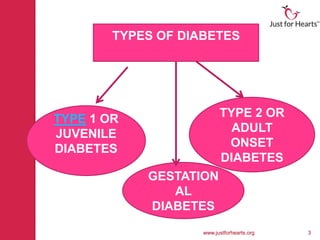
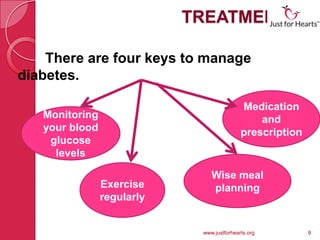
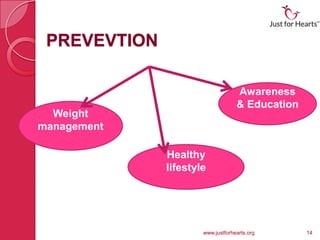
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood glucose levels, with three main types: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Symptoms vary by type, including frequent urination and blurred vision, with risk factors encompassing family history and lifestyle choices. Management includes monitoring blood glucose, medication, wise meal planning, and regular exercise to minimize complications.