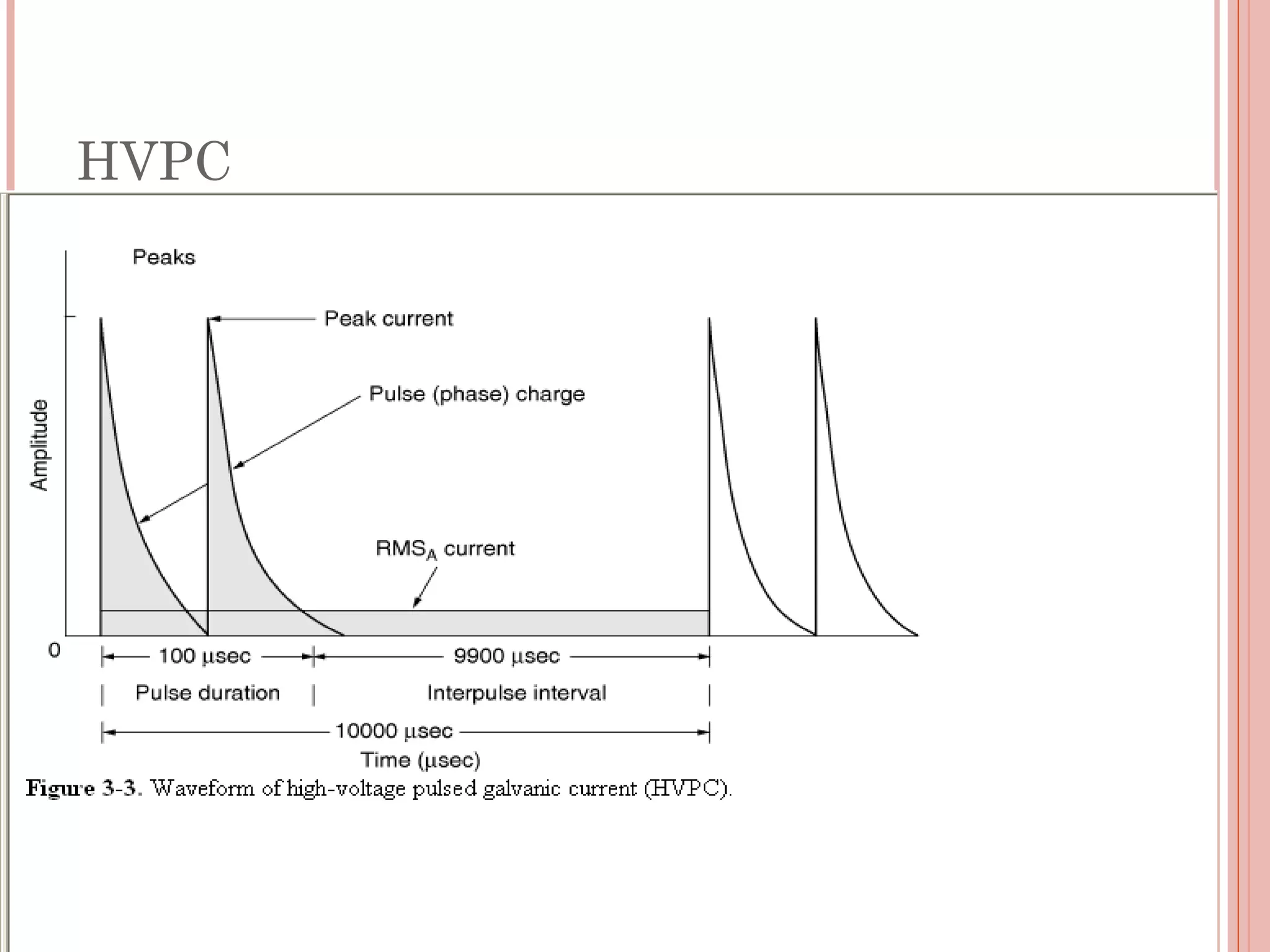
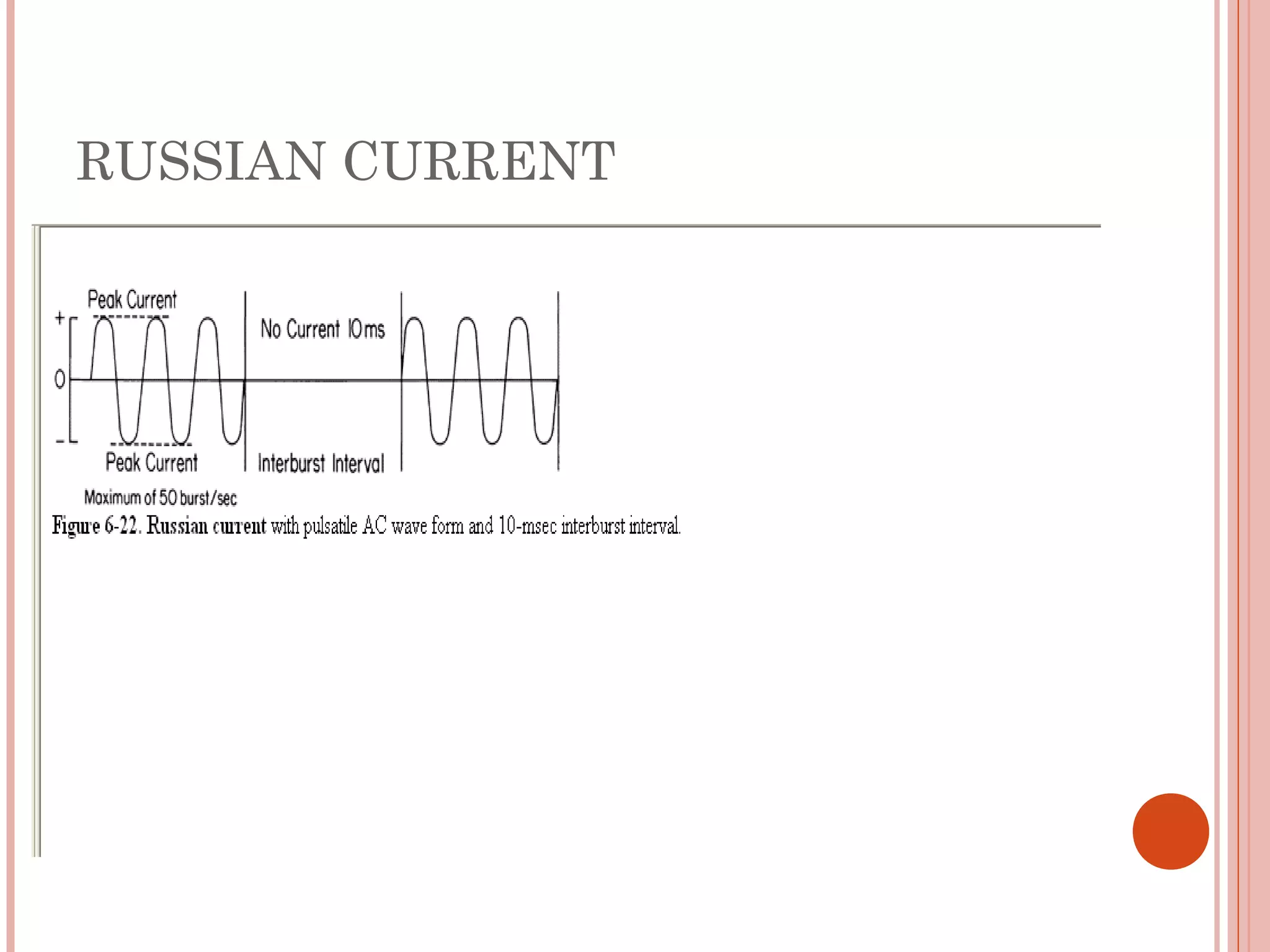
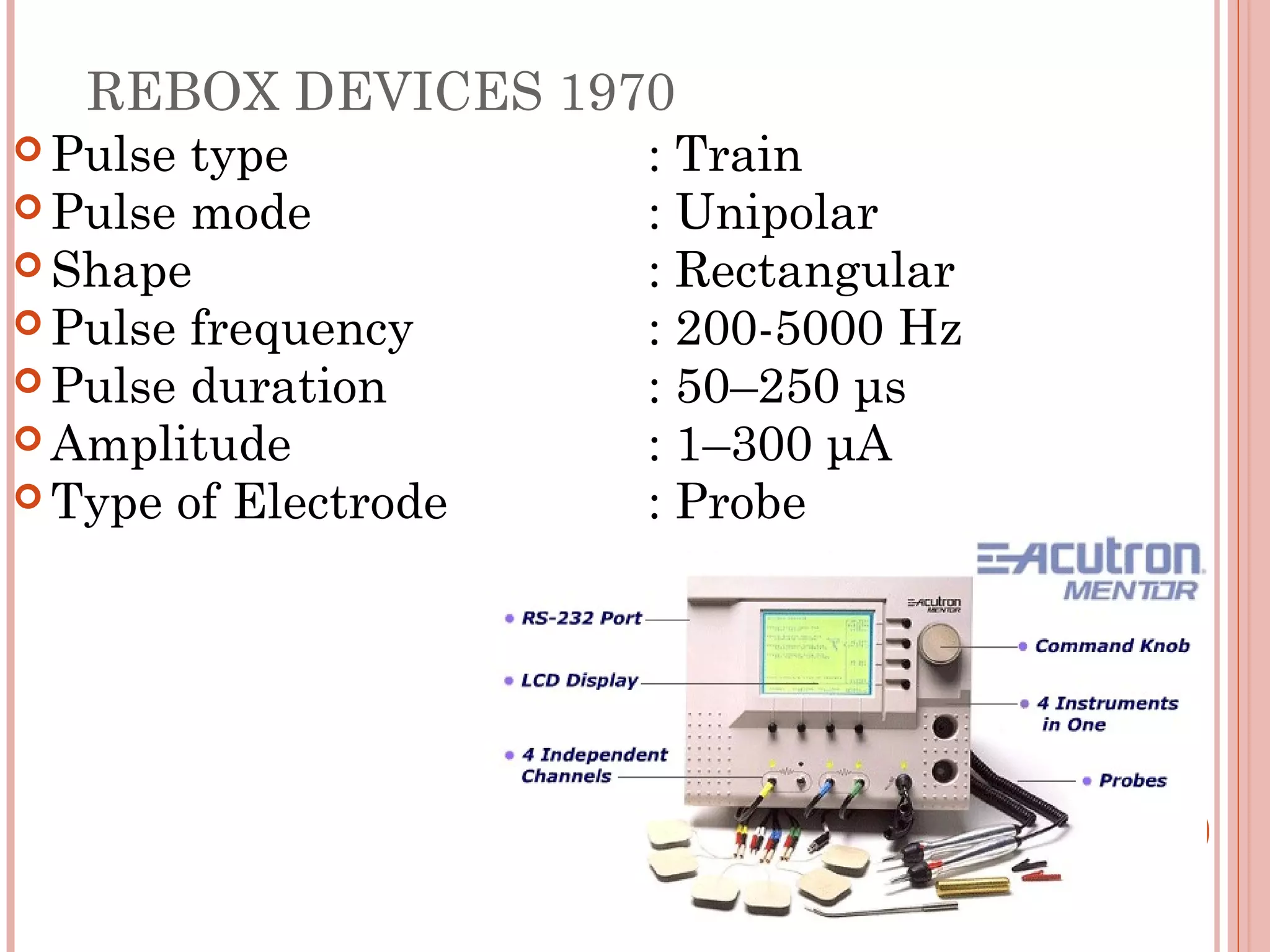
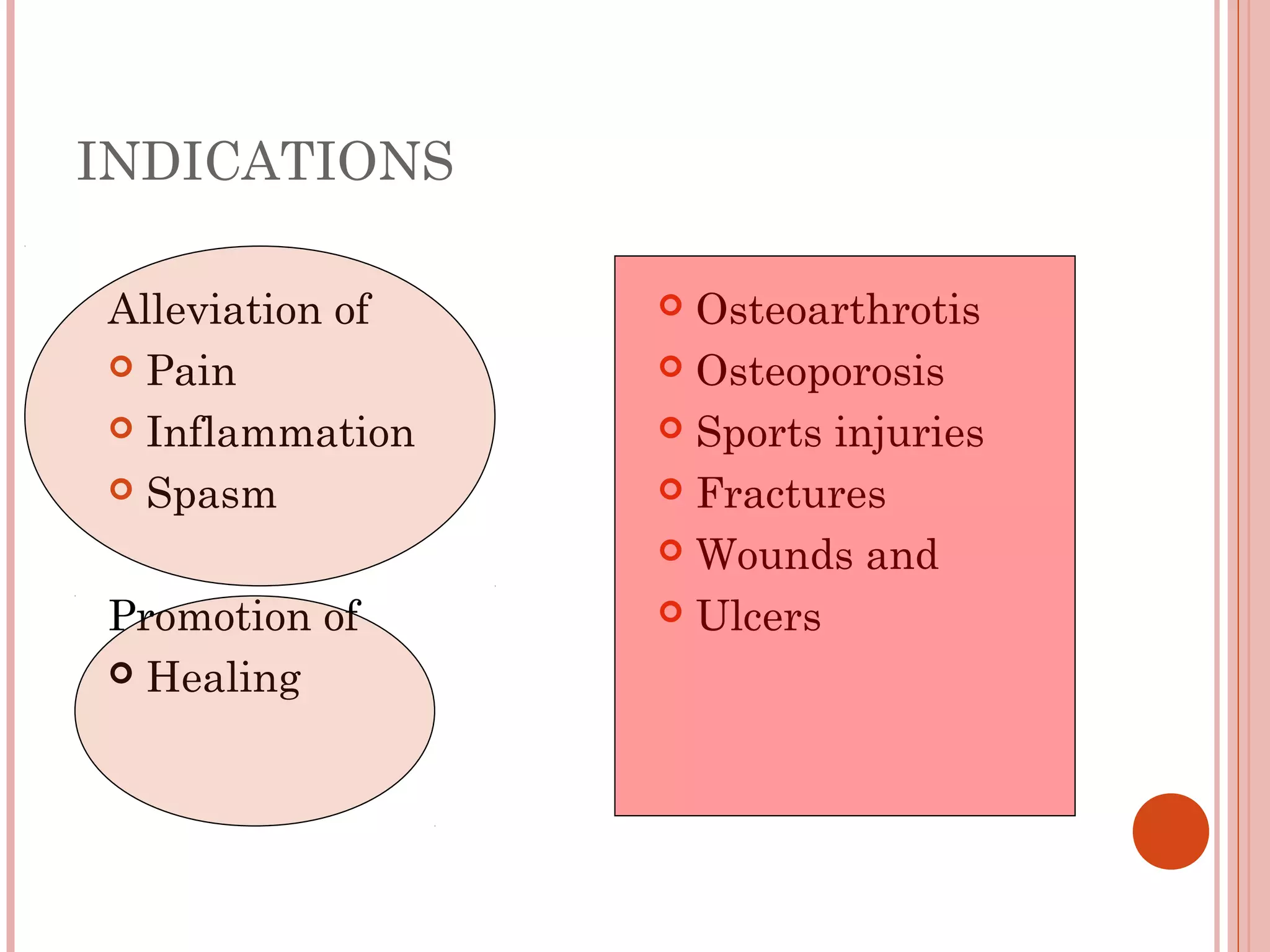
This document discusses different modalities used in low frequency electrical stimulation. It outlines various agents used including TENS, IFT, NMES, FES, faradic stimulation, iontophoresis, HVPGS, LIDC, twin peak monophasic stimulation, diadynamic therapy, H wave therapy, APS, Russian stimulation, Rebox therapy, and microcurrent therapy. It provides details on wave forms, currents, and specifications of different devices. Microcurrent therapy is described as using currents that are 1/1000th of an ampere smaller than TENS to alleviate pain, inflammation, spasm and promote healing for various injuries and conditions.